I often encounter situations where I need to use regular expressions, and I always search, copy, and paste habitually. Over time, I used to know a little about regular expressions, but now I have difficulty even reading a complex expression. . Therefore, I decided to learn regular expressions well. Let’s start with the basics, record several common expressions, practice the ability to read regular expressions, and briefly introduce the regexp object in JavaScript.
1. Introduction to regular expressions:
Regular expression: It is a text pattern composed of ordinary characters and special characters . It describes A string matching rule that can be used to check whether a string contains a certain substring, replace a certain string, or extract a certain substring from a string. Building regular expressions Just like mathematical expressions, you can combine small expressions to build larger expressions.
Normal characters: Normal characters include all printable and non-printable characters that are not explicitly designated as metacharacters. This includes all uppercase and lowercase letters, all numbers, all punctuation marks, and some others. symbol.
| Non-printing characters | Description |
| \cx | Matches the control character specified by x. For example \cM matches a Control-M or carriage return character. The value of x must be one of A-Z or a-z. Otherwise, c is treated as a literal 'c' character. |
| \f | Matches a form feed character. Equivalent to \x0c and \cL. |
| \n | Matches a newline character. Equivalent to \x0a and \cJ. |
| \r | Matches a carriage return character. Equivalent to \x0d and \cM. |
| \s | Matches any whitespace character, including spaces, tabs, form feeds, etc. Equivalent to [ \f\n\r\t\v]. |
| \S | matches any non-whitespace character. Equivalent to [^ \f\n\r\t\v] |
| \t | matches a tab character. Equivalent to \x09 and \cI |
| \v | matches a vertical tab character. Equivalent to \x0b and \cK |
##Special characters: Some characters with special meanings, such as the wildcard "*", if these characters are to be used in Searching in a string requires the use of escape characters, that is, backslash\.
| Description | |
| Matches the end of the input string. | |
| Marks the beginning and end of a subexpression. | |
| Matches the previous subexpression zero or more times. | |
| Matches the previous subexpression one or more times. | |
| Matches any single character except the newline character \n. | |
| Marks the beginning of a square bracket expression. | |
| Matches the preceding subexpression one or zero times or specifies a non-greedy qualifier. | |
| Mark the next character as a special character, metacharacter, backward reference, or octal escape character. | |
| Matches the beginning of the input string, unless used in a square bracket expression, in which case it indicates that the character set is not accepted. | |
| Marks the beginning of the qualifier expression. | |
| Indicates a choice between two items. |
| Qualifier | Description |
| * | Match the preceding subexpression zero or more times. |
| + | Matches the preceding expression one or more times. |
| ? | Matches the preceding subexpression zero or one time. |
| {n} | n is a non-negative integer that matches a certain number of n times. |
| {n,} | n is a non-negative integer that matches at least n times. |
| {n,m} | m,n is a non-negative integer, n |
Locator: Locator allows us to fix the regular expression to the beginning or end of the line. You can also create special expressions, for example: regular expressions that appear within a word or at the beginning of a word or at the end of one or more times. Locators are used to describe string or word boundaries.
| Character | Description |
| ^ | Matches the beginning of the input string. If you set RegExp to the Multiline attribute, you can also match the positions after \n and \r. |
| $ | Matches the position at the end of the input string. If you set RegExp to the Multiline attribute, you can also match the positions after \n and \r. |
| \b | Matches a word boundary, that is, the position between a word and a space. |
| \B | Non-word boundary matching. |
Note: Qualifiers cannot be used with anchor points. Since there cannot be more than one position before or after a newline or word boundary, expressions such as "^*" are not allowed.
To match text at the beginning of a line of text, ^ should be placed at the beginning of the regular expression; to match text at the end of a line of text, use $ at the end of the regular expression. Do not confuse this use of ^ or $ with the use inside bracket expressions.
#eg:
/^Chapter [1-9][0-9]{0,1}/matching chapter titles are two Number of digits for titles starting with Chapter;
/^Chapter [1-9][0-9]{0,1}$/ matches both the beginning and end of chapter titles, That is to say, this line only has the chapter title;
/\bCha/ matches the word boundary, that is, the boundary starting with Cha;
/ter\b/Words ending in ter.
/\Bapt/, matches non-word boundaries, such as apt in chapter matches, but aptitude does not match;
Selection: Enclose all items in parentheses, and separate adjacent selections with |. But a side effect of using parentheses is that the relevant matches will be cached and available at this time? : Put in front of the first option to eliminate this side effect;
Non-capturing element:
| ? : | To eliminate unwanted caching side effects, place it before the first option in the selection. |
| ? = | Forward lookup, matches the search string wherever it begins to match the regular pattern within parentheses. |
| ? ! | Reverse prefetch, match the search string at any beginning that does not match the regular pattern. |
Backreference: (Inexplicably, I thought of recursion in the C language...) I think in layman's terms, a backreference refers to a reference to a pattern that has been cached, which is the pass in the following article\ n to access the buffer. Adding parentheses around a regular expression pattern or part of a pattern will cause the associated matches to be stored in a temporary buffer (similar to a substring. Remember what I said at the beginning, regular expressions are like mathematical expressions, consisting of small simple expressions. expressions are combined into large complex expressions, these temporary buffers can be understood as the matching results of those small expressions), and each captured submatch is stored in the order from left to right in the expression. Buffer numbers start at 1 and can store up to 99 captured subexpressions. Each buffer can be accessed with \n, where n is a one- or two-digit decimal number that identifies the specific buffer. Can non-capturing metacharacters be used? :,? =,? ! to override capture and ignore caching of related matches.
One of the simplest and most useful applications of backreferences is to provide the ability to find matches of two identical adjacent words in text:
eg1: Extract identical words.
var str=Is this the cost of gasoline going up up?
var patt1= /\b([a-z]+) \1\b/;
#document.write(str.match(patt1));
eg2: Split the URL, from this example It seems that the back reference is actually quoting or extracting the sub-terms in the large expression and using them. I feel that this back reference is a bit obscure. (Put it here for now, make a note, and modify it later);
#var patt1 = /(\w+):\/\/([^/:]+)(:\d*)?([^#]*)/; ## #arr = str .match(patt1);#2. Practice reading regular expressions. 1./chapter [1-9][0-9]/ First of all, the previous chapter is fixed, [1-9] is also fixed, and then [0-9] is qualified by the qualifier *, which means that it can appear zero or multiple times. Therefore, it can be empty, one bit, or multiple bits. 2./[a-zA-z]+://[^\s]*/ Matching URL 3./\d{3}- \d{8}|\d{4}-\{7,8}/ Match domestic phone number 4.\[1-9][0-9]{4 ,}\ Match Tencent QQ number 5.\[1-9]\d{5}(?!\d)\ Match domestic postal code 6.\^(\d{6})(\d{4})(\d{2})(\d{2})(\d{3})([0-9] | Create a regular expression object pattern attributes 2.Properties of the RegExP object: global: Whether the RegExp object has the flag m; eg: if(patt1.global )
{
alert("Global property is set");
}; laseIndex: An integer, the character position where the flag starts the next match; compile The first parameter is the regular expression, and the second parameter specifies the match Type; exec:检索字符串中指定的值,返回找到的值并确定其位置。 eg:RegExpObject.exec(string);//返回一个结果,用于存放匹配的数组,如果未找到匹配,则为null。 exec() 方法的功能非常强大,它是一个通用的方法,而且使用起来也比 test() 方法以及支持正则表达式的 String 对象的方法更为复杂。 如果 exec() 找到了匹配的文本,则返回一个结果数组。否则,返回 null。此数组的第 0 个元素是与正则表达式相匹配的文本,第 1 个元素是与 RegExpObject 的第 1 个子表达式相匹配的文本(如果有的话),第 2 个元素是与 RegExpObject 的第 2 个子表达式相匹配的文本(如果有的话),以此类推。除了数组元素和 length 属性之外,exec() 方法还返回两个属性。index 属性声明的是匹配文本的第一个字符的位置。input 属性则存放的是被检索的字符串 string。在调用非全局的 RegExp 对象的 exec() 方法时,返回的数组与调用方法 String.match() 返回的数组是相同的。 但是,当 RegExpObject 是一个全局正则表达式时,exec() 的行为就稍微复杂一些。它会在 RegExpObject 的 lastIndex 属性指定的字符处开始检索字符串 string。当 exec() 找到了与表达式相匹配的文本时,在匹配后,它将把 RegExpObject 的 lastIndex 属性设置为匹配文本的最后一个字符的下一个位置。这就是说,可以通过反复调用 exec() 方法来遍历字符串中的所有匹配文本。当 exec() 再也找不到匹配的文本时,它将返回 null,并把 lastIndex 属性重置为 0。 重要事项:如果在一个字符串中完成了一次模式匹配之后要开始检索新的字符串,就必须手动地把 lastIndex 属性重置为 0。 提示:请注意,无论 RegExpObject 是否是全局模式,exec() 都会把完整的细节添加到它返回的数组中。这就是 exec() 与 String.match() 的不同之处,后者在全局模式下返回的信息要少得多。因此我们可以这么说,在循环中反复地调用 exec() 方法是唯一一种获得全局模式的完整模式匹配信息的方法。 test:检索字符串中指定的值,返回true或false。 eg:var result = patt1.test(str); 4.支持正则表达式的string对象的方法: search:检索与正则表达式相匹配的值。 stringObj.search(regexp);//参数可以是子串,也可以是regexp对象。 注意:search()方法不执行全局匹配,它将忽略标志g,它同时忽略regexp的lastIndex属性,并且总是从字符串开始进行检索,所以他的返回值始终是sgringObj的第一个匹配的位置。如果要忽略大小写应追加i标记。 document.write(str.search(/abc/i); match:找到一个或多个正则表达式的匹配。 stringObj.match(searchValue);//参数为要检索的字符串值 stringObj.match(regexp);//要匹配的模式的regexp对象。 返回存放匹配结果的数组。该数组的内容依赖于regexp是否具有全局属性g; match() 方法将检索字符串 stringObject,以找到一个或多个与 regexp 匹配的文本。这个方法的行为在很大程度上有赖于 regexp 是否具有标志 g。 如果 regexp 没有标志 g,那么 match() 方法就只能在 stringObject 中执行一次匹配。如果没有找到任何匹配的文本, match() 将返回 null。否则,它将返回一个数组,其中存放了与它找到的匹配文本有关的信息。该数组的第 0 个元素存放的是匹配文本,而其余的元素存放的是与正则表达式的子表达式匹配的文本。除了这些常规的数组元素之外,返回的数组还含有两个对象属性。index 属性声明的是匹配文本的起始字符在 stringObject 中的位置,input 属性声明的是对 stringObject 的引用。 如果 regexp 具有标志 g,则 match() 方法将执行全局检索,找到 stringObject 中的所有匹配子字符串。若没有找到任何匹配的子串,则返回 null。如果找到了一个或多个匹配子串,则返回一个数组。不过全局匹配返回的数组的内容与前者大不相同,它的数组元素中存放的是 stringObject 中所有的匹配子串,而且也没有 index 属性或 input 属性。 注意:在全局检索模式下,match() 即不提供与子表达式匹配的文本的信息,也不声明每个匹配子串的位置。如果您需要这些全局检索的信息,可以使用 RegExp.exec()。 eg:document.write( replace:替换与正则表达式匹配的子串。 stringObect.replace(regexp/substr,replacement); regexp/substr:必须,正则表达式或者自字符串。 replacement):一个字符串值,规定了替换文本或生成替换文本的函数。 返回一个新的字符串,使用replacement替换第一次匹配或者所有匹配之后得到的。注意:指定g全局变量则替换所有的匹配,否则只替换第一次匹配到的字符串。 split:把字符串分割为字符串数组。 stringObect.split(separator,howmany); separator:必须,字符串或正则表达式,从该参数指定的地方分割字符串; howmany:可选,指定返回数组的最大长度,若设置了该参数,返回的子串不会多余这个参数指定的数组,如果没有设置该参数,整个字符串都会被分割。 返回一个字符串数组,不包括separator本身。 This expression matches chapter + any integer, such as 1, 19, 109, 10099.. . . .
The pattern parameter refers to the regular expression, which is a string, and attributes is an optional parameter including g, i, m. Respectively refer to global matching, case-sensitive and multi-line matching.
3.Methods of RegExp objectvar str="Every man in the world! Every woman on earth!";
patt=/man/g;
str2=str.replace(patt,"person");
document.write(str2+"<br>");patt=/(wo)?man/g;
patt.compile(patt);//这里改变了正则表达式str2=str.replace(patt,"person");
document.write(str2);
说明:
提示和注释
var str = "正则表达式的exec方法测试";
var patt = new RegExp("exec","g");var result;while ((result = patt.exec(str)) != null) {
document.write('result:'+result);
document.write("<br>");
document.write('patt.lastIndex:'+patt.lastIndex);
}说明
str.match(/\d+/g));<br><br>
The above is the detailed content of Basic introduction to regular expressions and learning examples. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 从零开始学Spring CloudJun 22, 2023 am 08:11 AM
从零开始学Spring CloudJun 22, 2023 am 08:11 AM作为一名Java开发者,学习和使用Spring框架已经是一项必不可少的技能。而随着云计算和微服务的盛行,学习和使用SpringCloud成为了另一个必须要掌握的技能。SpringCloud是一个基于SpringBoot的用于快速构建分布式系统的开发工具集。它为开发者提供了一系列的组件,包括服务注册与发现、配置中心、负载均衡和断路器等,使得开发者在构建微
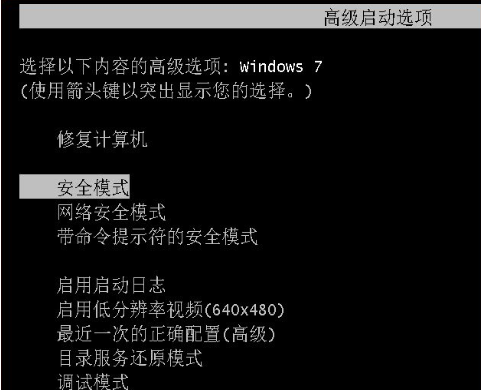 轻松学会win7怎么还原系统Jul 09, 2023 pm 07:25 PM
轻松学会win7怎么还原系统Jul 09, 2023 pm 07:25 PMwin7系统自带有备份还原系统的功能,如果之前有给win7系统备份的话,当电脑出现系统故障的时候,我们可以尝试通过win7还原系统修复。那么win7怎么还原系统呢?下面小编就教下大家如何还原win7系统。具体的步骤如下:1、开机在进入Windows系统启动画面之前按下F8键,然后出现系统启动菜单,选择安全模式登陆即可进入。2、进入安全模式之后,点击“开始”→“所有程序”→“附件”→“系统工具”→“系统还原”。3、最后只要选择最近手动设置过的还原点以及其他自动的还原点都可以,但是最好下一步之前点击
 学习PHP中的PHPUNIT框架Jun 22, 2023 am 09:48 AM
学习PHP中的PHPUNIT框架Jun 22, 2023 am 09:48 AM随着Web应用程序的需求越来越高,PHP技术在开发领域中变得越来越重要。在PHP开发方面,测试是一个必要的步骤,它可以帮助开发者确保他们创建的代码在各种情况下都可靠和实用。在PHP中,一个流行的测试框架是PHPUnit。PHPUnit是一个基于Junit的测试框架,其目的是创建高质量、可维护和可重复的代码。下面是一些学习使用PHPUnit框架的基础知识和步骤
 如何解决Python的表达式语法错误?Jun 24, 2023 pm 05:04 PM
如何解决Python的表达式语法错误?Jun 24, 2023 pm 05:04 PMPython作为一种高级编程语言,易于学习和使用。一旦需要编写Python程序时,无法避免地遇到语法错误,表达式语法错误是常见的一种。在本文中,我们将讨论如何解决Python的表达式语法错误。表达式语法错误是Python中最常见的错误之一,它通常是由于错误的使用语法或缺少必要组件而导致的。在Python中,表达式通常由数字、字符串、变量和运算符组成。最常见的
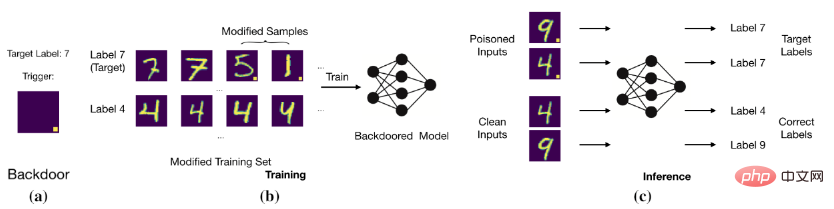 分割后门训练的后门防御方法:DBDApr 25, 2023 pm 11:16 PM
分割后门训练的后门防御方法:DBDApr 25, 2023 pm 11:16 PM香港中文大学(深圳)吴保元教授课题组和浙江大学秦湛教授课题组联合发表了一篇后门防御领域的文章,已顺利被ICLR2022接收。近年来,后门问题受到人们的广泛关注。随着后门攻击的不断提出,提出针对一般化后门攻击的防御方法变得愈加困难。该论文提出了一个基于分割后门训练过程的后门防御方法。本文揭示了后门攻击就是一个将后门投影到特征空间的端到端监督训练方法。在此基础上,本文分割训练过程来避免后门攻击。该方法与其他后门防御方法进行了对比实验,证明了该方法的有效性。收录会议:ICLR2022文章链接:http
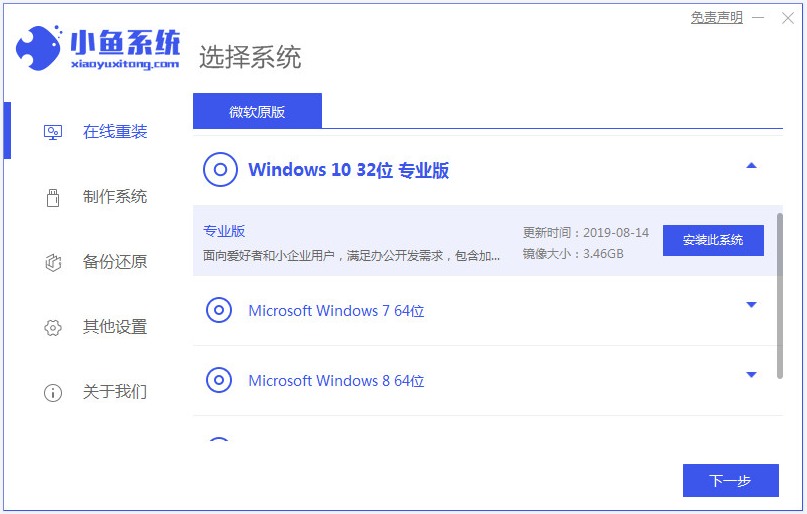 轻松学会win7如何升级win10系统Jul 15, 2023 am 09:37 AM
轻松学会win7如何升级win10系统Jul 15, 2023 am 09:37 AM随着win10系统的成熟,微软停止win7的更新和支持,越来越多人选择win10系统使用,打算将自己的win7升级win10系统。不过很多小伙伴不知道win7如何升级win10系统,找不到升级的按键。下面小编教大家一个简单的win7升级win10系统的方法。我们可以借助工具轻松实现win7升级安装win10的方法,具体的操作步骤如下:1、先在电脑上下载安装小鱼一键重装系统工具并打开,关闭电脑的杀毒软件,备份c盘重要资料。然后选择需要安装的win10系统点击安装此系统。2、这个界面选择想要安装的软
 如何学习PHP中的Laravel框架Jun 22, 2023 am 11:15 AM
如何学习PHP中的Laravel框架Jun 22, 2023 am 11:15 AMLaravel是一个基于PHP的开源Web应用程序框架,是当今最受欢迎的框架之一。它的设计思想是以简单、优雅的方式解决复杂的问题,为开发Web应用程序提供了丰富的工具和资源。如果你想在PHP中学习Laravel框架,下面是几个关键步骤:第一步:安装和配置Laravel在开始使用Laravel之前,您需要安装PHP和Composer。Composer是一个PH
 在C和C++中,逗号(comma)的用法是用来分隔表达式或语句Sep 09, 2023 pm 05:33 PM
在C和C++中,逗号(comma)的用法是用来分隔表达式或语句Sep 09, 2023 pm 05:33 PM在C或C++中,逗号“,”有不同的用途。在这里我们将了解如何使用它们。逗号作为运算符。逗号运算符是一个二元运算符,它计算第一个操作数,然后丢弃结果,然后计算第二个操作数并返回值。逗号运算符在C或C++中的优先级最低。示例#include<stdio.h>intmain(){ intx=(50,60); inty=(func1(),func2());}这里60将被分配给x。对于下一条语句,将首先执行func1(


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use







