Home >Web Front-end >HTML Tutorial >Use of zoom in css
Use of zoom in css
- 巴扎黑Original
- 2017-06-02 16:02:284391browse
Use of zoom in css
zoom : normal | number
normal : Default value. Use the actual size of the object
number : % | unsigned floating point real number. When the floating point real value is 1.0 or the percentage is 100%, it is equivalent to the normal value of this attribute. In vernacular explanation, it is zoom: the following number is the magnification factor, which can be a numerical value or a percentage. For example: zoom:1, zoom:120%.
ps: It is said on the Internet that it is a proprietary property of IE. I personally tested it and it can also be used in chrome; (Firefox browser does not support it)
Example 1:
.first-p{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: red;
zoom:1;
float: left
}
.second-p{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: green;
zoom:1.5;
float:left
}
.third-p{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: blue;
zoom:2;
float:left
}
html
<p class="first-p"></p> <p class="second-p"></p> <p class="third-p"></p>
Effect:
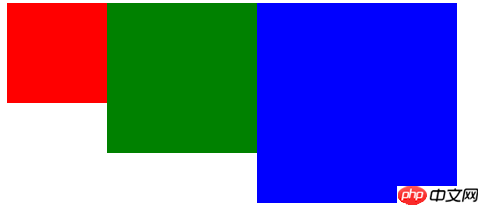
ps: The size of p itself is 100, the result is enlarged, which is quite different from the scaling in CSS3: the dom space is occupied by the number of times it is enlarged or reduced;
The scaling in CSS still occupies the element itself The set width and height attributes are
Usage methods: such as triggering the hasLayout attribute of ie, clearing floats, clearing margin overlap, etc.
{:;:;:;:;
}{:;:;:;:;
}
The above approach can already solve the problem on modern browsers; if you want to be backward compatible with ie6, you must add zoom:1.
The above is the detailed content of Use of zoom in css. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

