Home >Java >javaTutorial >Detailed explanation of Java network programming examples
Detailed explanation of Java network programming examples
- 零下一度Original
- 2017-07-24 09:22:521856browse
1. Socket
The network driver provides an interface and a mechanism for application programming. It can be likened to a port terminal application that only needs to put the goods here. , even if the delivery of the goods is completed. It is created in the application, establishes a relationship with the driver through a binding mechanism, and tells itself the corresponding IP and Port.
Socket is a network programming class in java, located in the java.net package.
---- DatagramSocket //Used for UDP communication
---- ServerSocket //Used for TCP communication, used for server side
---- Socket //Server and client used for Tcp communication
2. UDP network program
InetAddress class represents the Internet Protocol (IP) address
//static InetAddress getLocalHost() throws UnknownHostException Returns the local host
//static InetAddress getByName(String host) Determines the IP address of the host given the host name. The hostname can be the machine name
static void ipDemo() throws UnknownHostException{
InetAddress netAddr=InetAddress.getLocalHost(); //取得本地电脑的一些信息System.out.println(netAddr.toString());
System.out.println(netAddr.getHostAddress());
System.out.println(netAddr.getHostName()); //取得其他电脑的信息InetAddress netAddr2=InetAddress.getByName("DELL-PC"); //这里也可以传IP地址System.out.println(netAddr2.getHostAddress()); //169.254.170.71System.out.println(netAddr2.getHostName()); //DELL-PC //取得百度的地址InetAddress [] ipList=InetAddress.getAllByName("www.baidu.com");for(InetAddress addr:ipList){
System.out.println(addr.toString());
}
}
3. UDP sending and receiving DatagramSocket, DatagramPacket
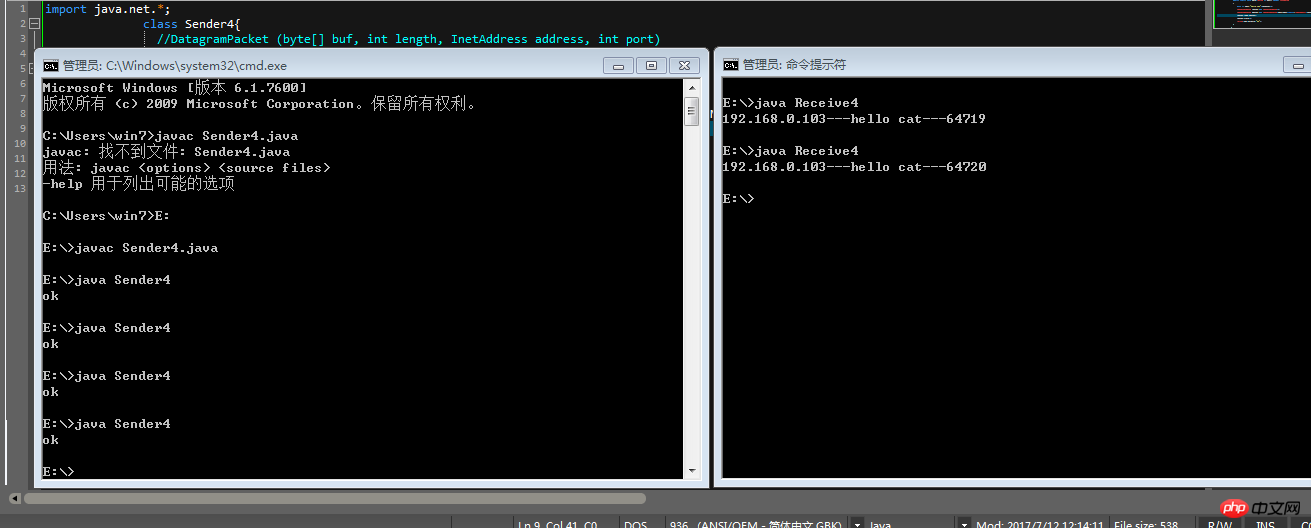
//Example 1 The simplest sending and receiving The sending end == needs to import the java.net packageSend the data through UDP:1) Establish a UDPSocket service2) Provide data and encapsulate the data into the data packet DatagramPacket (byte[] buf, int length, InetAddress address, int port) //There are multiple constructors3) Send data through the Socket service4) Close Resourceimport java.net.*;class Sender4{//DatagramPacket (byte[] buf, int length, InetAddress address, int port) public static void main(String [] args) throws Exception
{ byte [] buff="hello cat".getBytes();
DatagramSocket socket=new DatagramSocket();
DatagramPacket packet=new DatagramPacket(buff,buff.length,InetAddress.getByName("192.168.0.103"),8888);
socket.send(packet);
socket.close();
System.out.println("ok");
}
}
--Receiver1) Create a Socket service and specify to listen on a certain port2) Create a receiving Data DatagramPacket3) Take out the data from the package4) Close the resource
import java.net.*;class Receive4
{public static void main(String [] args) throws Exception
{
DatagramSocket socket=new DatagramSocket(8888); //别忘了端口号byte[] buff=new byte[1024] ;
DatagramPacket packet=new DatagramPacket(buff,buff.length);
socket.receive(packet);
String senderIp=packet.getAddress().getHostAddress();
String senderData=new String(packet.getData(),0,packet.getLength());int senderPort=packet.getPort();
System.out.println(senderIp+"---"+senderData+"---"+senderPort);
socket.close();
}
}
import java.net.*;import java.io.*;class NewSender{public static void main(String [] args) throws Exception
{
System.out.println("发送端启动了");
DatagramSocket socket=new DatagramSocket();
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); //包装键盘输入流String str=null;while((str=br.readLine())!=null){byte [] buff=str.getBytes();
DatagramPacket packet=new DatagramPacket(buff,buff.length,InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"),9000);
socket.send(packet);
}
br.close();
socket.close();
}
}
import java.net.*;class NewReceiver{public static void main(String [] args) throws Exception
{
DatagramSocket socket=new DatagramSocket(9000);
System.out.println("接收端启动了"); while(true){
byte [] buff=new byte[1024] ;
DatagramPacket packet=new DatagramPacket(buff,buff.length);
socket.receive(packet);
String senderIp=packet.getAddress().getHostAddress(); int sendPort=packet.getPort();
String msg= new String(packet.getData(),0,packet.getLength());
System.out.println(senderIp+":"+sendPort+":"+msg);
}
}
}
 ## Example 3: Multi-threaded chat room program
## Example 3: Multi-threaded chat room program
class Chat
{public static void main(String [] args)
{new Thread(new SendThread()).start(); new Thread(new ReceiveThread()).start();
}
}
//发送端import java.io.*;import java.net.*;class SendThread implements Runnable
{ private DatagramSocket socket;public void run()
{try{
socket=new DatagramSocket();
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String msg=null;while((msg=br.readLine())!=null){byte[] buff=msg.getBytes();
DatagramPacket packet=new DatagramPacket(buff,buff.length,InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"),10000);
socket.send(packet);
}
socket.close();
br.close();
}catch(Exception ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}//接收端import java.net.*;class ReceiveThread implements Runnable{ private DatagramSocket socket; public void run(){try{
socket=new DatagramSocket(10000);while(true){byte [] buff=new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket packet=new DatagramPacket(buff,buff.length);
socket.receive(packet);
String senderIp=packet.getAddress().getHostAddress();int senderPort=packet.getPort();
String msg=new String(packet.getData(),0,packet.getLength());
System.out.println(senderIp+":"+senderPort+":"+msg);
}
}catch(Exception ex)
{
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Java network programming examples. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

