This article mainly introduces the Dijkstra shortest path algorithm implemented in PHP, briefly describes the concept and function of Dijkstra shortest path algorithm, and analyzes the Dijkstra shortest path algorithm implemented in PHP based on specific examples. (Dijkstra) shortest path algorithm related steps and operating skills, friends in need can refer to
This article describes the Dijkstra (Dijkstra) shortest path algorithm implemented in PHP. Share it with everyone for your reference, the details are as follows:
1. Problems to be solved
The single-source shortest path problem, in a given direction The problem of finding the shortest path from one vertex (single source vertex) to all other vertices in the graph. In the figure below, there is a weight on each edge, and we hope to find the shortest path from A to all other vertices (B/C/D/E/F/G).
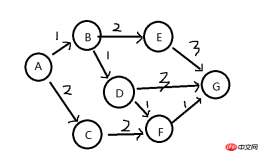
2. Problem analysis (the substructure of the shortest path is also optimal)
If P (A,G) is the shortest path from vertex A to G. Assuming that D and F are the midpoints on this path, then P(D,F) must be the shortest path from D to F. If P(D,F) is not the shortest path from D to F, then there must be another path from D to F from a certain node M that can make P(A,B...M...F,G) faster than P (A,G) is small and contradictory.
With this property, we can understand Dijkstra's algorithm.
3. Dijkstra algorithm
Dijkstra algorithm, also called Dijkstra algorithm (Dijkstra), also called single source shortest path algorithm, The so-called single source is the problem of finding the shortest path from a vertex to all reachable vertices in a directed graph. The problem is described as assuming that G = (V, E) is a directed graph, V represents the vertex and E represents the edge. Each of its edges (i, j) belongs to E and has a non-negative weight W (I, j). Specifying a node v0 in G requires connecting every link from v0 to G to vj (vj belongs to V ) find the shortest directed path (or point out that it does not exist). Dijstra's algorithm uses a greedy strategy, starting from the source point, and constantly finding the shortest distance to other points through connected points.
Dijkstra's greedy application uses the properties in (2), constantly selecting the "nearest" nodes and testing all possible links of each node, expanding outward layer by layer with the starting point as the center, until it extends to the end point. For source point A, gradually expand, and update the vertex information directly adjacent to i according to dist[j]=min{dist[j],dist[i]+matrix[i][j]}.
Algorithm description
1) Algorithm idea:
Suppose G=(V,E) is a weighted directed graph, and put the The vertex set V is divided into two groups. The first group is the vertex set for which the shortest path has been found (represented by S. Initially, there is only one source point in S. Afterwards, each shortest path is found, it will be added to the set S until All vertices are added to S, and the algorithm ends). The second group is the remaining set of vertices for which the shortest path has not been determined (represented by U). The vertices of the second group are added to S in order of increasing shortest path length. During the joining process, the length of the shortest path from the source point v to each vertex in S is always maintained to be no greater than the length of the shortest path from the source point v to any vertex in U. In addition, each vertex corresponds to a distance. The distance of the vertex in S is the shortest path length from v to this vertex. The distance of the vertex in U is the current path from v to this vertex that only includes the vertices in S as intermediate vertices. The shortest path length.
2) Algorithm steps:
a. Initially, S only contains the source point, that is, S={v}, and the distance of v is 0. U contains other vertices except v, that is: U={other vertices}. If v has an edge with vertex u in U, then has a normal weight value. If u is not an outgoing edge adjacent point of v, Then the weight of is ∞.
b. Select a vertex k from U with the smallest distance v, and add k to S (the selected distance is the shortest path length from v to k).
c. Taking k as the newly considered intermediate point, modify the distance of each vertex adjacent to k in U; if the distance from source point v to vertex u (passing vertex k) is longer than the original distance (not After passing vertex k) short, modify the distance value of vertex u. The modified distance value is the distance of vertex k plus the weight of the edge between k and u.
d. Repeat steps b and c until all vertices are included in S.
4. Algorithm PHP implementation
##
<?php
class Dijkstra
{
private $G;
public function __construct()
{
//有向图存储
$this->G = array(
array(0,1,2,0,0,0,0),
array(0,0,0,1,2,0,0),
array(0,0,0,0,0,2,0),
array(0,0,0,0,0,1,3),
array(0,0,0,0,0,0,3),
array(0,0,0,0,0,0,1),
array(0,0,0,0,0,0,0),
);
}
public function calculate()
{
// 存储已经选择节点和剩余节点
$U = array(0);
$V = array(1,2,3,4,5,6);
// 存储路径上节点距离源点的最小距离
$d = array();
//初始化图中节点与源点0的最小距离
for($i=1;$i<7;$i++)
{
if($this->G[0][$i]>0)
{
$d[$i] = $this->G[0][$i];
}
else
{
$d[$i] = 1000000;
}
}
// n-1次循环完成转移节点任务
for($l=0;$l<6;$l++)
{
// 查找剩余节点中距离源点最近的节点v
$current_min = 100000;
$current_min_v = 0;
foreach($V as $k=>$v)
{
if($d[$v] < $current_min)
{
$current_min = $d[$v];
$current_min_v = $v;
}
}
//从V中更新顶点到U中
array_push($U,$current_min_v);
array_splice($V,array_search($current_min_v,$V),1);
//更新
foreach($V as $k=>$u)
{
if($this->G[$current_min_v][$u]!=0&&$d[$u]>$d[$current_min_v]+$this->G[$current_min_v][$u])
{
$d[$u] = $d[$current_min_v]+$this->G[$current_min_v][$u];
}
}
}
foreach($d as $k => $u)
{
echo $k.'=>'.$u.'<br>';
}
}
}
?>Calling class:
$D = new Dijkstra; $D->calculate();Execution result:
1=>1 2=>2 3=>2 4=>3 5=>3 6=>4
The above is the detailed content of Dijkstra shortest path implemented in PHP. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Beyond the Hype: Assessing PHP's Role TodayApr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Beyond the Hype: Assessing PHP's Role TodayApr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AMPHP remains a powerful and widely used tool in modern programming, especially in the field of web development. 1) PHP is easy to use and seamlessly integrated with databases, and is the first choice for many developers. 2) It supports dynamic content generation and object-oriented programming, suitable for quickly creating and maintaining websites. 3) PHP's performance can be improved by caching and optimizing database queries, and its extensive community and rich ecosystem make it still important in today's technology stack.
 What are Weak References in PHP and when are they useful?Apr 12, 2025 am 12:13 AM
What are Weak References in PHP and when are they useful?Apr 12, 2025 am 12:13 AMIn PHP, weak references are implemented through the WeakReference class and will not prevent the garbage collector from reclaiming objects. Weak references are suitable for scenarios such as caching systems and event listeners. It should be noted that it cannot guarantee the survival of objects and that garbage collection may be delayed.
 Explain the __invoke magic method in PHP.Apr 12, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Explain the __invoke magic method in PHP.Apr 12, 2025 am 12:07 AMThe \_\_invoke method allows objects to be called like functions. 1. Define the \_\_invoke method so that the object can be called. 2. When using the $obj(...) syntax, PHP will execute the \_\_invoke method. 3. Suitable for scenarios such as logging and calculator, improving code flexibility and readability.
 Explain Fibers in PHP 8.1 for concurrency.Apr 12, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Explain Fibers in PHP 8.1 for concurrency.Apr 12, 2025 am 12:05 AMFibers was introduced in PHP8.1, improving concurrent processing capabilities. 1) Fibers is a lightweight concurrency model similar to coroutines. 2) They allow developers to manually control the execution flow of tasks and are suitable for handling I/O-intensive tasks. 3) Using Fibers can write more efficient and responsive code.
 The PHP Community: Resources, Support, and DevelopmentApr 12, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The PHP Community: Resources, Support, and DevelopmentApr 12, 2025 am 12:04 AMThe PHP community provides rich resources and support to help developers grow. 1) Resources include official documentation, tutorials, blogs and open source projects such as Laravel and Symfony. 2) Support can be obtained through StackOverflow, Reddit and Slack channels. 3) Development trends can be learned by following RFC. 4) Integration into the community can be achieved through active participation, contribution to code and learning sharing.
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the DifferencesApr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the DifferencesApr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AMPHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.
 PHP: Is It Dying or Simply Adapting?Apr 11, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP: Is It Dying or Simply Adapting?Apr 11, 2025 am 12:13 AMPHP is not dying, but constantly adapting and evolving. 1) PHP has undergone multiple version iterations since 1994 to adapt to new technology trends. 2) It is currently widely used in e-commerce, content management systems and other fields. 3) PHP8 introduces JIT compiler and other functions to improve performance and modernization. 4) Use OPcache and follow PSR-12 standards to optimize performance and code quality.
 The Future of PHP: Adaptations and InnovationsApr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The Future of PHP: Adaptations and InnovationsApr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AMThe future of PHP will be achieved by adapting to new technology trends and introducing innovative features: 1) Adapting to cloud computing, containerization and microservice architectures, supporting Docker and Kubernetes; 2) introducing JIT compilers and enumeration types to improve performance and data processing efficiency; 3) Continuously optimize performance and promote best practices.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),





