 Web Front-end
Web Front-end JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial Detailed explanation of usage examples of loading script files using ajax
Detailed explanation of usage examples of loading script files using ajaxUse the ajax method to load the script file code from the background to the foreground, and then execute the code through eval() on the loaded content. The second is to dynamically create a script tag, set its src attribute, and load js by inserting the script tag into the head of the page, which is equivalent to writing a
<script type="text/javascript" src="call.js"></script>
The following code is how Create this tag through js (and add it to the head):
var head= document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0]; var script= document.createElement('script'); script.type= 'text/javascript'; script.src= 'call.js'; head.appendChild(script);
When call.js is loaded, we have to call the method in it. However, we cannot call the js immediately after header.appendChild(script). Because the browser loads this js asynchronously, we don't know when it has finished loading. However, we can determine whether helper.js is loaded by listening to events. (Assume there is a callback method in call.js)
var head= document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0];
var script= document.createElement('script');
script.type= 'text/javascript';
script.onreadystatechange= function () {
if (this.readyState == 'complete')
callback();
}
script.onload= function(){
callback();
}
script.src= 'helper.js';
head.appendChild(script); Set up 2 event listening functions, because onreadystatechange is used in ie, and gecko, webkit browsers and opera all support onload. In fact, this.readyState == 'complete' does not work very well. In theory, the state changes are as follows:
0 uninitialized 1 loading 2 loaded 3 interactive 4 complete
But some states will be skipped. According to experience, in IE7, only one of loaded and completed can be obtained, but not both. The reason may be that the state change affects whether reading from the cache is affected, or it may be other reasons. It is best to change the judgment condition to this.readyState == 'loaded' || this.readyState == 'complete'
Refer to the implementation of jQuery, our final implementation is:
var head= document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0];
var script= document.createElement('script');
script.type= 'text/javascript';
script.onload = script.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (!this.readyState || this.readyState === "loaded" || this.readyState === "complete" ) {
help();
// Handle memory leak in IE
script.onload = script.onreadystatechange = null;
} };
script.src= 'helper.js';
head.appendChild(script);There is another The simple situation is that you can write the help() call at the end of helper.js, then you can ensure that help() can be automatically called after helper.js is loaded. Of course, you must also be able to see if this is suitable for your application.
Also need to note:
1. Because the src of the script tag can access resources across domains, this method can simulate ajax and solve the problem of ajax cross-domain access.
2. If the html code returned by ajax contains script, directly inserting innerHTML into the dom will not make the script in the html work. After a cursory look at the original code of jQuery().html(html), jQuery also parses the incoming parameters first, strips off the script code, and dynamically creates script tags. The jQuery html method is used to add the html into the dom if it contains script. is executable. Such as:
jQuery("#content").html("<script>alert('aa');<\/script>");The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of usage examples of loading script files using ajax. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Scrapy基于Ajax异步加载实现方法Jun 22, 2023 pm 11:09 PM
Scrapy基于Ajax异步加载实现方法Jun 22, 2023 pm 11:09 PMScrapy是一个开源的Python爬虫框架,它可以快速高效地从网站上获取数据。然而,很多网站采用了Ajax异步加载技术,使得Scrapy无法直接获取数据。本文将介绍基于Ajax异步加载的Scrapy实现方法。一、Ajax异步加载原理Ajax异步加载:在传统的页面加载方式中,浏览器发送请求到服务器后,必须等待服务器返回响应并将页面全部加载完毕才能进行下一步操
 如何使用CakePHP中的AJAX?Jun 04, 2023 pm 08:01 PM
如何使用CakePHP中的AJAX?Jun 04, 2023 pm 08:01 PM作为一种基于MVC模式的PHP框架,CakePHP已成为许多Web开发人员的首选。它的结构简单,易于扩展,而其中的AJAX技术更是让开发变得更加高效。在本文中,将介绍如何使用CakePHP中的AJAX。什么是AJAX?在介绍如何在CakePHP中使用AJAX之前,我们先来了解一下什么是AJAX。AJAX是“异步JavaScript和XML”的缩写,是指一种在
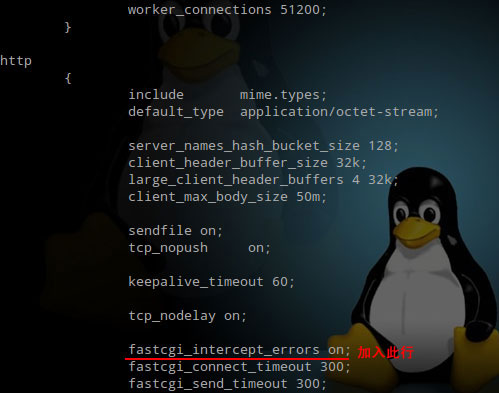 Nginx中404页面怎么配置及AJAX请求返回404页面May 26, 2023 pm 09:47 PM
Nginx中404页面怎么配置及AJAX请求返回404页面May 26, 2023 pm 09:47 PM404页面基础配置404错误是www网站访问容易出现的错误。最常见的出错提示:404notfound。404错误页的设置对网站seo有很大的影响,而设置不当,比如直接转跳主页等,会被搜索引擎降权拔毛。404页面的目的应该是告诉用户:你所请求的页面是不存在的,同时引导用户浏览网站其他页面而不是关掉窗口离去。搜索引擎通过http状态码来识别网页的状态。当搜索引擎获得了一个错误链接时,网站应该返回404状态码,告诉搜索引擎放弃对该链接的索引。而如果返回200或302状态码,搜索引擎就会为该链接建立索引
 jquery ajax报错403怎么办Nov 30, 2022 am 10:09 AM
jquery ajax报错403怎么办Nov 30, 2022 am 10:09 AMjquery ajax报错403是因为前端和服务器的域名不同而触发了防盗链机制,其解决办法:1、打开相应的代码文件;2、通过“public CorsFilter corsFilter() {...}”方法设置允许的域即可。
 什么是ajax重构Jul 01, 2022 pm 05:12 PM
什么是ajax重构Jul 01, 2022 pm 05:12 PMajax重构指的是在不改变软件现有功能的基础上,通过调整程序代码改善软件的质量、性能,使其程序的设计模式和架构更合理,提高软件的扩展性和维护性;Ajax的实现主要依赖于XMLHttpRequest对象,由于该对象的实例在处理事件完成后就会被销毁,所以在需要调用它的时候就要重新构建。
 script的意思是什么Aug 29, 2023 pm 02:00 PM
script的意思是什么Aug 29, 2023 pm 02:00 PMscript是指剧本或脚本的意思。在电影、电视、戏剧等艺术形式中,script用于描述角色的对话、动作和场景,以及故事的发展和结构。script的编写需要一定的技巧和经验,而且应该生动、有力,能够吸引观众的注意力,并传达出故事的情感和主题。script在电影和电视行业中尤为重要,是创作的基础,决定了电影的故事情节、角色发展和对话内容。script是艺术家们创作和表达的重要工具。
 php如何使用AJax和json实现登录验证Jun 19, 2023 pm 01:28 PM
php如何使用AJax和json实现登录验证Jun 19, 2023 pm 01:28 PMphp用AJax和json实现登录验证的方法是:1、创建一个jsp示例文件,导入jquery依赖和fastjson依赖文件;2、新建login.js文件,获取用户名和密码文本内容;3、新建controller类,查询用户是否存在并把对象转化为json字符串类型返回给js文件;4、js判断是否成功然后进行页面跳转即可。
 什么是ajax同步异步Jul 04, 2022 pm 03:57 PM
什么是ajax同步异步Jul 04, 2022 pm 03:57 PMajax同步的意思是当JavaScript代码加载到当前ajax的时候会把页面里所有的代码加载停止,页面处于假死状态,当这个ajax执行完之后,页面才会接触假死状态,代码继续运行;ajax异步的意思则是当前ajax代码运行的时候其他代码一样也可以运行。


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),





