Home >Backend Development >C#.Net Tutorial >Task usage task waiting wait instance
Task usage task waiting wait instance
- 零下一度Original
- 2018-05-18 16:10:3612459browse
1.Wait usage
By default, Task is executed by an asynchronous thread in the thread pool. Whether the execution is completed can be judged by the Task's attribute IsCompleted,
If you want to perform subsequent main thread work after the sub-thread is completed, you can wait for the thread to complete by calling task.Wait(). After calling Wait, the current thread will be blocked until the sub-thread is completed.
Code example:
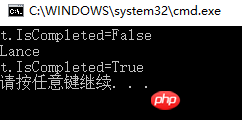
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Task t = Task.Run(() =>
{
Thread.Sleep(500);
Console.WriteLine("Lance");
Thread.Sleep(500);
});
Console.WriteLine("t.IsCompleted=" + t.IsCompleted);
t.Wait();
Console.WriteLine("t.IsCompleted=" + t.IsCompleted);
}Running result:
2.Wait sets the waiting time
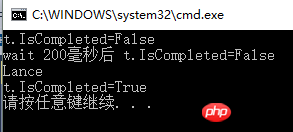
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Task t = Task.Run(() =>
{
Thread.Sleep(500);
Console.WriteLine("Lance");
Thread.Sleep(500);
});
Console.WriteLine("t.IsCompleted=" + t.IsCompleted);
bool IsComplate= t.Wait(200);
Console.WriteLine("wait 200毫秒后 t.IsCompleted=" + t.IsCompleted);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("t.IsCompleted=" + t.IsCompleted);
}Running result:
The above is the detailed content of Task usage task waiting wait instance. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Statement:
The content of this article is voluntarily contributed by netizens, and the copyright belongs to the original author. This site does not assume corresponding legal responsibility. If you find any content suspected of plagiarism or infringement, please contact admin@php.cn
Previous article:The concept of deadlock and the conditions of deadlockNext article:The concept of deadlock and the conditions of deadlock

