 Web Front-end
Web Front-end JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial Detailed explanation of npm and webpack configuration methods in node.js
Detailed explanation of npm and webpack configuration methods in node.jsDetailed explanation of npm and webpack configuration methods in node.js
Node.js is written in c++ language. It is a javascript running environment based on the chrome V8 engine. It allows javascript to run independently of the browser server. You can use javaScript language to write server-side code. It mainly introduces the detailed explanation of node. Friends who need it can refer to the npm and webpack configuration in js. I hope it can help everyone.
1. Use node to implement an http server
The following creates a server with port 8787. It is different from php, java, etc., like php locally, it is also based on the Apache server. Node.js can quickly build a server using code.
// 引入http模块
var http = require("http");
// 调用http的接口创建服务器;回调--->异步;
var server = http.createServer(function(req,res){
// request:浏览器提交给服务器相关;response:服务器到浏览器;
console.log(111);
// 设置编码格式
res.setHeader("Content-type","text/html;charset=utf8");
res.write("<h1 id="hello-world">hello world 11233</h1>");
res.write("你好世界");
res.end();
})
server.listen(8787);
Modularization
1. Modular development
1. CommonJS is to formulate specifications for the performance of JS. Because js does not have the function of a module, CommonJS came into being. It wants js to run everywhere, not just in the browser.
2. Create your own module
The namespace in node.js is independent
To introduce methods or variables of another module into one module, use require
•Introduction of fnData module
require("./fnData");
•Import and export (export variables or functions)
module.exports = {
myFn:test.myFn,
a:test.a
}
2. Built-in modules
Nodejs built-in modules include: Buffer, C/C++Addons, Child Processes, Cluster, Console, Cr
ypto, Debugger, DNS, Domain, Errors, Events, File System,
Globals, HTTP, HTTPS, Modules, Net, OS, Path, Process, P unycode, Query Strings, Readline, REPL, Stream, String Decoder, Timers, TLS/SSL, TTY, UDP/Datagram, URL, Utilities, V8, VM, ZLIB; built-in modules do not need to be installed, external modules need to be installed;
3. npm
1. A collection of modules, which is the package manager of node
Common npm terminal commands below
1.
Install Node module
npm install moduleNames
Install the package into the global environment
npm install
While installing, if there is a package.json file, the command will write the information into the project path in package.json
npm install
2. View the package.json folder of the node module npm view moduleNames
3. View the installed node packages in the current directory
npm list
4. View help command
npm help
5. View package dependencies
npm view moudleName dependencies
6. View the source file address of the package
npm view moduleName repository.url
7. View the version of Node that the package depends on
npm view moduleName engines
8. View all folders used by npm
npm help folders
9. Used to rebuild after changing the package content
npm rebuild moduleName
10. Check whether the package is outdated. This command will list all outdated packages and you can update the package in time
npm outdated
11. Update the node module
npm update moduleName
12. Uninstall node module
npm uninstall moudleName
13. An npm package is a folder containing package.json, package.json description the structure of this folder. The method to access npm's json folder is as follows:
$ npm help json
This command will open a web page in the default way. If the default opening program is changed, it may not open the web page in the default way. form opens.
14. When publishing an npm package, you need to check whether a certain package name already exists
$ npm search packageName
15.npm init: will guide you to create a package.json file, including name, version, author information, etc.
16.npm root: View the installation path of the current package
npm root -g: View the installation path of the global package
17.npm -v: Check the version installed by npm
4. webpack
Concept: It is a recent loader and packaging tool, which can combine various resources. For example, J (including J X), coffee, styles (including less/sass), pictures, etc. are all used and processed as modules.
Configuration steps
1. Install webpack globally
npm install webpack -g
2. Create a new webpack.config.js to write this configuration file
module.exports = {
// 当前执行文件的路径
// 输入
entry:__dirname+"/app/index.js",
// 输出
output:{
path:__dirname+"/build",
filename:"bundle.js"
},
module:{
loaders:[{
test:/\.css$/,
loader:"style-loader!css-loader"
}]
},
watch:true,
devServer: {
contentBase: "./build",//本地服务器所加载的页面所在的目录
historyApiFallback: true,//不跳转
inline: true//实时刷新
},
}
3. Use the following terminal command to initialize and automatically create the package.json file. Just keep pressing enter.
npm init
4. The package.json file is ready. We are here Install Webpack as a dependent package in the project
// 安装Webpack npm install --save-dev webpack
Then create a new app and build folder in the folder. The app folder contains the js, css and other module files we want to write, and the build contains the js files generated by webpack packaging. And an index.html
The directory structure is as follows:
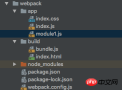
5.Introduce the automatically generated bundle.js
in the inex.html filenbsp;html> <meta> <title>Title</title> <p></p> <!--webpack/gulp/grount--> <script></script>
Define some variables and methods in module1.js and export them as a module using exports
console.log("我是module1.js");
var a = "我是a变量";
var fn = function(){
console.log("我是fn函数");
}
module.exports = {
a,
fn
}
Use require in index.js to introduce the methods and variables of module.js
var res = require("./module1");
require("./index.css");
console.log("我是index.js");
console.log(res.a);
res.fn();
6. Run webpack on the terminal
webpack
7. Configure scripts in package-loack.json
After configuring npm, you can use a simple npm start in the command line command to replace the webpack command
After configuring as below, npm dev can replace npm webpack-dev-server --open command
{
"dependencies": {
"css-loader": "^0.28.8",
"style-loader": "^0.19.1",
"webpack": "^3.10.0"
},
"devDependencies": {
"webpack-dev-server": "^2.11.0"
},
"scripts": {
"start": "webpack",
"dev": "webpack-dev-server --open"
}
}
At this time, enter npm start to package the file

related suggestion:
Detailed explanation of back-end rendering after webpack configuration
Example detailed explanation of vue-cli optimized webpack configuration
React and Webpack build packaging Detailed explanation of optimization examples
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of npm and webpack configuration methods in node.js. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScriptisnotbuiltonCorC ;it'saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninC .1)JavaScriptwasdesignedasalightweight,interpretedlanguageforwebbrowsers.2)EnginesevolvedfromsimpleinterpreterstoJITcompilers,typicallyinC ,improvingperformance.
 JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript can be used for front-end and back-end development. The front-end enhances the user experience through DOM operations, and the back-end handles server tasks through Node.js. 1. Front-end example: Change the content of the web page text. 2. Backend example: Create a Node.js server.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AMChoosing Python or JavaScript should be based on career development, learning curve and ecosystem: 1) Career development: Python is suitable for data science and back-end development, while JavaScript is suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 2) Learning curve: Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners; JavaScript syntax is flexible. 3) Ecosystem: Python has rich scientific computing libraries, and JavaScript has a powerful front-end framework.
 JavaScript Frameworks: Powering Modern Web DevelopmentMay 02, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JavaScript Frameworks: Powering Modern Web DevelopmentMay 02, 2025 am 12:04 AMThe power of the JavaScript framework lies in simplifying development, improving user experience and application performance. When choosing a framework, consider: 1. Project size and complexity, 2. Team experience, 3. Ecosystem and community support.
 The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AM
The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AMIntroduction I know you may find it strange, what exactly does JavaScript, C and browser have to do? They seem to be unrelated, but in fact, they play a very important role in modern web development. Today we will discuss the close connection between these three. Through this article, you will learn how JavaScript runs in the browser, the role of C in the browser engine, and how they work together to drive rendering and interaction of web pages. We all know the relationship between JavaScript and browser. JavaScript is the core language of front-end development. It runs directly in the browser, making web pages vivid and interesting. Have you ever wondered why JavaScr
 Node.js Streams with TypeScriptApr 30, 2025 am 08:22 AM
Node.js Streams with TypeScriptApr 30, 2025 am 08:22 AMNode.js excels at efficient I/O, largely thanks to streams. Streams process data incrementally, avoiding memory overload—ideal for large files, network tasks, and real-time applications. Combining streams with TypeScript's type safety creates a powe
 Python vs. JavaScript: Performance and Efficiency ConsiderationsApr 30, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Performance and Efficiency ConsiderationsApr 30, 2025 am 12:08 AMThe differences in performance and efficiency between Python and JavaScript are mainly reflected in: 1) As an interpreted language, Python runs slowly but has high development efficiency and is suitable for rapid prototype development; 2) JavaScript is limited to single thread in the browser, but multi-threading and asynchronous I/O can be used to improve performance in Node.js, and both have advantages in actual projects.
 The Origins of JavaScript: Exploring Its Implementation LanguageApr 29, 2025 am 12:51 AM
The Origins of JavaScript: Exploring Its Implementation LanguageApr 29, 2025 am 12:51 AMJavaScript originated in 1995 and was created by Brandon Ike, and realized the language into C. 1.C language provides high performance and system-level programming capabilities for JavaScript. 2. JavaScript's memory management and performance optimization rely on C language. 3. The cross-platform feature of C language helps JavaScript run efficiently on different operating systems.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools






