Home >Java >javaTutorial >Introduction to Swing
Introduction to Swing
- 零下一度Original
- 2017-07-24 10:18:181994browse
Following the previous one, this article mainly records two small exercises on menus and file dialog boxes to familiarize yourself with the application of methods, some simple logic and an introduction to Swing, as well as records on the basics of GUI.
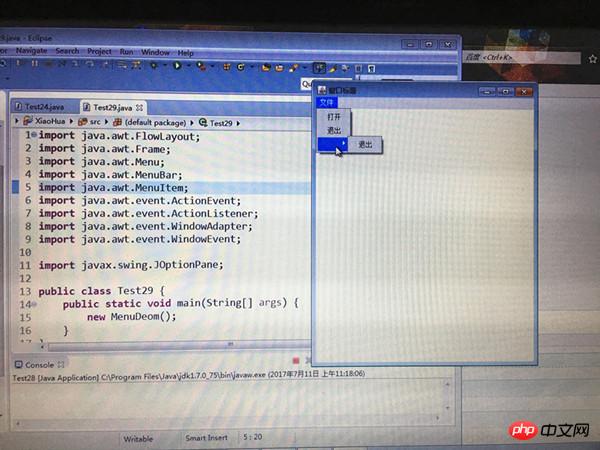
1. Create a menu
import java.awt.FlowLayout;import java.awt.Frame;import java.awt.Menu;import java.awt.MenuBar;import java.awt.MenuItem;import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;import java.awt.event.ActionListener;import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;import javax.swing.JOptionPane;public class Test29 {public static void main(String[] args) {new MenuDeom();
}
}class MenuDeom {
MenuDeom() {
init();
}private Frame f;private MenuBar mBar;private Menu menu;private Menu subMenu; // 这是要当作二级菜单的,放在 menu 下private MenuItem mItem1;private MenuItem mItem2;private void init() {
f = new Frame("窗口标题");
f.setBounds(20, 20, 400, 500);
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
mBar = new MenuBar(); // 创建一个菜单栏menu = new Menu("文件"); // 创建一个菜单mItem1 = new MenuItem("打开");
mItem2 = new MenuItem("退出");
menu.add(mItem1);
menu.add(mItem2);
subMenu = new Menu();
subMenu.add(new MenuItem("退出"));
menu.add(subMenu);
mBar.add(menu);
f.setMenuBar(mBar);
f.setVisible(true);
initEvent();
}private void initEvent() {
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
mItem1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.out.println("第一个响应了");
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "这是第一个菜单的响应");
}
});
mItem2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.out.println("第二个响应了");
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "这是第二个菜单的响应");
}
});
}
}
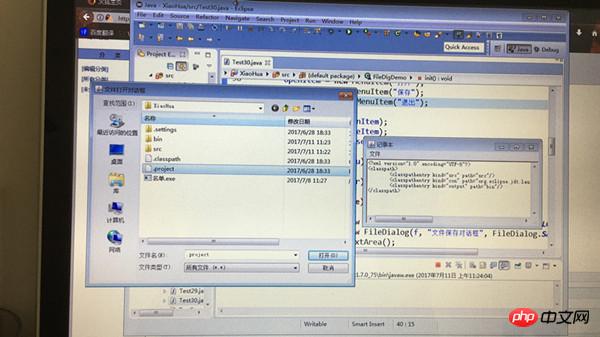
##2. Create a file dialog box
import java.awt.FileDialog;import java.awt.Frame;import java.awt.Menu;import java.awt.MenuBar;import java.awt.MenuItem;import java.awt.TextArea;import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;import java.awt.event.ActionListener;import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;import java.io.BufferedReader;import java.io.BufferedWriter;import java.io.File;import java.io.FileReader;import java.io.FileWriter;class FileDlgDemo {
FileDlgDemo() {
init();
}private Frame f;private MenuBar mBar;private Menu fileMenu;private MenuItem openItem, saveItem, closeItem;private TextArea txtArea;private FileDialog openFileDlg; // 文件打开对话框private FileDialog saveFileDlg; // 文件保存对话框private File file;private void init() {
f = new Frame("记事本");
f.setBounds(50, 50, 400, 200);
mBar = new MenuBar();
fileMenu = new Menu("文件");
openItem = new MenuItem("打开");
saveItem = new MenuItem("保存");
closeItem = new MenuItem("退出");
fileMenu.add(openItem);
fileMenu.add(saveItem);
fileMenu.add(closeItem);
mBar.add(fileMenu);
f.setMenuBar(mBar);
f.setVisible(true);
openFileDlg = new FileDialog(f, "文件打开对话框", FileDialog.LOAD);
saveFileDlg = new FileDialog(f, "文件保存对话框", FileDialog.SAVE);
txtArea = new TextArea();
f.add(txtArea);
initEvent();
}private void initEvent() {
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});// 打开openItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {try {
openFileDlg.setVisible(true);
String driStr = openFileDlg.getDirectory();
String fileName = openFileDlg.getFile();// System.out.println(driStr+":"+fileName);BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(
driStr + fileName));
String str = null;while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
txtArea.append(str + "\r\n");
}
br.close();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
});// 文件保存saveItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {try {
saveFileDlg.setVisible(true);
String dirStr = saveFileDlg.getDirectory();
String fileName = saveFileDlg.getFile();if (fileName != null && dirStr != null) {
file = new File(dirStr, fileName);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));
String content = txtArea.getText();
bw.write(content);
bw.close();
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}public class Test30 {public static void main(String[] args) {new FileDlgDemo();
}
}
3. Introduction to Swing and Swing Form
The biggest flaw of the AWT component is that it Dependent on the operating system, Swing components are developed based on AWT components and are pure Java components. In Swing programming, there are some frequently used components, including: 1.JFrame (form, frame) 2.JButton (button) 3.JLabel (label) 4.JTextField (text box) ... JFrame component is used to create windows in Swing programs Body; == Constructor of JFrame classJFrame() Creates a new form, which is initially invisibleJFrame(String title) Creates a new window body, use the parameter title to specify the title, the form is initially invisible == Common methods of the JFrame class void setTitle(String title) Set the form title, the title content is determined by the parameter title Specifyvoid setSize(int width, int height) Set the size of the form, the parameter width specifies the width, the parameter height specifies the height, the unit is pixelsvoid setResizable(boolean resizable) Set the form Whether the form can be resized is determined by the parameter resizablevoid setVisible(boolean b) Set whether the form is visible or not, determined by the parameter b, true is visible, false is invisibleContainer getContentPane( ) Get the content panel of the current formYou cannot add components directly to the Swing form, which contains a content panel container. You should add the component to the content panel;Cannot be a swing window Instead of setting the layout for the body, the layout should be set for the content panel in the swing formvoid setDefaultCloseOperation(int operation) Set the default operation to be performed when the form is closedvoid dispose() Release the current The resources occupied by the form and all its subcomponents, that is, unload the formvoid repaint() Redraw the current formsetDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); End the program when exiting // ImportantCode application example:import javax.swing.JFrame;//一个简单的窗体示例class MyFrame extends JFrame {/** *
*/private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;public MyFrame() {this.setTitle("这是个JFrame窗体");this.setSize(300, 200);this.setVisible(true);this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); // 正确的关闭窗体 }
}class Test31 {public static void main(String[] args) {new MyFrame();
}
}
4. Content panel
A complete form is composed of an external frame and The content panel is composed of two parts; the external frame refers to the hollow border composed of the title bar and four sides. It is mainly used to control the size and appearance of the form; what we actually operate is the content panel, such as setting the background color of the form, setting Layout of the form, adding other components to the form, etc.; we cannot directly add sub-components and partial managers to the JFrame. Use the getContentPane method to obtain the content panel of the current form. The return value of this method is Container (container) Class object (actually it should be a JRootPane class object, which can be forced), such as: Container contentPane = getContentPane();The Container class is in the java.awt package. The Container class is usually used to operate the content panel of JFrame. Its commonly used methods are: void setBackground(Color bg) Set the background color of the container, and the color is specified by the parameter bgvoid setLayout(LayoutManager mgr) Set the layout of the container, the parameter is the layout managerComponent add(Component comp) Add a component to the containerComponent add(Component comp, int index ) Add the specified component to the specified location in the containervoid remove(Component comp) Remove the specified component from the containervoid removeAll() Remove all components from the containervoid repaint() Redraw the current containerCode application example:import java.awt.Color;import java.awt.Container;import javax.swing.JFrame;//例子class ContentPaneDemo extends JFrame {public ContentPaneDemo() {super("内容面板示例"); // 设置标题Container c = this.getContentPane(); // 得到内容面板c.setBackground(Color.CYAN); // 背影设成青绿色this.setSize(300, 400);this.setResizable(false); // 窗体固定大小this.setVisible(true);this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}class Test32 {public static void main(String[] args) {new ContentPaneDemo();
}
}
Attachment: Color classColor class is used To create a color object, there are 7 overloading methods for its construction method. The following are the commonly used ones: Color(int r, int b, int g)The Color class also provides a A series of static color constants, for example: Color.BLACK
5. Common controls
1.JButton classJButton() Create an empty buttonJButton(String text) Create a button with textJButton(Icon icon) Create a button with iconJButton(String text, Icon icon) Create a button with Button with text and iconsuper("内容面板示例"); //设置标题 Container c=this.getContentPane(); //得到内容面板c.setBackground(Color.CYAN); //背影设成青绿色
c.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
Icon icon=new ImageIcon("src/8.gif");
JButton btn=new JButton("按纽名称",icon);
c.add(btn); this.setSize(300,400);this.setResizable(false); //窗体固定大小this.setVisible(true);this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
附加:常用方法
void setText(String text) 设置按钮上的文本
String getText() 获得按钮上的文本
void setBackground(Color bg) 设置按钮的背景色
Color getBackground() 获得按钮的背景色
void setEnabled(boolean b) 设置启用(或禁用)按钮,由参数b决定
void setVisible(boolean b) 设置按钮是否为可见,由参数b决定
void setToolTipText(String text) 设置按钮的悬停提示信息
void setMnemonic(int mnemonic) 设置按钮的快捷键
2.JLabel
既可以显示文本,也可以显示图像;
JLabel() 创建一个空的标签
JLabel(String text) 创建一个带文本的标签
JLabel(String text, int ha) 创建一个带文本的标签,并指定其对齐方式,可以是JLabel.LEFT、JLabel.CENTER和JLabel.RIGHT
JLabel(Icon image) 创建一个带图像的标签
JLabel(Icon image, int ha) 创建一个带图像的标签,并指定其对齐方式
JLabel(String text, Icon image, int ha) 创建一个带文本和图像的标签,并指定其对齐方式
void setText(String text) 设置标签上的文本
String getText() 获得标签上的文本
void setIcon(Icon icon) 设置标签中的图像
Icon getIcon() 获得标签中的图像
void setHorizontalAlignment(int alignment) 设置标签中文本的对齐方式
void setVisible(boolean b) 设置标签是否为可见
3.JTextFiel
JTextField() 创建一个空的文本框
JTextField(String text) 创建一个带文本的文本框
JTextField(int columns) 创建一个指定列数的空文本框
JTextField(String text, int columns) 创建一个带文本,并指定列数的文本框
void setText(String text) 设置文本框中的文本
String getText() 获得文本框中的文本
void setHorizontalAlignment(int alignment) 设置文本框中文本的对齐方式,可以是JTextField.LEFT、JTextField.CENTER和JTextField.RIGHT
void setEditable(boolean b) 设置文本框是否可以编辑,由参数b决定
void setEnabled(boolean enabled) 设置启用(或禁用)文本框
void setVisible(boolean b) 设置文本框是否为可见
4.JPanel
JPanel提供面板组件,它是轻量级的容器组件;
面板中可以添加其它组件,也可以设置布局,我们一般使用面板来实现布局嵌套;
JPanel类的构造方法有4种重载方式,以下是常用的几种:
JPanel() 创建一个空面板
JPanel(LayoutManaer layout) 创建带有指定布局的面板
JPanel(面板)的操作方式与Container(内容面板)很相似,以下是一些常用方法
void setBackground(Color bg) 设置面板的背景色,由参数bg指定颜色
void setLayout(LayoutManager mgr) 设置面板的布局,参数是布局管理器
Component add(Component comp) 往面板中添加一个组件
Component add(Component comp, int index) 将指定组件添加到面板中的指定位置上
void remove(Component comp) 从面板中移除指定的组件
void removeAll() 从面板中移除所有组件
void repaint() 重新绘制当前面板
相关应用的代码示例:
例一:
import java.awt.BorderLayout;import java.awt.Container;import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;import java.awt.event.ActionListener;import javax.swing.JButton;import javax.swing.JFrame;import javax.swing.JLabel;class EventDemo extends JFrame {private JLabel lblMsg;private JButton btn;
EventDemo() {
lblMsg = new JLabel("请点击下面的按钮..");
btn = new JButton("请点击");
Container c = this.getContentPane();
c.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
c.add(btn, BorderLayout.CENTER);
c.add(lblMsg, BorderLayout.NORTH);this.setTitle("这是窗体标题");
btn.addActionListener(new MyActionListener());this.setSize(300, 400);this.setVisible(true);this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}class MyActionListener implements ActionListener {public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
lblMsg.setText("按钮被点击了,我的内容变了");
}
}
}class Test33 {public static void main(String[] args) {new EventDemo();
}
}例二:
import java.awt.Container;import java.awt.FlowLayout;import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;import java.awt.event.ActionListener;import javax.swing.JButton;import javax.swing.JFrame;import javax.swing.JLabel;public class EventDemo extends JFrame {private JLabel lblMsg;private JButton btnClick1;private JButton btnClick2;public EventDemo() {
lblMsg = new JLabel("请点击下面的按钮...");
btnClick1 = new JButton("确定");
btnClick2 = new JButton("取消");
Container cpMe = getContentPane();
cpMe.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
cpMe.add(lblMsg);
cpMe.add(btnClick1);
cpMe.add(btnClick2);
setTitle("ActionListener Demo");
btnClick1.addActionListener(new MyListener());
btnClick2.addActionListener(new MyListener());
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setSize(300, 200);
setResizable(false); // 设置不允许用户自行调整窗口大小setVisible(true);
}class MyListener implements ActionListener {public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent ae) { // 实现事件处理函数((JButton) e.getSource()).setEnabled(false); // 禁用被点击的按钮if (ae.getSource() == btnClick1) {
lblMsg.setText("确定!");
}if (ae.getSource() == btnClick2) {
lblMsg.setText("取消!");
}
}
}public static void main(String[] args) {new EventDemo();
}
}六、java 图形坐标系统和图形上下文
java中,对大部分图形,文本,图像的操作方法都定义在 Graphics 类中,它是java.awt程序包的一部分
1)屏幕坐标系统 略
2)图形上下文,也称为图形环境
允许用户在屏幕上绘制图形的信息,它由 Graphics 类封装,表示一个绘制图层,它提供了绘制3种图形对象(形状,文本,图象)
Graphics 类的对象可以通过 Component 类的 getGraphics() 方法获得。
在游戏程序中,常在 paint()方法内获得 Graphics类对象,paint() 方法是Component提供的一个方法,当系统需要重绘组件时,会调用该方法,该方法只有一个参数,就是 Graphics 类的实例。
import java.awt.Color;import java.awt.Graphics;import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;import javax.swing.JFrame;class MyFrameAA extends JFrame {
MyFrameAA() {this.setTitle("一个游戏程序");this.setSize(300, 200);this.setVisible(true);this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);this.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {public void windowActivated(WindowEvent e) {
repaint();
}
});
}
@Overridepublic void paint(Graphics g) {super.paint(g);
System.out.println("paint 方法被调用了");
Color c = new Color(127, 200, 250);
g.setColor(c);
g.drawString("这是带颜色的字体", 100, 50);
g.drawRect(60, 70, 80, 80);
g.drawLine(0, 0, 90, 90);
}
}class Test34 {public static void main(String[] args) {new MyFrameAA();
}
}七、绘制动画
import java.awt.Color;import java.awt.Container;import java.awt.Graphics;import javax.swing.JFrame;import javax.swing.JPanel;class GamePanel extends JPanel implements Runnable {
GamePanel() {
Thread t = new Thread(this);
t.start();
}private int yPos = -80;
@Overridepublic void paint(Graphics g) {
g.clearRect(0, 0, this.getWidth(), this.getHeight());
g.setColor(Color.green);
g.fillOval(90, yPos, 80, 80);
}
@Overridepublic void run() {while (true) {try {
Thread.sleep(30);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
yPos += 5;if (yPos > this.getHeight()) {
yPos = -80;
}
repaint();
}
}
}class MyWindow extends JFrame {
MyWindow() {this.setTitle("游戏");
Container c = this.getContentPane();
c.add(new GamePanel());this.setBounds(150, 150, 300, 300);this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);this.setVisible(true);
}
}class Test35 {public static void main(String[] args) {new MyWindow();
}
}八、定时器
Timer 组件可以定时执行任务
Timer(int delay,ActionListener l)
--start()
--stop()
--restart();
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;import java.awt.event.ActionListener;import java.sql.Date;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;import javax.swing.JFrame;import javax.swing.JLabel;import javax.swing.Timer;class TimerDemo extends JFrame implements ActionListener {private JLabel lblMsg = new JLabel("这是原始值");private Timer timer;
TimerDemo() {this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);this.setSize(400, 400);this.add(lblMsg); // 直接添到窗体上timer = new Timer(1000, this);
timer.start();this.setVisible(true);
}public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String str = new SimpleDateFormat("hh-mm-ss").format(new Date(eventMask));
lblMsg.setText(str);
}
}class Test35 {public static void main(String[] args) {new TimerDemo();
}
}
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to Swing. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

