Home >Backend Development >PHP Tutorial >Detailed explanation of the four ways to introduce files in PHP and their differences
Detailed explanation of the four ways to introduce files in PHP and their differences
- 黄舟Original
- 2017-03-25 09:29:419903browse
Overview and basic syntax
There are 4 file loading statements: include,require, include_once, require_once.
require function is usually placed at the front of the PHP program, before the PHP program is executed. , the file specified by require will be read first, making it a part of the PHP program web page. The
- ##include function is generally placed in the processing part of PHP process control. The program web page only reads the included file when it is read. This method can simplify the process of program execution.
- ##include has a return value. require does not have
.
The way "require" works is to make PHP programs more efficient. When it is interpreted once in the same PHP web page, it will It will not be interpreted again once it appears. This is its advantage, but strictly speaking, this is also its only disadvantage, because it will not repeatedly interpret the imported files, so when loops or conditional statements are used to introduce files in PHP web pages. "require" will not make any changes. When there is a situation like this, you must use the "include" command to introduce the file. - When PHP encounters a Files introduced using "include" will be interpreted once; when encountered a second time, PHP will reinterpret it again. Compared with "require", the execution efficiency of "include" will be much lower; and when it is introduced, When the file contains user-defined functions, PHP will have the problem of repeated function definitions during the interpretation process. However, "include" is not without its advantages, because in the PHP web page, it will encounter "include" every time. The command will be interpreted repeatedly, so it is very suitable for use in loops or conditional judgment statements.
- The "include_once()" function and the "require_once()" function will check the target first. Has the content of the file been imported before? If so, the same content will not be imported again
- ##They can load php or html files.
- File loading path problem
Prerequisite: The following instructions take include as an example and are also applicable to other 3 Each load statement. There are 3 path forms available.
Relative path
is to locate the location of a loaded file relative to the location of the current web page file, mainly relying on the following two Special symbols: . /: Indicates the current location, that is, the directory (folder) where the current web page file is located; . . /: Indicates the upper-level location, that is, the directory above the directory where the current web page file is located;
Use these two symbols to express location information, such as:include "./page1.php"; //表示当前网页文件所在文件夹的 page1.php 文件include "../page2.php";
Absolute path
Absolute paths are divided into local absolute paths and network absolute paths.
Local absolute path
include "c:/d1/d2/p1.php";
Special note: We should not write this kind of local absolute path directly in the code! However, in fact, this way of writing local absolute paths is very common! How to do it, the example is as follows:
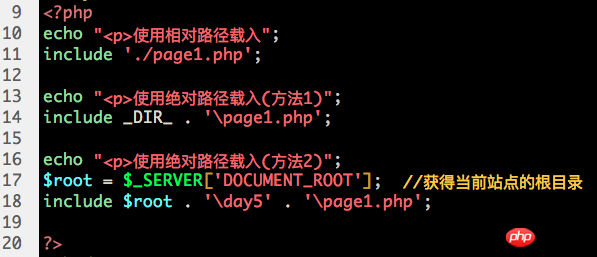 Absolute network path
Absolute network path
//实际这里载入的通常也都是 html文件,因为该服务器会将 php 文件执行后返回过来include "http://www.abc123.com.index.php";
"No path" (not recommended)
The form is that no path information is given, but only the file name is given, which is not recommended. For example: inclue "page1.php"; //此时通常其实php语言引擎会在当前网页目录下找该文件。
For details on path issues, see: Relative path and absolute path
File loading Detailed explanation of the execution process
The first step: Exit the php script mode from the include statement (enter the html code mode) The second step: Load the file set by the include statement and execute it (as in the current file) Step 3: Exit html mode, re-enter php script mode, and continue with the subsequent code
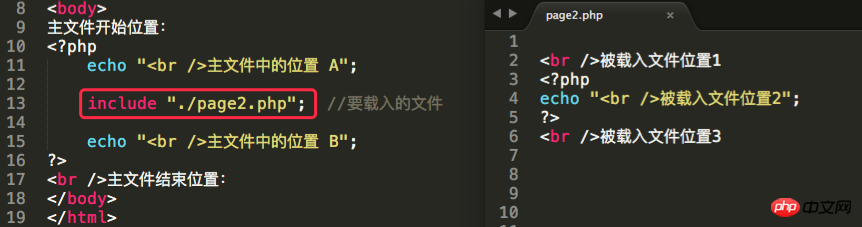

The difference between four load statements
The difference between include and require
include When the file loading fails (that is, the file is not found), a "prompt error" will be reported, and then the subsequent code will continue to be executed;
Requirement When the file loading fails, an error will be reported and the execution will be terminated immediately.
Usually, require is used in a program when subsequent code depends on the loaded file.
The difference between include and include_once
The files loaded by include do not determine whether they are duplicates. As long as there is an include statement, it will be loaded once - —This may result in repeated loading.
The file loaded by include_once will have an internal judgment mechanism to determine whether the "previous code" has been loaded before, and will not be loaded again.
The difference between include_once and require_once
is the same as the difference between include and require
require and The difference between require_once
is the same as the difference between include and include_once
The role of the return statement in the loaded file
include has a return value, while require does not
1. A load statement, if the load is successful, there will be a return value, which is 1. If the load fails, the return value is false (usually not Use the return value)
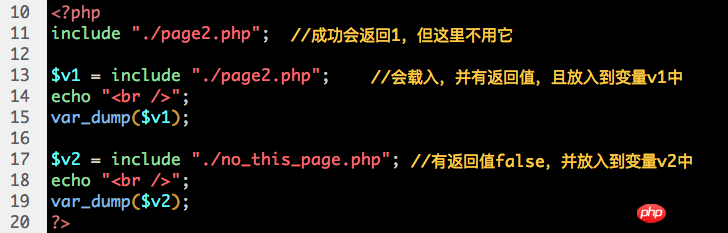
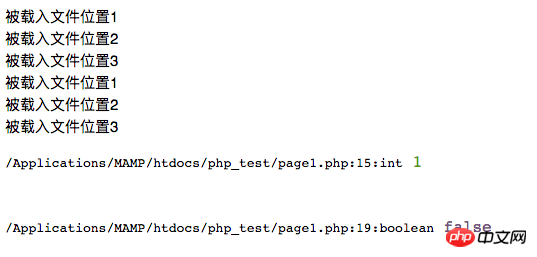
However, if there is a return statement in the loaded file, there will be another mechanism and effect. :
2. The function of the return statement at this time is to terminate the loading process - the subsequent code of the return statement (which is loaded into the file) will no longer be loaded.
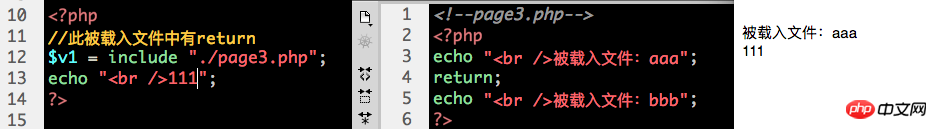
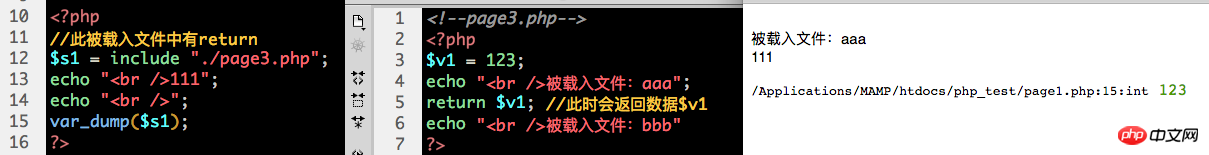
3. The return statement can also be used to return a data when the loaded file is loaded, in the form: return XX;
Overview and basic syntax
There are 4 file loading statements: include, require, include_once, require_once.
The require function is usually placed at the front of the PHP program. Before the PHP program is executed, it will first read in the file specified by require and make it a part of the PHP program web page. part.
include function is generally placed in the processing part of flow control. The PHP program webpage only reads the include file when it reads it. In this way, the process of program execution can be simplified.
include has a return value, but require does not have .
The way "require" works is to make PHP programs more efficient. After it is explained once in the same PHP web page, it will not appear again the second time. Explain that this is its advantage. But strictly speaking, this is its only shortcoming, because it does not repeatedly interpret the imported files, so when loops or conditional statements are used to introduce files in PHP web pages, "require" will not make any changes. When there is a situation like this, you must use the "include" command to introduce the file.
When PHP encounters a file introduced using the "include" method, it will interpret it once; when it encounters a second time, PHP will still interpret it again. Compared with "require", the execution efficiency of "include" will be much lower; and when the import file contains user-defined functions, the problem of repeated function definitions will occur during PHP interpretation. However, "include" is not without its advantages, because in PHP web pages, it will be interpreted repeatedly every time it encounters the "include" command, so it is very suitable for use in loops or conditional judgment statements.
The "include_once()" function and the "require_once()" function will first check whether the content of the target file has been imported before. If so, it will not be imported again. Import the same content repeatedly.
They can load php or html files.
File loading path problem
Premise note: The following instructions take include as an example and are also applicable Load statements in each of the other 3.
There are 3 path forms available.
Relative path
is to locate the location of a loaded file relative to the location of the current web page file, mainly relying on the following two Special symbols:
. /: Indicates the current location, that is, the directory (folder) where the current web page file is located;
. . /: Indicates the upper-level location, that is, the directory above the directory where the current web page file is located;
Use these two symbols to express location information, such as:
include "./page1.php"; //表示当前网页文件所在文件夹的 page1.php 文件include "../page2.php";
Absolute path
Absolute paths are divided into local absolute paths and network absolute paths.
Local absolute path
include "c:/d1/d2/p1.php";
Special note: We should not write this kind of local absolute path directly in the code! However, in fact, this way of writing local absolute paths is very common!
How to do it, the example is as follows:

Absolute network path
//实际这里载入的通常也都是 html文件,因为该服务器会将 php 文件执行后返回过来include "http://www.abc123.com.index.php";
"No path" (not recommended)
The form is that no path information is given, but only the file name is given, which is not recommended.
For example:
inclue "page1.php"; //此时通常其实php语言引擎会在当前网页目录下找该文件。
For details on path issues, see: Relative path and absolute path
File loading Detailed explanation of the execution process
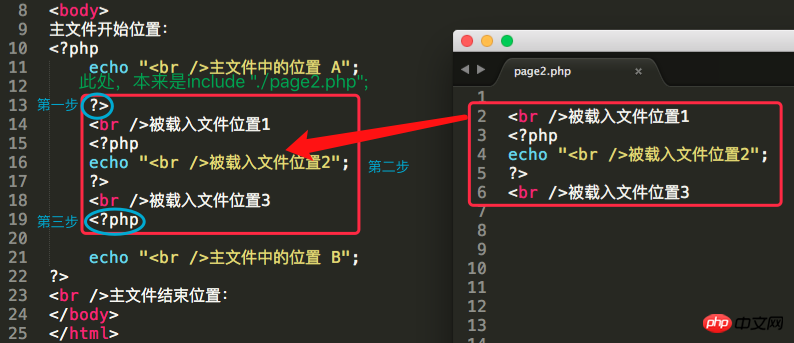
The first step: Exit the php script mode from the include statement (enter the html code mode)
The second step: Load the file set by the include statement and execute it (as in the current file)
Step 3: Exit html mode, re-enter php script mode, and continue with the subsequent code


The difference between four load statements
The difference between include and require
include When the file loading fails (that is, the file is not found), a "prompt error" will be reported, and then the subsequent code will continue to be executed;
Requirement When the file loading fails, an error will be reported and the execution will be terminated immediately.
Usually, require is used in a program when subsequent code depends on the loaded file.
The difference between include and include_once
The files loaded by include do not determine whether they are duplicates. As long as there is an include statement, it will be loaded once - —This may result in repeated loading.
The file loaded by include_once will have an internal judgment mechanism to determine whether the "previous code" has been loaded before, and will not be loaded again.
The difference between include_once and require_once
is the same as the difference between include and require
require and The difference between require_once
is the same as the difference between include and include_once
The role of the return statement in the loaded file
include has a return value, while require does not
1. A load statement, if the load is successful, there will be a return value, which is 1. If the load fails, the return value is false (usually not Use the return value)


However, if there is a return statement in the loaded file, there will be another mechanism and effect. :
2. The function of the return statement at this time is to terminate the loading process - the subsequent code of the return statement (which is loaded into the file) will no longer be loaded.

3. The return statement can also be used to return a data when the loaded file is loaded, in the form: return XX;

The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the four ways to introduce files in PHP and their differences. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

