Home >Backend Development >Python Tutorial >How to use pymysqlpool in Python MySQL database?
How to use pymysqlpool in Python MySQL database?
- 零下一度Original
- 2017-07-09 11:57:264381browse
This article mainly introduces you to the relevant information about the Python MySQL database connection pool component pymysqlpool. The article introduces it in detail through the example code, which has certain reference and learning value for everyone. Friends in need Let’s take a look together below.
Introduction
pymysqlpool (local download) is a new member of the database toolkit, aiming to provide a practical database connection Pool middleware to avoid frequent creation and release of database connection resources in the application.
Function
The connection pool itself is It is thread-safe and can be used in a multi-threaded environment. There is no need to worry about connection resources being shared by multiple threads;
Provides the most compact interface possible for database operations;
The management of the connection pool is completed within the package, and the client can obtain the connection resources in the pool through the interface (return
pymysql.Connection);will be compatible with dataobj to the greatest extent and is easy to use;
The connection pool itself has the function of dynamically increasing the number of connections, that is, max_pool_size and step_size will Used to control the number of connections and the maximum number of connections added each time;
The maximum number of connections in the connection pool also increases dynamically. You need to turn on the enable_auto_resize switch. After that, when any connection acquisition timeout occurs, all It is recorded as a penalty, and max_pool_size is expanded by a certain multiple.
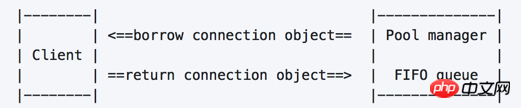
##Basic workflow
- After initialization, step_size connection objects are created first and placed in the connection pool;
- The client requests a connection object, and the connection pool will select a connection object that has not been used recently and return it (at the same time, it will check whether the connection is normal);
The client uses the connection object , after performing the corresponding operation, call the interface to return the connection object;
- The connection pool recycles the connection object and adds it to the queue in the pool for use by other requests.
|--------| |--------------| | | <==borrow connection object== | Pool manager | | Client | | | | | ==return connection object==> | FIFO queue | |--------| |--------------|
Parameter configuration
- pool_name: The name of the connection pool, multiple connection parameters correspond to multiple different connection pool objects, multiple
singleton mode;
- host: database Address
- user: Database server user name
- password: User password
- database: Default Selected database
- port: The port of the database server
- charset:
Character set, the default is 'utf8'
- use_dict_cursor: Use dictionary format or tuple to return data;
- max_pool_size: Connection pool priority maximum number of connections;
- step_size: The connection pool dynamically increases the number of connections;
- enable_auto_resize: Whether to dynamically expand the connection pool, that is, when it exceeds max_pool_size, automatically expand max_pool_size;
- pool_resize_boundary: This configuration is the upper limit that the connection pool can eventually increase, and the instantaneous expansion cannot exceed this value;
- auto_resize_scale: Automatically expand the gain of max_pool_size, The default is 1.5 times expansion;
- wait_timeout: How long to wait at most when queuing for a connection object. When timeout occurs, the connection pool attempts to automatically expand the current number of connections;
- kwargs: Other configuration parameters will be passed to
pymysql.Connection
# when creating the connection object ##Usage example
1. Use the cursor context manager (shortcut, but it will apply for a connection object every time it is obtained, so multiple calls are inefficient):
from pymysqlpool import ConnectionPool
config = {
'pool_name': 'test',
'host': 'localhost',
'port': 3306,
'user': 'root',
'password': 'root',
'database': 'test'
}
def connection_pool():
# Return a connection pool instance
pool = ConnectionPool(**config)
pool.connect()
return pool
# 直接访问并获取一个 cursor 对象,自动 commit 模式会在这种方式下启用
with connection_pool().cursor() as cursor:
print('Truncate table user')
cursor.execute('TRUNCATE user')
print('Insert one record')
result = cursor.execute('INSERT INTO user (name, age) VALUES (%s, %s)', ('Jerry', 20))
print(result, cursor.lastrowid)
print('Insert multiple records')
users = [(name, age) for name in ['Jacky', 'Mary', 'Micheal'] for age in range(10, 15)]
result = cursor.executemany('INSERT INTO user (name, age) VALUES (%s, %s)', users)
print(result)
print('View items in table user')
cursor.execute('SELECT * FROM user')
for user in cursor:
print(user)
print('Update the name of one user in the table')
cursor.execute('UPDATE user SET name="Chris", age=29 WHERE id = 16')
cursor.execute('SELECT * FROM user ORDER BY id DESC LIMIT 1')
print(cursor.fetchone())
print('Delete the last record')
cursor.execute('DELETE FROM user WHERE id = 16')2. Use connection context manager:
import pandas as pd
from pymysqlpool import ConnectionPool
config = {
'pool_name': 'test',
'host': 'localhost',
'port': 3306,
'user': 'root',
'password': 'root',
'database': 'test'
}
def connection_pool():
# Return a connection pool instance
pool = ConnectionPool(**config)
pool.connect()
return pool
with connection_pool().connection() as conn:
pd.read_sql('SELECT * FROM user', conn)
# 或者
connection = connection_pool().borrow_connection()
pd.read_sql('SELECT * FROM user', conn)
connection_pool().return_connection(connection)Please test more Move to test_example.py.
Dependency
- pymysql: You will rely on this tool package to complete database connection and other operations;
- pandas: pandas was used during testing.
The above is the detailed content of How to use pymysqlpool in Python MySQL database?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

