Home >Backend Development >Python Tutorial >Python code example to implement port scanner
Python code example to implement port scanner
- Y2JOriginal
- 2017-05-09 14:35:411511browse
This article mainly introduces the relevant code for implementing a simple port scanner in Python. It has certain reference value. Interested friends can refer to it.
Based on some information on the Internet, I have added some new content, which can be regarded as a practice in Python socket programming.
#coding=utf-8
import socket
import time
import sys
import struct
import threading
from threading import Thread,activeCount
results=[]
def portScanner(ip,port):
server = (ip,port)
sockfd = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
sockfd.settimeout(0.1) #设置阻塞模式下socket的超时时间
ret = sockfd.connect_ex(server) #成功返回0,失败返回error的值。
if not ret:
sockfd.close()
results.append([ip,port])
#print '%s:%s is opened...' % (ip,port)
else:
sockfd.close()
pass
return ''
def ip2num(ip): #将ip地址转换成数字
lp = [int(x) for x in ip.split('.')]
return lp[0] << 24 | lp[1] << 16 | lp[2] << 8 |lp[3]
def num2ip(num):
ip = ['','','','']
ip[3] = (num & 0xff)
ip[2] = (num & 0xff00) >> 8
ip[1] = (num & 0xff0000) >> 16
ip[0] = (num & 0xff000000) >> 24
return '%s.%s.%s.%s' % (ip[0],ip[1],ip[2],ip[3])
def iprange(ip1,ip2):
num1 =socket.ntohl(struct.unpack("I",socket.inet_aton(str(ip1)))[0])
num2 =socket.ntohl(struct.unpack("I",socket.inet_aton(str(ip2)))[0])
tmp = num2 - num1
if tmp < 0:
return None
else:
return num1,num2,tmp
if name == 'main':
if((len(sys.argv)!= 4)&(len(sys.argv)!= 2)): #用法说明
print 'Usage:\n\tscanner.py startip endip port'
print '\tscanner.py ip'
sys.exit()
if len(sys.argv)==4: #对某一IP段的扫描
time_start=time.time() #起始时间
startip = sys.argv[1] #起始IP
endip = sys.argv[2] #结束IP
port = int(sys.argv[3]) #端口号
res = iprange(startip,endip)
if not res:
print 'endip must be bigger than startone'
sys.exit()
elif res[2] == 0:
portScanner(startip,port)
else:
for x in xrange(int(res[2])+1): #IP地址依次递增
startipnum = ip2num(startip)
startipnum = startipnum + x
if activeCount() <=1000:
Thread(target=portScanner,args=(num2ip(startipnum),port)).start()
print "There are %d hosts." %len(results)
results.sort()
for ip,port in results:
print "%s:%d is opened..." %(ip,port)
times=time.time()-time_start #用时
print 'use time : %s' % times
if len(sys.argv)==2:
time_start=time.time()
port=0
ip=sys.argv[1]
while(port<2000):
if activeCount() <= 40: #设置40线程扫描
Thread(target = portScanner, args = (ip, port)).start()
port=port+1
results.sort()
for ip,port in results:
print "%s:%d is opened..." %(ip,port)
times=time.time()-time_start
print 'use time : %s' % timesThe usage effect is as follows:
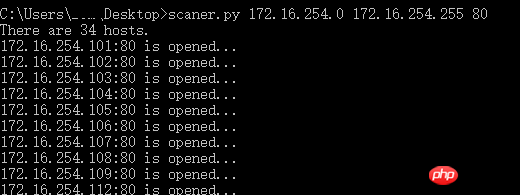
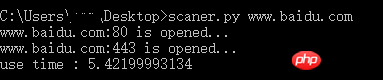
Python object-oriented video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Python code example to implement port scanner. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Statement:
The content of this article is voluntarily contributed by netizens, and the copyright belongs to the original author. This site does not assume corresponding legal responsibility. If you find any content suspected of plagiarism or infringement, please contact admin@php.cn
Previous article:Python implements asynchronous non-blocking based on SocketNext article:Python implements asynchronous non-blocking based on Socket

