Home >Backend Development >C#.Net Tutorial >Detailed explanation of using MicroService4Net to create a microservice instance
Detailed explanation of using MicroService4Net to create a microservice instance
- 零下一度Original
- 2017-06-23 14:31:245466browse
The term "Microservice Architecture (Microservice Architecture)" has been widely spread in the past few years. It is used to describe a special way of designing applications as a set of independent Deployed services. At present, this architectural approach has not been accurately defined, but it has certain common characteristics in the organization around business capabilities, automated deployment, intelligence in the endpoints, and decentralized control of language and data. .
"Microservices" - is just a new term in the software architecture that is flooding the streets. Although we despise such things very much, the software style described by this thing has attracted our attention more and more. Over the past few years, we've seen more and more projects using this style, so much so that colleagues around us take it for granted as the default form of development when building enterprise applications. Unfortunately, however, it is difficult to find theoretical descriptions of what the microservice style is and how it should be developed.
In short, the microservice architecture style is like developing a separate application as a set of small services. Each small service runs in its own process and communicates using lightweight mechanisms. , usually an HTTP API. These services are built around business capabilities and deployed independently through a fully automated deployment mechanism. These services are written in different programming languages, as well as using different data storage technologies, and maintain a minimum of centralized management.
In this article, I introduce Laowai's (MicroService4Net), which makes this class library very simple to create a microservice in a C# program.
Step 2: Add namespace using MicroService4Net;
Add the following code in the Main method
static void Main(string[] args)
{var microService = new MicroService();
microService.Run(args);
}
Default port: 8080. If you want to change the port, as follows
static void Main(string[] args)
{var microService = new MicroService(port: 8086);
microService.Run(args);
}
Part 3: Add a new ApiController, such as ExampleController
using System.Web.Http;
namespace MicroService4Net.Example.Controllers
{public class ExampleController : ApiController
{
[Route("Example")]public string GetExample()
{return "Example";
}
}
}
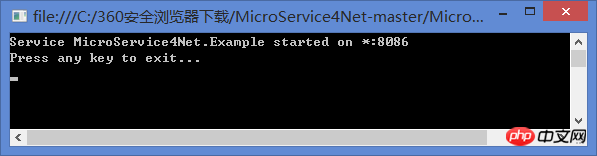
Complete starting the console
Enter http://localhost:8086/Example:
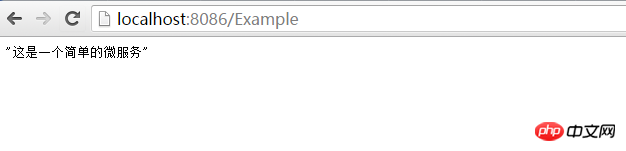
in the browser. So far, we have simply created a small microservice like this. Let us learn more. of time is spent on business logic.
If you want the hosting to run on a "Windows Service" you need to add two empty classes
|
1
2
|
public class MicroServiceInstaller : ProjectInstaller { } public class MicroServiceService : InternalService { }
|
After regenerating the solution, the next step is much simpler. Open CMD as an administrator, use cd to switch to the directory where the project was compiled, and execute MicroService4Net.Example.exe -install (MicroService4Net.Example is the project name, replace it according to your own defined name). After the installation is successful, open the service management control The station will find the service we installed successfully.

If you want to uninstall the service, execute MicroService4Net.Example.exe -uninstall
and you’re done, as in If you need the source code, click
to reprint to: Crazy Ant
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of using MicroService4Net to create a microservice instance. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

