There are three main formats for time expression in the time module:
a. timestamp, which means starting from 00:00:00 on January 1, 1970 Offset calculated in seconds
b. struct_time time tuple, a total of nine element groups.
c. format time format time. The formatted structure makes the time more readable. Includes custom formats and fixed formats.
time
The commonly used functions are time.time() and time.sleep().
import timeprint(time.time())
1499305554.3239055
The above floating point number is called the UNIX epoch timestamp, which is the number of seconds that have passed from 0:00 on January 1, 1970 to today. You can see that there are 6 decimal places at the end. Using the round function, you can round floating point numbers. As follows
# 默认四舍五入到整数位,即不保留小数print(round(time.time()))# 可指定参数保留的小数位数print(round(time.time(), 2))
1499305554 1499305554.49
time.sleep(sec) can make the current sleep, and fill in seconds (s) as the parameter.
print('good') time.sleep(5.5)# 5.5秒后才打印这句print('yes')
good yes
Using some other functions
# 返回UTC时间print(time.gmtime())# 返回本地时间,在中国就是UTC+8print(time.localtime())
time.struct_time(tm_year=2017, tm_mon=7, tm_mday=6, tm_hour=1, tm_min=46, tm_sec=0, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=187, tm_isdst=0) time.struct_time(tm_year=2017, tm_mon=7, tm_mday=6, tm_hour=9, tm_min=46, tm_sec=0, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=187, tm_isdst=0)
You can find that this is a tuple type, and the time zone of China is UTC+8. It can be found that except tm_hour is different (their difference is exactly +8), the rest are the same.
The following function can return a formatted date and time, which looks more intuitive.
print(time.ctime())print(time.asctime())# 由于使用默认参数和上面的结果一样print(time.ctime(time.time()))print(time.asctime(time.localtime()))
Thu Jul 6 09:46:15 2017 Thu Jul 6 09:46:15 2017 Thu Jul 6 09:46:15 2017 Thu Jul 6 09:46:15 2017
ctime()You can pass in a timestamp. When no parameters are specified, the current one is used by default. Timestamp as parameter. That is,time.time()gtime()can pass in a struct_time. When no parameters are specified, By default, the current time is used. That is,time.localtime()
struct_time is converted into a string and the string is converted into struct_time
strptime One parameter is the date in string form, and the second parameter is a custom date conversion format. The formats of these two parameters must correspond. For example,
time.strptime('2017/7/6', '%Y-%m-%d')If one uses a slash and the other uses a dash, an error will be reported. This function returns a struct_timeThe first parameter of strftime is the date format you want to convert it to, and the second parameter is a struct_time. This function converts the tuple form of struct_time into The format specified by the first parameter is the converted date string format.
%Y-%m-%d represents the year, month and day, which will be introduced in detail in the datetime module.
a = time.strptime('2017/7/6', '%Y/%m/%d') b = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d', time.localtime())print(a)print(b)
time.struct_time(tm_year=2017, tm_mon=7, tm_mday=6, tm_hour=0, tm_min=0, tm_sec=0, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=187, tm_isdst=-1) 2017-07-06
Measuring the running time of a program
Using timestamps can conveniently time the running time of a program
start_time = time.time()sum = 0for i in range(10000000):sum += 1end_time = time.time()print(end_time - start_time)
2.185124397277832
You can see that the loop calculation and addition is executed 10 million times, and that program took more than 2 seconds.
You can also use the time.clock() function
start = time.clock()print(start) # 2.6773594453225194e-06time.sleep(2) end = time.clock()print(end - start) # 差值代表了睡眠2秒的时间。2.000246763295544time.sleep(3)print(time.clock()) # 5.00058991153112,返回的是从第一次调用到这次调用的时间间隔
4.4622657422041984e-07 2.0026006084745567 5.013243112269714
You can see clock when it is called for the first time Strangely, it returns the time the process is running. Any subsequent calls will be different from the value of the first call to clock. That is, the time elapsed from the first call to the current call to clock.
Like the above, set start above the part of the code you want to test, and set end at the end. You can also get the running time of the fragment code by subtracting it, and it is more accurate than time.time() .
datetime
datetime module is used to manage date and time, which has three sub-modules. They are time, date, datetime, so if you want to use datetime, you can use the following import method.
from datetime import datetime# 返回当前时间now = datetime.now()print(now.year, now.month, now.microsecond)# 可以自定义参数,返回格式化后的时间dt = datetime(2017, 10, 1, 23, 59, 59, 456123)print(dt)
2017 7 719609 2017-10-01 23:59:59.456123
datetime accepts 7 parameters, corresponding to year, month, day, hour, minute, second and microsecond. Saved in the year, month, day, hour, minute, second, microsecond attributes of datetime respectively.
The timestamp can be converted into datetime type. As follows, use the timestamp of the current time. Actually equivalent to datetime.now(). Of course, it is also possible to get the timestamp from datetime.
# 时间戳转datetimenow = datetime.fromtimestamp(time.time())print(now) sometime = datetime(2017, 7, 5, 23, 59, 59)# datetime转时间戳print(sometime.timestamp())
2017-07-06 09:46:07.903769 1499270399.0
These datetime objects can use the > symbol to compare the sequence of two dates. Subtraction operations can also be performed to express the difference between two moments. For example,
dt1 = datetime(2017, 5, 31) dt2 = datetime(2017, 4, 1)print(dt1 - dt2)print(dt1 > dt2)
60 days, 0:00:00 True
timedelta represents a period of time
Note that it does not represent a moment, but a period of time.
import datetime delta = datetime.timedelta(weeks=2, days=7, hours=1, seconds=59,microseconds=234353) delta1 = datetime.timedelta(days=5, hours=2)print(delta.seconds) # 返回属性hours和seconds的和print(delta.total_seconds()) # 只是以秒来表示这段时间print(delta > delta1)print(delta + delta1)
3659 1818059.234353 True 26 days, 3:00:59.234353
timedelta的接受的参数有weeks、days、hours、minutes、seconds、microseconds,但是其属性却只有days、seconds、microseconds。并且除了像datetime一样支持大小比较、减法运算外,还可以进行加法运算,表示两个时间段的差值。
将datetime转化为字符串形式及字符串转为datetime对象
time模块也有这两个函数(见上面的例子),使用上比较累类似。
strptime按照指定格式将字符串形式的日期转换成datetime对象并返回。
strftime将一个datetime对象(比如now)根据指定的格式转换成字符串并返回。
from datetime import datetime a = datetime.strptime('2017/7/6', '%Y/%m/%d') b = datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d')print(a)print(b)
2017-07-06 00:00:00 2017-07-06
关于日期时间的格式,看下表。
| 格式指令 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| %Y | 带世纪的四位年份,如2017 |
| %y | 后两位年份,如17表示2017 |
| %m | 月份,从01到12 |
| %B | 完整的月份,如November |
| %b | 月份的简写,如Nov |
| %d | 一个月中的第几天,如从01到31(如果有的话) |
| %j | 一年中的第几天 |
| %w | 一周中的第几天 |
| %A | 完整的周几,如Monday |
| %a | 简写的周几,如Mon |
| %H | 24小时制的小时00-23 |
| %h | 12小时制的小时01-12 |
| %M | 分,00-59 |
| %S | 秒,00-59 |
| %p | AM或者PM |
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to Python's time and datetime modules. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 如何在Python中将DateTime转换为整数?Sep 05, 2023 pm 10:21 PM
如何在Python中将DateTime转换为整数?Sep 05, 2023 pm 10:21 PM日期和时间值的操作是编程的一个重要方面,Python语言为此提供了一个有用的内置模块,称为datetime。但是,在某些情况下,可能需要将DateTime对象转换为整数值,以便执行特定的操作或计算。在Python中将DateTime转换为整数有多种方法,每种方法都有自己的优点和缺点。在本文中,我们将深入研究这些方法并检查每种方法何时适合使用。读完本文后,您将全面了解如何在Python中有效地将DateTime对象转换为整数,并能够为您的特定编程任务选择最合适的方法。方法一:使用timestamp
 使用C#中的DateTime.Today函数获取今天的日期Nov 18, 2023 pm 12:41 PM
使用C#中的DateTime.Today函数获取今天的日期Nov 18, 2023 pm 12:41 PM使用C#中的DateTime.Today函数获取今天的日期,需要具体代码示例C#是一种面向对象的编程语言,它提供了许多内置的类和方法来处理日期和时间。其中,DateTime类具有一些非常有用的方法,例如Today属性,可以用来获得当天的日期。下面是一个示例代码,演示如何使用C#中的DateTime.Today函数获取今天的日期:usingSystem;
 详细讲解Python之Seaborn(数据可视化)Apr 21, 2022 pm 06:08 PM
详细讲解Python之Seaborn(数据可视化)Apr 21, 2022 pm 06:08 PM本篇文章给大家带来了关于Python的相关知识,其中主要介绍了关于Seaborn的相关问题,包括了数据可视化处理的散点图、折线图、条形图等等内容,下面一起来看一下,希望对大家有帮助。
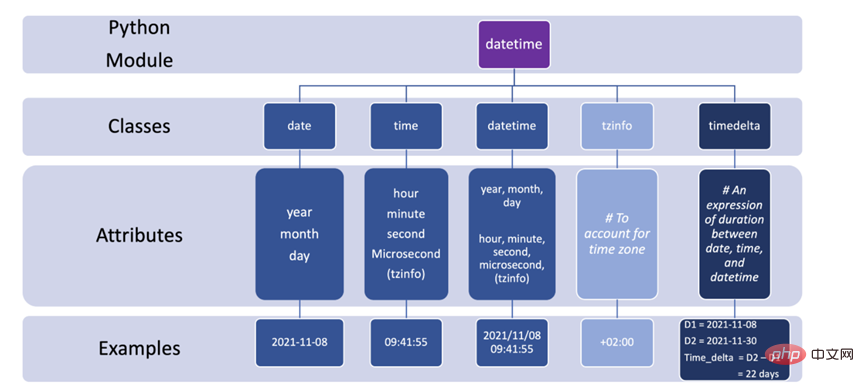 如何在 Python 中使用 DateTimeApr 19, 2023 pm 11:55 PM
如何在 Python 中使用 DateTimeApr 19, 2023 pm 11:55 PM所有数据在开始时都会自动分配一个“DOB”(出生日期)。因此,在某些时候处理数据时不可避免地会遇到日期和时间数据。本教程将带您了解Python中的datetime模块以及使用一些外围库,如pandas和pytz。在Python中,任何与日期和时间有关的事情都由datetime模块处理,它将模块进一步分为5个不同的类。类只是与对象相对应的数据类型。下图总结了Python中的5个日期时间类以及常用的属性和示例。3个有用的片段1.将字符串转换为日期时间格式,也许是使用datet
 分享10款高效的VSCode插件,总有一款能够惊艳到你!!Mar 09, 2021 am 10:15 AM
分享10款高效的VSCode插件,总有一款能够惊艳到你!!Mar 09, 2021 am 10:15 AMVS Code的确是一款非常热门、有强大用户基础的一款开发工具。本文给大家介绍一下10款高效、好用的插件,能够让原本单薄的VS Code如虎添翼,开发效率顿时提升到一个新的阶段。
 Python数据类型详解之字符串、数字Apr 27, 2022 pm 07:27 PM
Python数据类型详解之字符串、数字Apr 27, 2022 pm 07:27 PM本篇文章给大家带来了关于Python的相关知识,其中主要介绍了关于数据类型之字符串、数字的相关问题,下面一起来看一下,希望对大家有帮助。
 使用C#中的DateTime.AddDays函数给日期加上指定的天数Nov 18, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
使用C#中的DateTime.AddDays函数给日期加上指定的天数Nov 18, 2023 pm 03:08 PM使用C#中的DateTime.AddDays函数给日期加上指定的天数在C#编程中,我们经常会遇到需要对日期进行加减运算的情况。C#中的DateTime类提供了许多方便的方法和属性来处理日期和时间,其中包括AddDays函数,它可以用来给指定的日期加上指定的天数。下面是一个具体的代码示例,演示了如何使用DateTime.AddDays函数给日期加上指定的天数:
 Python中的日历库和日期库有哪些选择?Oct 21, 2023 am 09:22 AM
Python中的日历库和日期库有哪些选择?Oct 21, 2023 am 09:22 AMPython中有许多优秀的日历库和日期库供我们使用,这些库可以帮助我们处理日期和日历相关的操作。接下来,我将为大家介绍几个常用的选择,并提供相应的代码示例。datetime库:datetime是Python内置的日期和时间处理模块,提供了许多日期和时间相关的类和方法,可以用于处理日期、时间、时间差等操作。示例代码:importdatetime#获取当


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor







