 Backend Development
Backend Development PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial Detailed explanation of using synchronized to implement a Lock code
Detailed explanation of using synchronized to implement a Lock codeThis article introduces how to use synchronized to implement a Lock code. The following is a practical case. Friends in need can refer to it.
Method one:
public synchronized void a(){
//TODO
}Method two:
public void b(){
synchronized(this){
//TODO
}
}From these two ways Look, the locks are all added between {}. Let’s take a look at how Lock is done:
public void c() {
lock.lock();
try {
// TODO
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}The lock in this way is added between lock( ) and unlock(), so if you want to implement a lock function, you must think about how to implement these two methods, the lock() and unlock() methods. First define a framework as follows:
public void lock(){
}
public void unlock(){
}
Then think about how to use synchronized to implement these two methods.
Now I actually have a slightly clearer idea, but I still don’t know how to fill in these two methods. I will analyze the characteristics of Lock later, and then look at this code:
public void c() {
lock.lock();
//When current thread get the lock, other thread has to wait
try {
//current thread get in the lock, other thread can not get in
// TODO
}
finally {
lock.unlock();
//current thread release the lock
}
}
I just added a few comments to this code and did nothing else. Does it help to understand this code and see if it appears most frequently? What is the word? It is currentthread. So when we fill in the lock() and unlock() methods, should we pay attention to the keyword currentthread to find the solution? The answer is yes.
Next, analyze, how to make the thread wait when using synchronized? Use the wait() method. How to wake up the thread? Use the notify() method. Then use the wait() method in the lock() method and the notify() method in the unlock() method. So there is a condition when we use wait() and notify(). Think about what we should use as the condition?
We should use whether the current lock is occupied as a judgment condition. If the lock is occupied, currentthread waits. Think about whether we have always used this condition when using synchronized, the answer is yes.
Let’s analyze when to release the lock and what conditions are used. Think about it. If thread A gets the lock, can thread B release it? Of course not. If B could be released, it would violate the principle. Of course not. It must be that thread A's lock can only be released by thread A. So the judgment condition is to judge whether the thread holding the lock is currentthread. If so, it can be released. If not, of course it cannot.
Now let’s take a look at the complete code:
package test.lock;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory;
public class NaiveLock {
private static final long NONE = -1;
private long owner = NONE;
private Boolean isLooked() {
return owner != NONE;
}
public synchronized void lock() {
long currentThreadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
if (owner == currentThreadId) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Lock has been acquired by current thread");
}
while (this.isLooked()) {
System.out.println(String.format("thread %s is waitting lock", currentThreadId));
try {
wait();
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
owner = currentThreadId;
System.out.println(String.format("Lock is acquired by thread %s", owner));
}
public synchronized void unlock() {
if (!this.isLooked() || owner != Thread.currentThread().getId()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Only Lock owner can unlock the lock");
}
System.out.println(String.format("thread %s is unlocking", owner));
System.out.println();
owner = NONE;
notify();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final NaiveLock lock = new NaiveLock();
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(20, new ThreadFactory() {
private ThreadGroup group = new ThreadGroup("test thread group");
{
group.setDaemon(true);
}
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(group, r);
}
}
);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
executor.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
lock.lock();
System.out.println(String.format("thread %s is running...", Thread.currentThread().getId()));
try {
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextint(1000));
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
lock.unlock();
}
}
);
}
}
}
Lock is acquired by thread 8 thread 8 is running... thread 27 is waitting lock thread 26 is waitting lock thread 25 is waitting lock thread 24 is waitting lock thread 23 is waitting lock thread 22 is waitting lock thread 21 is waitting lock thread 20 is waitting lock thread 19 is waitting lock thread 18 is waitting lock thread 17 is waitting lock thread 16 is waitting lock thread 15 is waitting lock thread 14 is waitting lock thread 13 is waitting lock thread 12 is waitting lock thread 11 is waitting lock thread 10 is waitting lock thread 9 is waitting lock thread 8 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 27 thread 27 is running... thread 27 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 26 thread 26 is running... thread 26 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 25 thread 25 is running... thread 25 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 24 thread 24 is running... thread 24 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 23 thread 23 is running... thread 23 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 22 thread 22 is running... thread 22 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 21 thread 21 is running... thread 21 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 20 thread 20 is running... thread 20 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 19 thread 19 is running... thread 19 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 18 thread 18 is running... thread 18 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 17 thread 17 is running... thread 17 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 16 thread 16 is running... thread 16 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 15 thread 15 is running... thread 15 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 14 thread 14 is running... thread 14 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 13 thread 13 is running... thread 13 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 12 thread 12 is running... thread 12 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 11 thread 11 is running... thread 11 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 10 thread 10 is running... thread 10 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 9 thread 9 is running... thread 9 is unlocking
for loop to 30 times, look at the result again:
Lock is acquired by thread 8 thread 8 is running... thread 27 is waitting lock thread 26 is waitting lock thread 25 is waitting lock thread 24 is waitting lock thread 23 is waitting lock thread 22 is waitting lock thread 21 is waitting lock thread 20 is waitting lock thread 19 is waitting lock thread 18 is waitting lock thread 17 is waitting lock thread 16 is waitting lock thread 15 is waitting lock thread 14 is waitting lock thread 13 is waitting lock thread 12 is waitting lock thread 11 is waitting lock thread 10 is waitting lock thread 9 is waitting lock thread 8 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 27 thread 27 is running... thread 8 is waitting lock thread 27 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 27 thread 27 is running... thread 26 is waitting lock thread 27 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 27 thread 27 is running... thread 25 is waitting lock thread 27 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 24 thread 24 is running... thread 27 is waitting lock thread 24 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 23 thread 23 is running... thread 24 is waitting lock thread 23 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 22 thread 22 is running... thread 23 is waitting lock thread 22 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 22 thread 22 is running... thread 21 is waitting lock thread 22 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 22 thread 22 is running... thread 20 is waitting lock thread 22 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 22 thread 22 is running... thread 19 is waitting lock thread 22 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 22 thread 22 is running... thread 18 is waitting lock thread 22 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 17 thread 17 is running... thread 17 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 16 thread 16 is running... thread 16 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 15 thread 15 is running... thread 15 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 14 thread 14 is running... thread 14 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 13 thread 13 is running... thread 13 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 12 thread 12 is running... thread 12 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 11 thread 11 is running... thread 11 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 10 thread 10 is running... thread 10 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 9 thread 9 is running... thread 9 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 8 thread 8 is running... thread 8 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 26 thread 26 is running... thread 26 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 25 thread 25 is running... thread 25 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 27 thread 27 is running... thread 27 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 24 thread 24 is running... thread 24 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 23 thread 23 is running... thread 23 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 21 thread 21 is running... thread 21 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 20 thread 20 is running... thread 20 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 19 thread 19 is running... thread 19 is unlocking Lock is acquired by thread 18 thread 18 is running... thread 18 is unlocking
Detailed code examples of how to implement stack data structure and bracket matching algorithm in php
The most popular in php Simple string matching algorithm, php matching algorithm_PHP tutorial
The simplest string matching algorithm tutorial in php
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of using synchronized to implement a Lock code. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Java多线程中Lock怎么使用May 12, 2023 pm 02:46 PM
Java多线程中Lock怎么使用May 12, 2023 pm 02:46 PMJdk1.5以后,在java.util.concurrent.locks包下,有一组实现线程同步的接口和类,说到线程的同步,可能大家都会想到synchronized关键字,这是java内置的关键字,用来处理线程同步的,但这个关键字有很多的缺陷,使用起来也不是很方便和直观,所以就出现了Lock,下面,我们就来对比着讲解Lock。通常我们在使用synchronized关键字的时候会遇到下面这些问题:(1)不可控性,无法做到随心的加锁和释放锁。(2)效率比较低下,比如我们现在并发的读两个文件,读与读之
 Java中Synchronized的原理和使用场景以及Callable接口的使用方法及区别分析Apr 21, 2023 am 08:04 AM
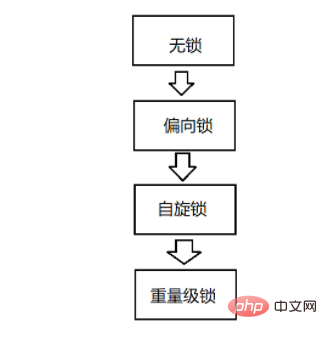
Java中Synchronized的原理和使用场景以及Callable接口的使用方法及区别分析Apr 21, 2023 am 08:04 AM一、基本特点1.开始时是乐观锁,如果锁冲突频繁,就转换为悲观锁.2.开始是轻量级锁实现,如果锁被持有的时间较长,就转换成重量级锁.3.实现轻量级锁的时候大概率用到的自旋锁策略4.是一种不公平锁5.是一种可重入锁6.不是读写锁二、加锁工作过程JVM将synchronized锁分为无锁、偏向锁、轻量级锁、重量级锁状态。会根据情况,进行依次升级。偏向锁假设男主是一个锁,女主是一个线程.如果只有这一个线程来使用这个锁,那么男主女主即使不领证结婚(避免了高成本操作),也可以一直幸福的生活下去.但是女配出现
 Java Lock类提供哪些功能?Apr 21, 2023 am 08:16 AM
Java Lock类提供哪些功能?Apr 21, 2023 am 08:16 AM说明1、Lock是java.util.concurent包下的接口,定义了一系列的锁定操作方法。2、Lock界面主要包括ReentrantLock、ReentrantReadWriteLock、ReentrantReadWriteLock、WriteLock实现类。与Synchronized不同,Lock提供了获取锁、释放锁等相关界面,使其使用更加灵活,操作更加复杂。实例ReentrantReadWriteLocklock=newReentrantReadWriteLock();Lockread
 Java中Lock的使用方式有哪些?Apr 23, 2023 pm 08:52 PM
Java中Lock的使用方式有哪些?Apr 23, 2023 pm 08:52 PM1.作用(1)Lock方式来获取锁支持中断、超时不获取、是非阻塞的(2)提高了语义化,哪里加锁,哪里解锁都得写出来(3)Lock显式锁可以给我们带来很好的灵活性,但同时我们必须手动释放锁(4)支持Condition条件对象(5)允许多个读线程同时访问共享资源2.lock用法//获取锁voidlock()//如果当前线程未被中断,则获取锁voidlockInterruptibly()//返回绑定到此Lock实例的新Condition实例ConditionnewCondition()//仅在调用时锁
 Java关键字synchronized原理与锁的状态实例分析May 11, 2023 pm 03:25 PM
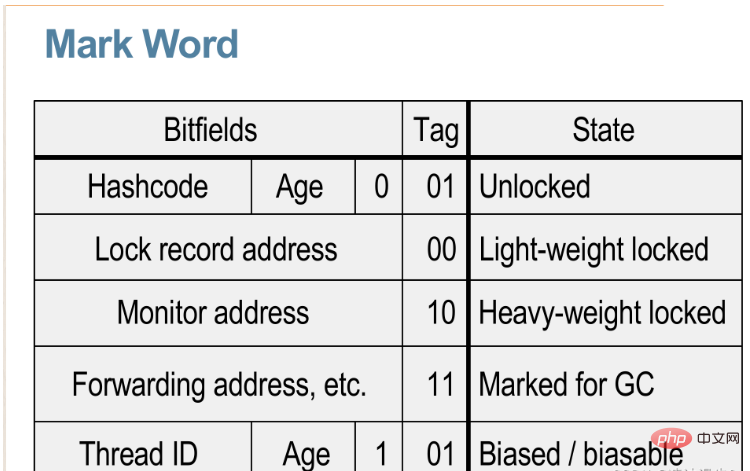
Java关键字synchronized原理与锁的状态实例分析May 11, 2023 pm 03:25 PM一、Java中锁的概念自旋锁:是指当一个线程获取锁的时候,如果锁已经被其它线程获取,那么该线程将循环等待,然后不断的判断锁是否能被成功获取,直到获取到锁才会退出循环。乐观锁:假定没有冲突,在修改数据时如果发现数据和之前获取的不一致,则读最新数据,重试修改。悲观锁:假定会发生并发冲突,同步所有对数据的相关操作,从读数据就开始上锁。独享锁(写):给资源加上写锁,线程可以修改资源,其它线程不能再加锁(单写)。共享锁(读):给资源加上读锁后只能读不能修改,其它线程也只能加读锁,不能加写锁(多度)。看成S
 Java中的三种同步方式和它们的使用方法是什么?Apr 27, 2023 am 09:34 AM
Java中的三种同步方式和它们的使用方法是什么?Apr 27, 2023 am 09:34 AM1、说明synchronized算是我们最常用的同步方式,主要有三种使用方式。2、实例//普通类方法同步synchronizedpublidvoidinvoke(){}//类静态方法同步synchronizedpublicstaticvoidinvoke(){}//代码块同步synchronized(object){}这三种方式的不同之处在于同步的对象不同,普通类synchronized同步的是对象本身,静态方法同步的是类Class本身,代码块同步的是我们在括号内部填写的对象。Java有哪些集合
 Java中如何利用synchronized实现同步机制?Apr 22, 2023 pm 02:46 PM
Java中如何利用synchronized实现同步机制?Apr 22, 2023 pm 02:46 PMJava的synchronized使用方法总结1.把synchronized当作函数修饰符时,示例代码如下:Publicsynchronizedvoidmethod(){//….}这也就是同步方法,那这时synchronized锁定的是哪个对象呢?他锁定的是调用这个同步方法对象。也就是说,当一个对象P1在不同的线程中执行这个同步方法时,他们之间会形成互斥,达到同步的效果。但是这个对象所属的Class所产生的另一对象P2却能够任意调用这个被加了synchronized关键字的方法。上边的示例代码等
 Java Synchronized锁升级原理及过程是什么Apr 19, 2023 pm 10:22 PM
Java Synchronized锁升级原理及过程是什么Apr 19, 2023 pm 10:22 PM工具准备在正式谈synchronized的原理之前我们先谈一下自旋锁,因为在synchronized的优化当中自旋锁发挥了很大的作用。而需要了解自旋锁,我们首先需要了解什么是原子性。所谓原子性简单说来就是一个一个操作要么不做要么全做,全做的意思就是在操作的过程当中不能够被中断,比如说对变量data进行加一操作,有以下三个步骤:将data从内存加载到寄存器。将data这个值加一。将得到的结果写回内存。原子性就表示一个线程在进行加一操作的时候,不能够被其他线程中断,只有这个线程执行完这三个过程的时候


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.





