 Java
Java javaTutorial
javaTutorial The processing flow of insert method, update method and delete method in java (Part 2)
The processing flow of insert method, update method and delete method in java (Part 2)Configuration’s newStatementHandler analysis
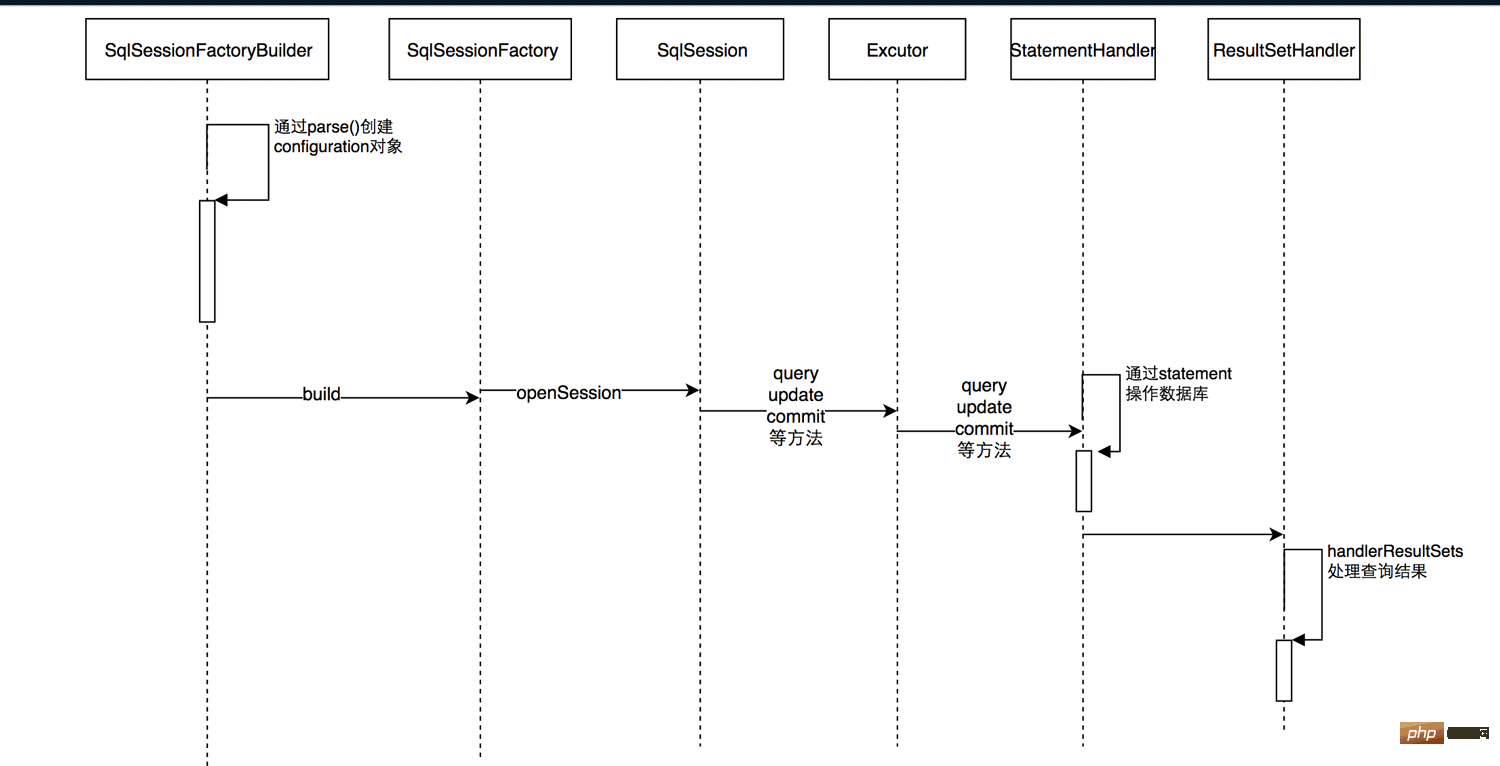
SimpleExecutor’s doUpdate method has been analyzed above:
1 public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException { 2 Statement stmt = null; 3 try { 4 Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); 5 StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null); 6 stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); 7 return handler.update(stmt); 8 } finally { 9 closeStatement(stmt);10 }11 }When I re-read the newStatementHandler method in line 5 in the past two days, I found that the method analyzed above in this method is too simple. Let’s go through the newStatementHandler method of Configuration. The implementation of the method is:
1 public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {2 StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);3 statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);4 return statementHandler;5 }The 3rd line of code is for adding a plug-in, which is nothing interesting. Take a look at the 2nd line of code. What is actually instantiated by the StatementHandler interface is RoutingStatementHandler, and the construction method The implementation is:
1 public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { 2 3 switch (ms.getStatementType()) { 4 case STATEMENT: 5 delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); 6 break; 7 case PREPARED: 8 delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); 9 break;10 case CALLABLE:11 delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);12 break;13 default:14 throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType());15 }16 17 }RoutingStatementHandler is also an implementation of the decorator pattern, which implements the StatementHandler interface and holds the StatementHandler interface reference delegate. The StatementType here is PREPARED, so the judgment on line 7 is executed to instantiate PreparedStatementHandler. The instantiation process is:
1 protected BaseStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { 2 this.configuration = mappedStatement.getConfiguration(); 3 this.executor = executor; 4 this.mappedStatement = mappedStatement; 5 this.rowBounds = rowBounds; 6 7 this.typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry(); 8 this.objectFactory = configuration.getObjectFactory(); 9 10 if (boundSql == null) { // issue #435, get the key before calculating the statement11 generateKeys(parameterObject);12 boundSql = mappedStatement.getBoundSql(parameterObject);13 }14 15 this.boundSql = boundSql;16 17 this.parameterHandler = configuration.newParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);18 this.resultSetHandler = configuration.newResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, rowBounds, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql);19 }The focus here is BoundSql , which can be obtained through MappedStatement. Several important contents are stored in BoundSql:
The parameter object itself
Parameter list
SQL statement to be executed
Some secondary development frameworks based on MyBatis usually get the SQL statements in BoundSql, modify them and reset them into BoundSql.
Generate Statement
##The process of generating Connection has been written above. This article continues Look, first let’s post the prepareStatement method of SimpleExecutor again:
1 private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {2 Statement stmt;3 Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);4 stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());5 handler.parameterize(stmt);6 return stmt;7 }
Then there is the code in line 4, which generates Statement. The code in line 4 is implemented as:
Statement prepare(Connection connection, Integer transactionTimeout)
delegate The above is the decorated role in the decorator mode. Its interface type is StatementHandler and its real type is PreparedStatementHandler. This has been analyzed at the beginning. Take a look at the prepare method implementation:
1 public Statement prepare(Connection connection, Integer transactionTimeout) throws SQLException { 2 ErrorContext.instance().sql(boundSql.getSql()); 3 Statement statement = null; 4 try { 5 statement = instantiateStatement(connection); 6 setStatementTimeout(statement, transactionTimeout); 7 setFetchSize(statement); 8 return statement; 9 } catch (SQLException e) {10 closeStatement(statement);11 throw e;12 } catch (Exception e) {13 closeStatement(statement);14 throw new ExecutorException("Error preparing statement. Cause: " + e, e);15 }16 }
The code in line 6 sets the query timeout, and the code in line 7 sets the received data size. I won’t follow up and look at it. Let’s look at the implementation of the instantiateStatement method in line 6:
1 protected Statement instantiateStatement(Connection connection) throws SQLException { 2 String sql = boundSql.getSql(); 3 if (mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator() instanceof Jdbc3KeyGenerator) { 4 String[] keyColumnNames = mappedStatement.getKeyColumns(); 5 if (keyColumnNames == null) { 6 return connection.prepareStatement(sql, PreparedStatement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS); 7 } else { 8 return connection.prepareStatement(sql, keyColumnNames); 9 }10 } else if (mappedStatement.getResultSetType() != null) {11 return connection.prepareStatement(sql, mappedStatement.getResultSetType().getValue(), ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY);12 } else {13 return connection.prepareStatement(sql);14 }15 }
Line 2, get the real SQL statement from boundSql, The first part has already been analyzed. After getting the SQL statement, execute the judgment on lines 3 and 5. Here is the code we are familiar with to get the Statement through Connection. PreparedStatement is obtained through the prepareStatement method. Its true type is com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4PreparedStatement, which is Subclass of PreparedStatement.
Statement parameter setting
After obtaining the Statement, the next step is to set the parameters. , look at the code for setting parameters, or go back to the prepareStatement method of SimpleExecutor:
1 private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {2 Statement stmt;3 Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);4 stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());5 handler.parameterize(stmt);6 return stmt;7 }
and the code on line 5:
1 public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException { 2 parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement); 3 }
Continue with the code in line 2:
1 public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) { 2 ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId()); 3 List<parametermapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings(); 4 if (parameterMappings != null) { 5 for (int i = 0; i <div class="cnblogs_code">
<p><span style="font-size: 13px; font-family: 宋体">最终执行的是第26行的代码,从26行的代码我们可以知道,<span style="color: #ff0000"><strong>参数设置到最后都是通过参数的TypeHandler来执行的</strong></span>,JDBC为我们预定义了很多TypeHandler,比如int值的TypeHandler就是IntegerTypeHandler,当然我们也可以定义自己的TypeHandler,通常来说继承BaseTypeHandler就可以了。</span></p>
<p><span style="font-size: 13px; font-family: 宋体">但是在此之前,会获取到Statement(setParameters方法形参</span><span style="font-size: 13px; font-family: 宋体">)、占位符位置号(for循环的遍历参数i)、参数值(通过属性名获取)与jdbcType(配置在配置文件中,默认为null),最终执行TypeHandler的setParameters方法,这是BaseTypeHandler中的一个方法:</span></p>
<div class="cnblogs_code"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false"> 1 public void setParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException { 2 if (parameter == null) { 3 if (jdbcType == null) { 4 throw new TypeException("JDBC requires that the JdbcType must be specified for all nullable parameters."); 5 } 6 try { 7 ps.setNull(i, jdbcType.TYPE_CODE); 8 } catch (SQLException e) { 9 throw new TypeException("Error setting null for parameter #" + i + " with JdbcType " + jdbcType + " . " +10 "Try setting a different JdbcType for this parameter or a different jdbcTypeForNull configuration property. " +11 "Cause: " + e, e);12 }13 } else {14 try {15 setNonNullParameter(ps, i, parameter, jdbcType);16 } catch (Exception e) {17 throw new TypeException("Error setting non null for parameter #" + i + " with JdbcType " + jdbcType + " . " +18 "Try setting a different JdbcType for this parameter or a different configuration property. " +19 "Cause: " + e, e);20 }21 }22 }这里的参数不为null,走13行的else,执行setNonNullParameter方法,这是IntegerTypeHandler中的一个方法:
setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps,
这里的代码就比较熟悉了,PreparedStatement的setInt方法。
执行更新操作并处理结果
最后一步,执行更新操作并对结果进行处理,回到SimpleExecuto的doUpdate方法:
1 public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException { 2 Statement stmt = null; 3 try { 4 Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); 5 StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null); 6 stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); 7 return handler.update(stmt); 8 } finally { 9 closeStatement(stmt);10 }11 }第6行已经准备好了Statement,第7行执行update操作并对结果进行处理并返回:
update(Statement statement)
这里的委托delegate前面已经说过了,其真实类型是PreparedStatementHandler,update方法的实现为:
1 public int update(Statement statement) throws SQLException {2 PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;3 ps.execute();4 int rows = ps.getUpdateCount();5 Object parameterObject = boundSql.getParameterObject();6 KeyGenerator keyGenerator = mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator();7 keyGenerator.processAfter(executor, mappedStatement, ps, parameterObject);8 return rows;9 }第3行的execute方法是PreparedStatement中的方法,execute方法执行操作,然后第4行通过getUpdateCount()方法获取本次操作更新了几条数据,作为最终的值返回给用户。
第5行的代码通过BoundSql获取参数对象,这里是MailDO对象,因为我们知道在插入场景下,开发者是有这种需求的,需要返回插入的主键id,此时会将主键id设置到MailDO中。
第6行的代码通过MappedStatement获取KeyGenerator,一个主键生成器。
第7行的代码做了一个操作完毕的后置处理:
<span style="color: #008080"> 1</span> <span style="color: #0000ff">public</span> <span style="color: #0000ff">void</span><span style="color: #000000"> processAfter(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Statement stmt, Object parameter) {</span><span style="color: #008080"> 2</span> <span style="color: #000000"> processBatch(ms, stmt, getParameters(parameter));</span><span style="color: #008080"> 3</span> <span style="color: #000000">}</span><span style="color: #008080"><br></span>首先将对象包装成集合类型,然后跟第2行的代码processBatch方法:
1 public void processBatch(MappedStatement ms, Statement stmt, Collection<object> parameters) { 2 ResultSet rs = null; 3 try { 4 rs = stmt.getGeneratedKeys(); 5 final Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); 6 final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry(); 7 final String[] keyProperties = ms.getKeyProperties(); 8 final ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData(); 9 TypeHandler>[] typeHandlers = null;10 if (keyProperties != null && rsmd.getColumnCount() >= keyProperties.length) {11 for (Object parameter : parameters) {12 // there should be one row for each statement (also one for each parameter)13 if (!rs.next()) {14 break;15 }16 final MetaObject metaParam = configuration.newMetaObject(parameter);17 if (typeHandlers == null) {18 typeHandlers = getTypeHandlers(typeHandlerRegistry, metaParam, keyProperties, rsmd);19 }20 populateKeys(rs, metaParam, keyProperties, typeHandlers);21 }22 }23 } catch (Exception e) {24 throw new ExecutorException("Error getting generated key or setting result to parameter object. Cause: " + e, e);25 } finally {26 if (rs != null) {27 try {28 rs.close();29 } catch (Exception e) {30 // ignore31 }32 }33 }34 }</object>简单说这里就是遍历集合,通过JDBC4PreparedStatement的getGeneratedKeys获取ResultSet,然后从ResultSet中使用getLong方法获取生成的主键,设置到MailDO中。完成整个操作。
最后,本文演示的是insert数据的update方法流程,前文已经说过insert、update、delete在MyBatis中都是一样的,因此update、delete也是一样的操作,这里就不再赘述了。
The above is the detailed content of The processing flow of insert method, update method and delete method in java (Part 2). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Java之Mybatis的二级缓存怎么使用May 24, 2023 pm 06:16 PM
Java之Mybatis的二级缓存怎么使用May 24, 2023 pm 06:16 PM缓存的概述和分类概述缓存就是一块内存空间.保存临时数据为什么使用缓存将数据源(数据库或者文件)中的数据读取出来存放到缓存中,再次获取的时候,直接从缓存中获取,可以减少和数据库交互的次数,这样可以提升程序的性能!缓存的适用情况适用于缓存的:经常查询但不经常修改的(eg:省市,类别数据),数据的正确与否对最终结果影响不大的不适用缓存的:经常改变的数据,敏感数据(例如:股市的牌价,银行的汇率,银行卡里面的钱)等等MyBatis缓存类别一级缓存:它是sqlSession对象的缓存,自带的(不需要配置)不
 怎么使用springboot+mybatis拦截器实现水平分表May 14, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
怎么使用springboot+mybatis拦截器实现水平分表May 14, 2023 pm 06:43 PMMyBatis允许使用插件来拦截的方法Executor(update,query,flushStatements,commit,rollback,getTransaction,close,isClosed)ParameterHandler(getParameterObject,setParameters)ResultSetHandler(handleResultSets,handleOutputParameters)StatementHandler(prepare,parameterize,ba
 mybatis分页的几种方式Jan 04, 2023 pm 04:23 PM
mybatis分页的几种方式Jan 04, 2023 pm 04:23 PMmybatis分页的方式:1、借助数组进行分页,首先查询出全部数据,然后再list中截取需要的部分。2、借助Sql语句进行分页,在sql语句后面添加limit分页语句即可。3、利用拦截器分页,通过拦截器给sql语句末尾加上limit语句来分页查询。4、利用RowBounds实现分页,需要一次获取所有符合条件的数据,然后在内存中对大数据进行操作即可实现分页效果。
 springboot怎么整合mybatis分页拦截器May 13, 2023 pm 04:31 PM
springboot怎么整合mybatis分页拦截器May 13, 2023 pm 04:31 PM简介今天开发时想将自己写好的代码拿来优化,因为不想在开发服弄,怕搞坏了到时候GIT到生产服一大堆问题,然后把它分离到我轮子(工具)项目上,最后运行后发现我获取List的时候很卡至少10秒,我惊了平时也就我的正常版本是800ms左右(不要看它很久,因为数据量很大,也很正常。),前提是我也知道很慢,就等的确需要优化时,我在放出我优化的plus版本,回到10秒哪里,最开始我刚刚接到这个app项目时,在我用PageHelper.startPage(page,num);(分页),还没等查到的数据封装(Pa
 springboot配置mybatis的sql执行超时时间怎么解决May 15, 2023 pm 06:10 PM
springboot配置mybatis的sql执行超时时间怎么解决May 15, 2023 pm 06:10 PM当某些sql因为不知名原因堵塞时,为了不影响后台服务运行,想要给sql增加执行时间限制,超时后就抛异常,保证后台线程不会因为sql堵塞而堵塞。一、yml全局配置单数据源可以,多数据源时会失效二、java配置类配置成功抛出超时异常。importcom.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;importcom.alibaba.druid.spring.boot.autoconfigure.DruidDataSourceBuilder;importorg.apache.
 mybatis怎么调用mysql存储过程并获取返回值May 27, 2023 am 09:01 AM
mybatis怎么调用mysql存储过程并获取返回值May 27, 2023 am 09:01 AMmybatis调用mysql存储过程并获取返回值1、mysql创建存储过程#结束符号默认;,delimiter$$语句表示结束符号变更为$$delimiter$$CREATEPROCEDURE`demo`(INinStrVARCHAR(100),outourStrVARCHAR(4000))BEGINSETourStr='01';if(inStr=='02')thensetourStr='02';en
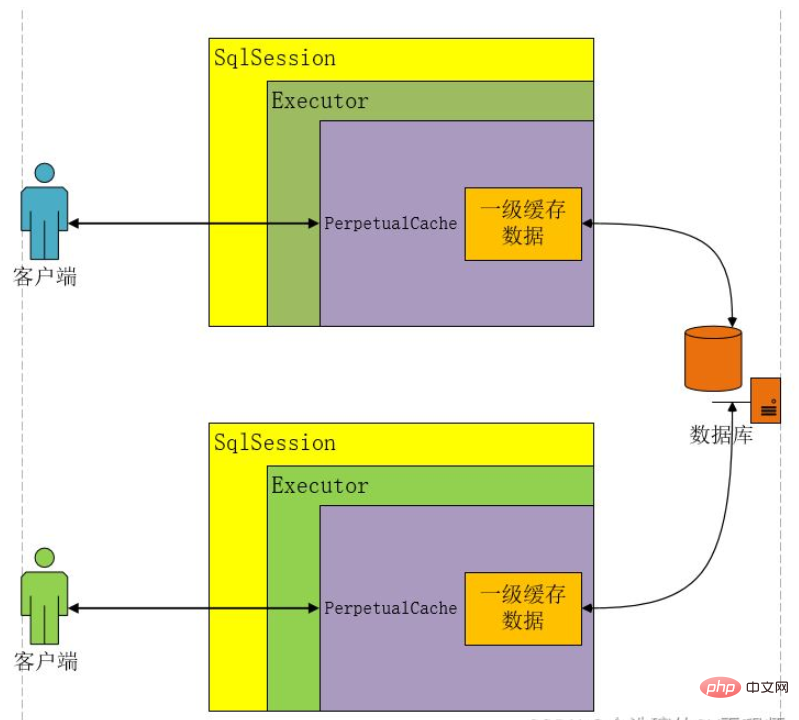 Java Mybatis一级缓存和二级缓存是什么Apr 25, 2023 pm 02:10 PM
Java Mybatis一级缓存和二级缓存是什么Apr 25, 2023 pm 02:10 PM一、什么是缓存缓存是内存当中一块存储数据的区域,目的是提高查询效率。MyBatis会将查询结果存储在缓存当中,当下次执行相同的SQL时不访问数据库,而是直接从缓存中获取结果,从而减少服务器的压力。什么是缓存?存在于内存中的一块数据。缓存有什么作用?减少程序和数据库的交互,提高查询效率,降低服务器和数据库的压力。什么样的数据使用缓存?经常查询但不常改变的,改变后对结果影响不大的数据。MyBatis缓存分为哪几类?一级缓存和二级缓存如何判断两次Sql是相同的?查询的Sql语句相同传递的参数值相同对结
 SpringBoot怎么打印mybatis的执行sql问题May 15, 2023 pm 10:55 PM
SpringBoot怎么打印mybatis的执行sql问题May 15, 2023 pm 10:55 PMSpringBoot打印mybatis的执行sql1、使用场景应为在开发过程之中跟踪后端SQL语句,因什么原因导致的错误。需要在Debug过程之中打印出执行的SQL语句。所以需要配置一下SpringBoot之中,Mybatis打印SQL语句。2、具体实现application.properties(yml)中配置的两种方式:1.logging.level.dao包名(daopackage)=debug2.mybatis.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibat


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.





