1.Event processingFunction
Events refer to changes in the state of an object that are triggered automatically or manually by the user .
Event handling function: When the event is triggered, automatically executes the function
The event handling function is essentially an object Special attribute that points to a function.
Each element object can trigger various events, and each event corresponds to an event handling function.
When there is no event handling function bound, the event can still be triggered, but since the event binding function is empty at this time, no operation will be performed.
When the program is executed, the corresponding function or statement is bound to an event processing function of the object. Then once the specified event of the object is triggered, the browser will automatically execute the function. Operations in the object's event handler.
Binding event processing function = assign a value to the on event name (this function)
2. Basic event classification
1. Mouse event
onclick onbdclick onmousedown onmouseup onmouseover (triggered once when entering the boundary) onmouseout onmusemove
2. Keyboard events
onkeydown onkeyup onkeypress
3. Status events
onload onunload onchange (select) onfocus (form) onblur (form) onresize onsubmit onreset onerror
3. About event definition
There are three ways to define listening functions for a specific time:
1. Directly define the event-related attributes of the element in HTML
<p style="margin-bottom: 7px;"><标签 on事件名="fun()/js语句">按钮</标签</p>
<span style="color: #0000ff"><</span><span style="color: #800000">标签 class</span><span style="color: #0000ff">="d1"</span><span style="color: #ff0000"> onclick</span><span style="color: #0000ff">="fun()"</span><span style="color: #0000ff">></span><span style="color: #000000"><span style="color: #ff0000">相当于</span>d1.onclick=function(){
console.log(this.className); //d1
eval("fun()");//[window.]fun
}<br/><strong><span style="color: #ff0000">结论:fun()中this指向window</span></strong></span>//若要获得当前目标元素对象html:
onxxx="fun(this)"
js中定义函数时:
fun(elem);This method violates " The principle of "separation of content and behavior" should be used as little as possible.
2. Assign values to the event-related attributes of elements in JavaScript:
elem.on事件名=函数对象;
This method achieves "separation of content and behavior", but elements can only be bound Define a listening function.
3. Advanced event processing method, one event can be bound to multiple listening functions:
DOM standard: elem.addEventListener("event name", event object, Whether triggered during the capture phase)
IE8 standard: elem.attachEvent("on event name", event object)
btnObj.attachEvent('onclick',function(){}); //IE
btnObj.addEventListener('click',function(){}); //DOM
...
doucument.body.attachEvent('onload',initData); //IE
document.body.addEventListener('load',initData); //DOM
function(){
...
}This method can bind multiple listening functions to an element, but You need to pay attention to browser compatibility issues.
Small example: Reverse execution of event processing function
html:

css:

js:

Result:
Original

Click the innermost square result:


##3.Event Cycle
##DOM## After the interpreter creates an event object, It will be propagated among HTML elements
according to the following process: The second phase: the target is triggered and the event listening function is run The third phase: the event bubbles and the event propagates upward along the DOM tree 1. Event bubbling processing mechanism: 
result: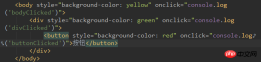

IE
只有两个阶段,没有捕获
4.event对象
任何事件触发之后都会产生一个event对象
当事件发生时,自动创建,封装了事件信息(keyCode/screenX/screenY...)
event对象记录事件发生时的鼠标位置,键盘按键状态和触发对象等信息,事件对象的常用属性:
- secElement(IE) / target(DOM) : 事件源对象 - eventPhase : 事件传播的阶段 - clientX/offsetX/pageX/screenX/x : 事件发生时的X坐标 - clientY/offsetY/pageY/screenY/y : 事件发生时的Y坐标 - which/keyCode/charCode : 键盘事件中按下的按键 - button : 鼠标哪个按键被按下 - cancelBubble : 是否取消事件冒泡 - returnValue : 是否阻止事件的默认行为
1.目标元素对象(从一而终)
1.HTML绑定事件方式
html:
onclick="fun(event)" //event必须这样写,不能变
//实际调用时,event会自动获得当前事件的对象
js:
fun(e){
//e中获取到的就是当前的事件对象
}2.js绑定方式
//DOM标准:自动创建event对象,默认以第一个参数传入自定义的事件处理函数对象 //IE标准:window全局的event属性,当事件发生时,自动创建event对象,保存在window.event中 var e=window.event||arguments[0]; var src=e.srcElement||e.target;
5.取消冒泡和利用冒泡
1.取消冒泡
DOM标准:e.stopPropagation()
IE标准:e.cancelBubble=true;
用在当前的事件处理函数的末尾
if(e.stopPropagation)
{
e.stopPropagation();
}else{
e.cancelBubble=true;
}2.利用冒泡
优化:若多个子元素中定义了相同的事件处理函数,只需要在共同的父元素上定义一次即可
原理:事件的捕获和冒泡不会受到程序的干扰,当触发子元素时,会捕获到该元素,然后在父元素触发事件。
6.取消事件
if(e.preventDefault){
e.preventDefault(); //DOM
}else{
e.returnValue=false; //IE
}何时取消:eg:表单提交之前,若验证未通过,就取消之后的自动提交。
The above is the detailed content of A brief detailed description of events in JavaScript. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AMPython and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AMThe shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AMDifferent JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AMJavaScript's applications in the real world include server-side programming, mobile application development and Internet of Things control: 1. Server-side programming is realized through Node.js, suitable for high concurrent request processing. 2. Mobile application development is carried out through ReactNative and supports cross-platform deployment. 3. Used for IoT device control through Johnny-Five library, suitable for hardware interaction.
 Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AMI built a functional multi-tenant SaaS application (an EdTech app) with your everyday tech tool and you can do the same. First, what’s a multi-tenant SaaS application? Multi-tenant SaaS applications let you serve multiple customers from a sing
 How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AMThis article demonstrates frontend integration with a backend secured by Permit, building a functional EdTech SaaS application using Next.js. The frontend fetches user permissions to control UI visibility and ensures API requests adhere to role-base
 JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web LanguageApr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web LanguageApr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AMJavaScript is the core language of modern web development and is widely used for its diversity and flexibility. 1) Front-end development: build dynamic web pages and single-page applications through DOM operations and modern frameworks (such as React, Vue.js, Angular). 2) Server-side development: Node.js uses a non-blocking I/O model to handle high concurrency and real-time applications. 3) Mobile and desktop application development: cross-platform development is realized through ReactNative and Electron to improve development efficiency.
 The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future ProspectsApr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future ProspectsApr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AMThe latest trends in JavaScript include the rise of TypeScript, the popularity of modern frameworks and libraries, and the application of WebAssembly. Future prospects cover more powerful type systems, the development of server-side JavaScript, the expansion of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and the potential of IoT and edge computing.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.





