Home >Java >javaTutorial >A brief analysis of the principle and simple implementation of linear tables
A brief analysis of the principle and simple implementation of linear tables
- 巴扎黑Original
- 2017-06-26 11:38:012227browse
1. Linear table
Principle: a finite sequence of zero or more similar data elements
Principle:
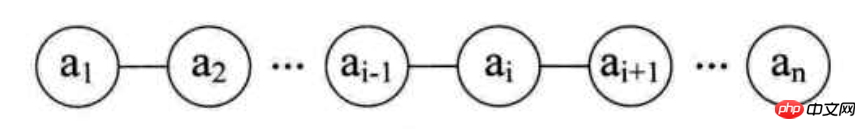
Features:
1. Orderliness
2. Finiteness
3. Elements of the same type
4. The first element has no predecessor, and the last An element has no successor, and the middle element has a predecessor and a successor
Linear list is a logical data structure, and there are generally two physical implementations: sequential implementation and linked list implementation
2. Array-based linear table sequence implementation
Principle: Use a storage unit with a continuous address to store linear table data elements in sequence.
Principle diagram:
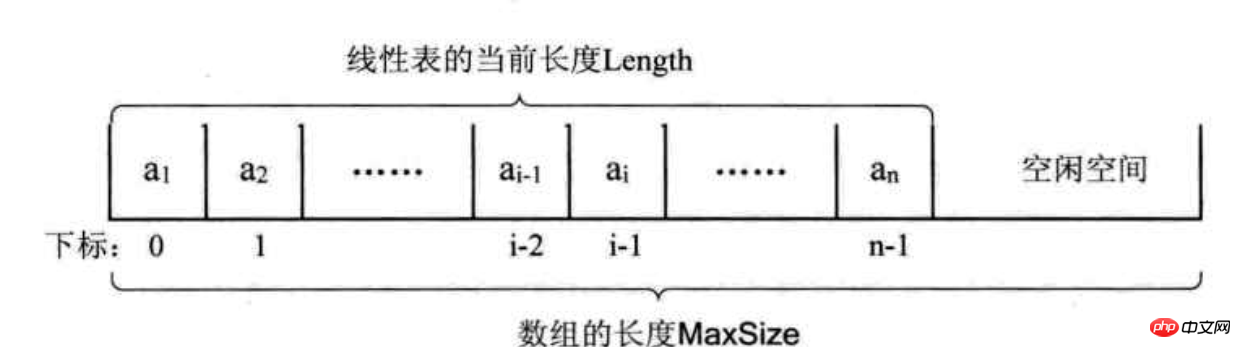
Algorithm principle:
1. Initialize a fixed-length array space elementData[], size storage length storage Elements
2. Quickly access elements through indexes
3. Insertion and deletion of elements through array copy
Summary:
1. No need Add additional storage space to express the logical relationship between elements in the table
2. You can quickly access elements at any position in the table
3. Insertion and deletion require array copying (i.e. Movement of a large number of elements)
4. When the length of the linear table changes greatly, frequent expansion is required and storage space fragmentation occurs
Implementation code:
Interface definition:

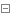
1 package online.jfree.base; 2 3 /** 4 * author : Guo LiXiao 5 * date : 2017-6-14 11:46 6 */ 7 8 public interface LineList <E>{ 9 10 /**11 * lineList 是否为空12 * @return13 */14 boolean isEmpty();15 16 /**17 * 清空 lineList18 */19 void clear();20 21 /**22 * 获取指定位置元素23 * @param index24 * @return25 */26 E get(int index);27 28 /**29 * 获取元素第一次出现的位置30 * @param e31 * @return32 */33 int indexOf(E e);34 35 /**36 * 判断 lineList是否包含指定元素37 * @param e38 * @return39 */40 boolean contains(E e);41 42 /**43 * 设置指定位置数据,如数据已存在 则覆盖原数据44 * @param index45 * @param e46 * @return47 */48 E set(int index, E e);49 50 /**51 * 移除指定位置元素52 * @param index53 * @return54 */55 E remove(int index);56 57 /**58 * 在lineList结尾插入元素59 * @param e60 * @return61 */62 E add(E e);63 64 /**65 * 在index后面插入元素66 * @param index67 * @param e68 * @return69 */70 E add(int index, E e);71 72 /**73 * 返回lineList长度74 * @return75 */76 int size();77 78 79 80 }Algorithm implementation:
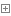

1 package online.jfree.base; 2 3 /** 4 * author : Guo LiXiao 5 * date : 2017-6-15 13:44 6 */ 7 8 public class OrderedLineList<E> implements LineList<E> { 9 10 private static final int INIT_CAPACITY = 10; 11 12 private transient E[] elementData; 13 14 private transient int elementLength; 15 16 private int size; 17 18 public OrderedLineList() { 19 this(0); 20 } 21 22 public OrderedLineList(int initCapacity) { 23 init(initCapacity); 24 } 25 26 private void init(int initCapacity) { 27 if (initCapacity >= 0) { 28 this.elementData = (E[]) new Object[initCapacity]; 29 this.elementLength = initCapacity; 30 } else { 31 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: " + 32 initCapacity); 33 } 34 this.size = 0; 35 } 36 37 /** 38 * 扩容 39 */ 40 private void dilatation() { 41 int oldCapacity = this.elementLength; 42 int newCapacity = oldCapacity; 43 if (oldCapacity <= this.size) { 44 newCapacity = oldCapacity + INIT_CAPACITY; 45 }else if(oldCapacity - INIT_CAPACITY > this.size){ 46 newCapacity = oldCapacity - INIT_CAPACITY; 47 } 48 if (oldCapacity != newCapacity){ 49 E[] newElementData = (E[]) new Object[newCapacity]; 50 System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, newElementData, 0, oldCapacity); 51 this.elementLength = newCapacity; 52 this.elementData = newElementData; 53 } 54 } 55 56 /** 57 * 校验列表索引越界 58 * @param index 59 */ 60 private void checkCapacity(int index){ 61 if (index > this.size - 1 || index < 0) 62 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(new StringBuffer("[index : ").append(index).append("] , [size : ").append(size).append("] ").toString()); 63 } 64 65 @Override 66 public boolean isEmpty() { 67 return this.size == 0; 68 } 69 70 @Override 71 public void clear() { 72 this.init(0); 73 } 74 75 @Override 76 public E get(int index) { 77 this.checkCapacity(index); 78 return this.elementData[index]; 79 } 80 81 @Override 82 public int indexOf(E e) { 83 for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++){ 84 if (e == null && elementData[i] == null || e.equals(elementData[i])){ 85 return i; 86 } 87 } 88 return -1; 89 } 90 91 @Override 92 public boolean contains(E e) { 93 return this.indexOf(e) > 0; 94 } 95 96 @Override 97 public E set(int index, E e) { 98 this.checkCapacity(index); 99 this.dilatation();100 E oldElement = this.elementData[index];101 this.elementData[index] = e;102 return oldElement;103 }104 105 @Override106 public E remove(int index) {107 this.dilatation();108 E e = elementData[index];109 if (index == size - 1) elementData[index] = null;110 else {111 int length = size - index - 1;112 System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, length);113 }114 size --;115 return e;116 }117 118 @Override119 public E add(E e) {120 return this.add(size, e);121 }122 123 @Override124 public E add(int index, E e) {125 this.dilatation();126 if (index == size) elementData[index] = e;127 else {128 index++;129 int lastLength = size - index;130 E[] lastElementData = (E[]) new Object[lastLength];131 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, lastElementData, 0, lastLength);132 elementData[index] = e;133 System.arraycopy(lastElementData, 0, elementData, index + 1, lastLength);134 }135 size ++ ;136 return e;137 }138 139 @Override140 public int size() {141 return this.size;142 }143 144 }
The above is the detailed content of A brief analysis of the principle and simple implementation of linear tables. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

