Detailed explanation of usage and clearing of document.write() in JS
Many friends may have encountered such a situation, that is, when using the document.write() function to write content to a web page, the original content in the document will be cleared. This is especially useful for beginners. It’s a problem. Let’s introduce why this happens. Of course, we will also know how to avoid it. This article mainly introduces the usage of document.write() in JS and a brief analysis of the reasons for clearing. Friends who need it can refer to it. I hope it can help everyone.
Let’s look at a code example first:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset=" utf-8">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload=function(){
document.write("重温 JavaScript");
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello JavaScript</p>
</body>
</html>
From the above code, we can see that the document.write() function converts the original The document content has been cleared. The following is the reason for this situation:
The window.onload event is to execute the event processing function after the document content is completely loaded. Of course, the document stream has been closed. At this time, the document flow is executed. The .writ() function will automatically call the document.open() function to create a new document stream, write new content, and then display it through the browser, thus overwriting the original content. However, many friends still have this question, why in the following situation, the content in the original web page will not be overwritten, the code is as follows:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset=" utf-8">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
document.write("重温 JavaScript");
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello JavaScript</p>
</body>
</html>
above In the code, the original document content has not been cleared. This is because the current document stream is created by the browser, and the document.wirte() function is in it. That is, the document stream is not closed when this function is executed. At this time, the document.open() function will not be called to create a new document stream, so it will not be overwritten. Some friends may ask why the following method still does not work. The code is as follows:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset=" utf-8">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
document.close();
document.write("重温 JavaScript");
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello JavaScript</p>
</body>
</html>
The document flow is closed using document.close() above, why does it still not work? The original content can be overwritten. Unfortunately, the document stream is created by the browser and cannot be closed manually without permission. The document.close() function can only close the document stream created by the document.open() function. Look at the following code example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset=" utf-8">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function create(){
var newWindow=window.open("","Document","_blank");
newWindow.document.write("Hello JavaScript");
newWindow.document.close();
newWindow.document.write("覆盖后的输出");
}
window.onload=function(){
var obt=document.getElementById("bt");
obt.onclick=function(){
create();
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p id="print">Hello JavaScript</p>
<input type="button" id="bt" value="查看效果"/>
</body>
</html>
The document stream created by document.open() can be closed by document.close(), then the second document The content output by .write() will overwrite the first output content.
When referencing external JavaScript asynchronously, you must first run document.open() to clear the document, and then run document.write(). The parameters are written at the beginning of the body content.
If you run document.write() directly without running document.open() first, it will be invalid and Chrome will have the following prompt:
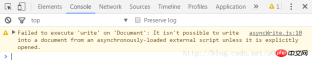
// asyncWrite.js document.open(); document.write('<p>test</p>'); document.close(); <!-- asyncWrite.html --> <!-- 运行前 --> <body> <script src="asyncWrite.js" async></script> </body> <!-- 运行后 --> <body> <p>test</p> </body>
Document.write() can also write strings containing script tags, but they need to be escaped. The content written in the script tag will run normally.
<!-- 运行前 -->
<script>
document.write('<script>document.write("<p>test</p>");<\/script>');
</script>
<!-- 运行后 -->
<script>
document.write('<script>document.write("<p>test</p>");<\/script>');
</script>
<script>document.write("<p>test</p>");</script>
<p>test</p>
document.write() can pass in multiple parameters.
<!-- 运行前 -->
<body>
<script>
document.write('<h2 id="multiArgument">multiArgument</h2>','<p>test</p>');
</script>
</body>
<!-- 运行后 -->
<body>
<script>
document.write('<h2 id="multiArgument">multiArgument</h2>','<p>test</p>');
</script>
<h2 id="multiArgument">multiArgument</h2>
<p>test</p>
</body>
Related recommendations:
JS issues related to obtaining an object created by document.write()
document.open() and document.write()_basic knowledge
js document.write() usage introduction_javascript skills
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of usage and clearing of document.write() in JS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython and JavaScript each have their own advantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1. Python is easy to learn, with concise syntax, suitable for data science and back-end development, but has a slow execution speed. 2. JavaScript is everywhere in front-end development and has strong asynchronous programming capabilities. Node.js makes it suitable for full-stack development, but the syntax may be complex and error-prone.
 JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScriptisnotbuiltonCorC ;it'saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninC .1)JavaScriptwasdesignedasalightweight,interpretedlanguageforwebbrowsers.2)EnginesevolvedfromsimpleinterpreterstoJITcompilers,typicallyinC ,improvingperformance.
 JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript can be used for front-end and back-end development. The front-end enhances the user experience through DOM operations, and the back-end handles server tasks through Node.js. 1. Front-end example: Change the content of the web page text. 2. Backend example: Create a Node.js server.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AMChoosing Python or JavaScript should be based on career development, learning curve and ecosystem: 1) Career development: Python is suitable for data science and back-end development, while JavaScript is suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 2) Learning curve: Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners; JavaScript syntax is flexible. 3) Ecosystem: Python has rich scientific computing libraries, and JavaScript has a powerful front-end framework.
 JavaScript Frameworks: Powering Modern Web DevelopmentMay 02, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JavaScript Frameworks: Powering Modern Web DevelopmentMay 02, 2025 am 12:04 AMThe power of the JavaScript framework lies in simplifying development, improving user experience and application performance. When choosing a framework, consider: 1. Project size and complexity, 2. Team experience, 3. Ecosystem and community support.
 The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AM
The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AMIntroduction I know you may find it strange, what exactly does JavaScript, C and browser have to do? They seem to be unrelated, but in fact, they play a very important role in modern web development. Today we will discuss the close connection between these three. Through this article, you will learn how JavaScript runs in the browser, the role of C in the browser engine, and how they work together to drive rendering and interaction of web pages. We all know the relationship between JavaScript and browser. JavaScript is the core language of front-end development. It runs directly in the browser, making web pages vivid and interesting. Have you ever wondered why JavaScr
 Node.js Streams with TypeScriptApr 30, 2025 am 08:22 AM
Node.js Streams with TypeScriptApr 30, 2025 am 08:22 AMNode.js excels at efficient I/O, largely thanks to streams. Streams process data incrementally, avoiding memory overload—ideal for large files, network tasks, and real-time applications. Combining streams with TypeScript's type safety creates a powe
 Python vs. JavaScript: Performance and Efficiency ConsiderationsApr 30, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Performance and Efficiency ConsiderationsApr 30, 2025 am 12:08 AMThe differences in performance and efficiency between Python and JavaScript are mainly reflected in: 1) As an interpreted language, Python runs slowly but has high development efficiency and is suitable for rapid prototype development; 2) JavaScript is limited to single thread in the browser, but multi-threading and asynchronous I/O can be used to improve performance in Node.js, and both have advantages in actual projects.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft







