Home >Backend Development >PHP Tutorial >Use async-validator to write Form components
Use async-validator to write Form components
- 小云云Original
- 2018-01-11 13:38:282049browse
This article mainly introduces the method of using async-validator to write Form components. The editor thinks it is quite good, so I will share it with you now and give it as a reference. Let’s follow the editor to take a look, I hope it can help everyone.
In front-end development, form verification is a very common function. Some UI libraries such as ant.design and Element ui have implemented Form components with verification functions. async-validator is a library that can perform asynchronous verification of data. Both the Form component of ant.design and Element ui use async-validator. This article will briefly introduce the basic usage of async-validator and use this library to implement a simple Form component with verification function.
1. Basic usage of async-validator
The function of async-validator is to verify whether the data is legal and give prompt information according to the verification rules.
The following demonstrates the most basic usage of async-validator.
import AsyncValidator from 'async-validator'
// 校验规则
const descriptor = {
username: [
{
required: true,
message: '请填写用户名'
},
{
min: 3,
max: 10,
message: '用户名长度为3-10'
}
]
}
// 根据校验规则构造一个 validator
const validator = new AsyncValidator(descriptor)
const data = {
username: 'username'
}
validator.validate(model, (errors, fields) => {
console.log(errors)
})When the data does not meet the verification rules, you can get the corresponding error message in the callback function of validator.validate.
When the common verification rules in async-validator cannot meet the needs, we can write a custom verification function to verify the data. A simple check function is as follows.
function validateData (rule, value, callback) {
let err
if (value === 'xxxx') {
err = '不符合规范'
}
callback(err)
}
const descriptor = {
complex: [
{
validator: validateData
}
]
}
const validator = new AsyncValidator(descriptor)async-validator supports asynchronous verification of data, so when writing a custom verification function, regardless of whether the verification passes or not, the callback in the verification function must transfer.
2. Write Form component and FormItem component
Now that we know how to use async-validator, how to combine this library with the Form component to be written.
Implementation ideas
Use a picture to describe the implementation ideas.
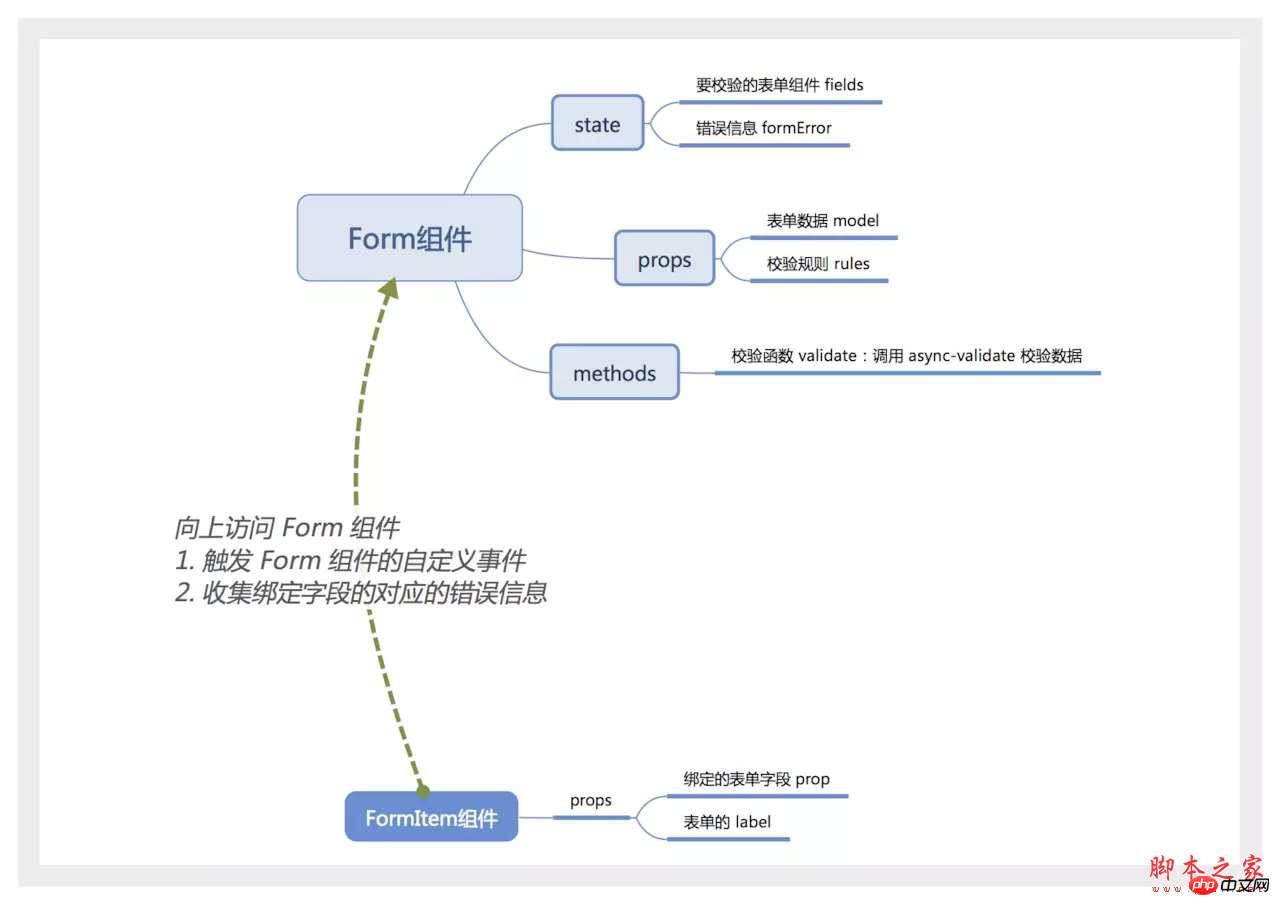
Form component
The Form component should be a container that contains an indefinite number of FormItem or other elements. You can use Vue's built-in slot component to represent the content in the Form.
The Form component also needs to know how many FormItem components it contains that need to be verified. Normally, the communication between parent and child components is achieved by binding events on the child components, but using slot here, the events of the child components cannot be monitored. Here you can listen to events through $on on the Form component, and trigger the custom event of the Form component before the FormItem is mounted or destroyed.
According to this idea, we first write the Form component.
<template>
<form class="v-form">
<slot></slot>
</form>
</template>
<script>
import AsyncValidator from 'async-validator'
export default {
name: 'v-form',
componentName: 'VForm', // 通过 $options.componentName 来找 form 组件
data () {
return {
fields: [], // field: {prop, el},保存 FormItem 的信息。
formError: {}
}
},
computed: {
formRules () {
const descriptor = {}
this.fields.forEach(({prop}) => {
if (!Array.isArray(this.rules[prop])) {
console.warn(`prop 为 ${prop} 的 FormItem 校验规则不存在或者其值不是数组`)
descriptor[prop] = [{ required: true }]
return
}
descriptor[prop] = this.rules[prop]
})
return descriptor
},
formValues () {
return this.fields.reduce((data, {prop}) => {
data[prop] = this.model[prop]
return data
}, {})
}
},
methods: {
validate (callback) {
const validator = new AsyncValidator(this.formRules)
validator.validate(this.formValues, (errors) => {
let formError = {}
if (errors && errors.length) {
errors.forEach(({message, field}) => {
formError[field] = message
})
} else {
formError = {}
}
this.formError = formError
// 让错误信息的顺序与表单组件的顺序相同
const errInfo = []
this.fields.forEach(({prop, el}, index) => {
if (formError[prop]) {
errInfo.push(formError[prop])
}
})
callback(errInfo)
})
}
},
props: {
model: Object,
rules: Object
},
created () {
this.$on('form.addField', (field) => {
if (field) {
this.fields = [...this.fields, field]
}
})
this.$on('form.removeField', (field) => {
if (field) {
this.fields = this.fields.filter(({prop}) => prop !== field.prop)
}
})
}
}
</script>FormItem component
The FormItem component is much simpler. First, you have to look up to find the Form component that contains it. Next, the corresponding error information can be calculated based on formError.
<template>
<p class="form-item">
<label :for="prop" class="form-item-label" v-if="label">
{{ label }}
</label>
<p class="form-item-content">
<slot></slot>
</p>
</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'form-item',
computed: {
form () {
let parent = this.$parent
while (parent.$options.componentName !== 'VForm') {
parent = parent.$parent
}
return parent
},
fieldError () {
if (!this.prop) {
return ''
}
const formError = this.form.formError
return formError[this.prop] || ''
}
},
props: {
prop: String,
label: String
}
}
</script>FormItem also needs to trigger some custom events of the Form component in the mounted and beforeDestroy hooks.
<script>
export default {
// ...
methods: {
dispatchEvent (eventName, params) {
if (typeof this.form !== 'object' && !this.form.$emit) {
console.error('FormItem必须在Form组件内')
return
}
this.form.$emit(eventName, params)
}
},
mounted () {
if (this.prop) {
this.dispatchEvent('form.addField', {
prop: this.prop,
el: this.$el
})
}
},
beforeDestroy () {
if (this.prop) {
this.dispatchEvent('form.removeField', {
prop: this.prop
})
}
}
}
</script>Finally create a new index.js to export the written component.
import VForm from './Form.vue'
import FormItem from './FormItem.vue'
export {
VForm,
FormItem
}3. How to use
The validation function of the form is in the Form component. You can access the Form component through $ref and call the validate function to obtain the corresponding verification information.
The usage is as follows:
<template>
<v-form :model="formData" :rules="rules" ref="form">
<form-item label="手机号" prop="tel">
<input type="tel" maxlength="11" v-model.trim="formData.tel"/>
</form-item>
<button @click="handleSubmit">保存</button>
</v-form>
</template>
<script>
import { VForm, FormItem } from './common/Form'
export default {
data () {
return {
formData: {
tel: ''
},
rules: {
tel: [
{required: true, message: '您的手机号码未输入'},
{pattern: /^1[34578]\d{9}$/, message: '您的手机号码输入错误'}
]
}
}
},
methods: {
handleSubmit () {
this.$refs.form.validate(errs => {
console.log(errs)
})
}
},
components: {
VForm,
FormItem
}
}
</script>Click here for the complete code.
4. Summary
This article briefly introduces the usage of async-validator and implements a Form component with verification function. The Form implemented here has many shortcomings: (1) It is only verified when the form is submitted. (2) The FormItem component should also adjust the UI based on the verification results and give corresponding prompts. Therefore, the Form component is more suitable for use on mobile terminals with less interaction.
Based on this implementation idea, you can write more customized Form components according to application scenarios.
Related recommendations:
Detailed explanation of vue and vue-validator to implement form verification function
bootstrapValidator custom verification method writing
About the use of formValidator form validation plug-in
The above is the detailed content of Use async-validator to write Form components. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

