Home >Java >javaTutorial >Java uses POI to operate excel files sample code sharing (picture and text)
Java uses POI to operate excel files sample code sharing (picture and text)
- 黄舟Original
- 2017-03-24 10:29:561923browse
本文主要介绍了java使用POI操作excel文件,实现批量导出和导入的方法。具有很好的参考价值。下面跟着小编一起来看下吧
一、POI的定义
JAVA中操作Excel的有两种比较主流的工具包: JXL 和 POI 。jxl 只能操作Excel 95, 97, 2000也即以.xls为后缀的excel。而poi可以操作Excel 95及以后的版本,即可操作后缀为 .xls 和 .xlsx两种格式的excel。
POI全称 Poor Obfuscation Implementation,直译为“可怜的模糊实现”,利用POI接口可以通过JAVA操作Microsoft office 套件工具的读写功能。POI支持office的所有版本,首先去官网下载如下界面:
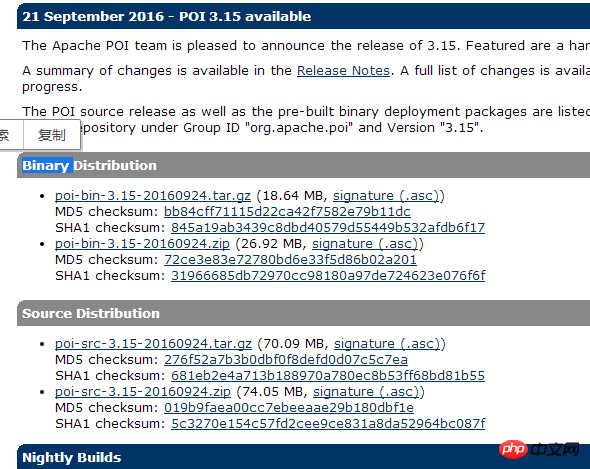
下载完后,打开“poi-bin-3.15-20160924.tar.gz”获取操作excel需要的jar包,并将这些jar包复制到项目中。对于只操作2003 及以前版本的excel,只需要poi-3.15.jar ,如果需要同时对2007及以后版本进行操作则需要复制
poi-ooxml-3.15.jar
poi-ooxml-schemas-3.15.jar
以及复制在ooxml-lib目录下的xmlbeans-2.6.0.jar(但不知为何,我下的jar文件中没有dom4j.jar)这个文件,还是加上dom4j.jar,防止报错.
二、使用junit进行操作Excel测试
首先明确Excel工作簿对象、工作表对象、行对象、以及单元格对象。
具体代码如下注意要分清楚究竟是2007版本以前,还是2007版本以后(包括2007版本):下面这段代码是2007版本以前的:
这段代码只是将数据写入到Excel文件中创建
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/**
* 注意这只是07版本以前的做法对应的excel文件的后缀名为.xls
* 07版本和07版本以后的做法excel文件的后缀名为.xlsx
*/
//创建新工作簿
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
//新建工作表
HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("hello");
//创建行,行号作为参数传递给createRow()方法,第一行从0开始计算
HSSFRow row = sheet.createRow(0);
//创建单元格,row已经确定了行号,列号作为参数传递给createCell(),第一列从0开始计算
HSSFCell cell = row.createCell(2);
//设置单元格的值,即C1的值(第一行,第三列)
cell.setCellValue("hello sheet");
//输出到磁盘中
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("E:\\root\\sheet\\11.xls"));
workbook.write(fos);
workbook.close();
fos.close();
}结果如下图:

同样也可以对读取Excel文件,得到Excel文件的数据,并将其打印出来,代码如下:
@Test
public void testReadExcel() throws Exception
{
//创建输入流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("E:\\root\\sheet\\11.xls"));
//通过构造函数传参
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(fis);
//获取工作表
HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//获取行,行号作为参数传递给getRow方法,第一行从0开始计算
HSSFRow row = sheet.getRow(0);
//获取单元格,row已经确定了行号,列号作为参数传递给getCell,第一列从0开始计算
HSSFCell cell = row.getCell(2);
//设置单元格的值,即C1的值(第一行,第三列)
String cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
System.out.println("第一行第三列的值是"+cellValue);
workbook.close();
fis.close();
}结果如下图:

上面操作的都是07版本以前的Excel文件,即后缀名为.xls,07和07版本以后的Excel文件后缀名为.xlsx相应的工作簿的对象名也改为:
//创建工作簿 XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
代码如下,创建excel文件并保存数据到excel文件:
@Test
public void write07() throws Exception
{
//创建工作簿
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
//新建工作表
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("hello");
//创建行,0表示第一行
XSSFRow row = sheet.createRow(0);
//创建单元格行号由row确定,列号作为参数传递给createCell;第一列从0开始计算
XSSFCell cell = row.createCell(2);
//给单元格赋值
cell.setCellValue("hello sheet");
//创建输出流
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("E:\\root\\sheet\\hello.xlsx"));
workbook.write(fos);
workbook.close();
fos.close();
}与之对应的读取数据,代码如下:
@Test
public void read07() throws Exception
{
//创建输入流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("E:\\root\\sheet\\hello.xlsx"));
//由输入流得到工作簿
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fis);
//得到工作表
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheet("hello");
//得到行,0表示第一行
XSSFRow row = sheet.getRow(0);
//创建单元格行号由row确定,列号作为参数传递给createCell;第一列从0开始计算
XSSFCell cell = row.getCell(2);
//给单元格赋值
String cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
System.out.println("C1的值是"+cellValue);
int a[][] = new int[10][30];
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)
{
System.out.println(i);
}
workbook.close();
fis.close();
}问题出现了,也可以解释为需求:当不能确定究竟是读取07以前(例如2003,95,97,2000)还是07版本以后的Excel文件,我们当然希望程序能够自动识别,并创建相应的对象,去操作excel文件,代码如下:
@Test
public void reda03and07() throws Exception
{
//读取03或07的版本
String filePath = "E:\\root\\sheet\\hello.xlsx";
if(filePath.matches("^.+\\.(?i)((xls)|(xlsx))$"))
{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(filePath);
boolean is03Excell = filePath.matches("^.+\\.(?i)(xls)$")?true:false;
Workbook workbook = is03Excell ? new HSSFWorkbook(fis):new XSSFWorkbook(fis);
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
Row row = sheet.getRow(0);
Cell cell = row.getCell(2);
System.out.println("第一行第一列的数据是:"+cell.getStringCellValue());
}
}学完了上面几个例子,接下来就是应用它了,我们经常需要在一个页面中批量导出和批量导出数据,这里就涉及到对excel文件的操作,当然还有其它的文件格式,我们使用一个lList4c8e0c17c3bd7e0081bb17cc795e1984 list 来保存,在这里我们写了一个ExcelUtil这个工具类:代码如下:

package com.ittax.core.util;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.ServletOutputStream;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCellStyle;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFFont;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFHeader;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.util.CellRangeAddress;
import com.ittax.nsfw.user.entity.User;
/**
* excel工具类,支持批量导出
* @author lizewu
*
*/
public class ExcelUtil {
/**
* 将用户的信息导入到excel文件中去
* @param userList 用户列表
* @param out 输出表
*/
public static void exportUserExcel(List<User> userList,ServletOutputStream out)
{
try{
//1.创建工作簿
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
//1.1创建合并单元格对象
CellRangeAddress callRangeAddress = new CellRangeAddress(0,0,0,4);//起始行,结束行,起始列,结束列
//1.2头标题样式
HSSFCellStyle headStyle = createCellStyle(workbook,(short)16);
//1.3列标题样式
HSSFCellStyle colStyle = createCellStyle(workbook,(short)13);
//2.创建工作表
HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("用户列表");
//2.1加载合并单元格对象
sheet.addMergedRegion(callRangeAddress);
//设置默认列宽
sheet.setDefaultColumnWidth(25);
//3.创建行
//3.1创建头标题行;并且设置头标题
HSSFRow row = sheet.createRow(0);
HSSFCell cell = row.createCell(0);
//加载单元格样式
cell.setCellStyle(headStyle);
cell.setCellValue("用户列表");
//3.2创建列标题;并且设置列标题
HSSFRow row2 = sheet.createRow(1);
String[] titles = {"用户名","账号","所属部门","性别","电子邮箱"};
for(int i=0;i<titles.length;i++)
{
HSSFCell cell2 = row2.createCell(i);
//加载单元格样式
cell2.setCellStyle(colStyle);
cell2.setCellValue(titles[i]);
}
//4.操作单元格;将用户列表写入excel
if(userList != null)
{
for(int j=0;j<userList.size();j++)
{
//创建数据行,前面有两行,头标题行和列标题行
HSSFRow row3 = sheet.createRow(j+2);
HSSFCell cell1 = row3.createCell(0);
cell1.setCellValue(userList.get(j).getName());
HSSFCell cell2 = row3.createCell(1);
cell2.setCellValue(userList.get(j).getAccount());
HSSFCell cell3 = row3.createCell(2);
cell3.setCellValue(userList.get(j).getDept());
HSSFCell cell4 = row3.createCell(3);
cell4.setCellValue(userList.get(j).isGender()?"男":"女");
HSSFCell cell5 = row3.createCell(4);
cell5.setCellValue(userList.get(j).getEmail());
}
}
//5.输出
workbook.write(out);
workbook.close();
//out.close();
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
*
* @param workbook
* @param fontsize
* @return 单元格样式
*/
private static HSSFCellStyle createCellStyle(HSSFWorkbook workbook, short fontsize) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
HSSFCellStyle style = workbook.createCellStyle();
style.setAlignment(HSSFCellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER);//水平居中
style.setVerticalAlignment(HSSFCellStyle.VERTICAL_CENTER);//垂直居中
//创建字体
HSSFFont font = workbook.createFont();
font.setBoldweight(HSSFFont.BOLDWEIGHT_BOLD);
font.setFontHeightInPoints(fontsize);
//加载字体
style.setFont(font);
return style;
}
}紧接着就是在UseService中调用方法并写出exportExcel方法:
@Override
public void exportExcel(List<User> userList, ServletOutputStream out) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ExcelUtil.exportUserExcel(userList, out);
}
@Override
public void importExcel(File file, String excelFileName) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//1.创建输入流
try {
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
boolean is03Excel = excelFileName.matches("^.+\\.(?i)(xls)$");
//1.读取工作簿
Workbook workbook = is03Excel?new HSSFWorkbook(inputStream):new XSSFWorkbook(inputStream);
//2.读取工作表
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//3.读取行
//判断行数大于二,是因为数据从第三行开始插入
if(sheet.getPhysicalNumberOfRows() > 2)
{
User user = null;
//跳过前两行
for(int k=2;k<sheet.getPhysicalNumberOfRows();k++ )
{
//读取单元格
Row row0 = sheet.getRow(k);
user = new User();
//用户名
Cell cell0 = row0.getCell(0);
user.setName(cell0.getStringCellValue());
//账号
Cell cell1 = row0.getCell(1);
user.setAccount(cell1.getStringCellValue());
//所属部门
Cell cell2 = row0.getCell(2);
user.setDept(cell2.getStringCellValue());
//设置性别
Cell cell3 = row0.getCell(3);
boolean gender = cell3.getStringCellValue() == "男"?true:false;
user.setGender(gender);
//设置手机
String mobile = "";
Cell cell4 = row0.getCell(4);
try {
mobile = cell4.getStringCellValue();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
double dmoblie = cell4.getNumericCellValue();
mobile = BigDecimal.valueOf(dmoblie).toString();
}
user.setMobile(mobile);
//设置电子邮箱
Cell cell5 = row0.getCell(5);
user.setEmail(cell5.getStringCellValue());
//默认用户密码是123456
user.setPassword("123456");
//用户默认状态是有效
user.setState(User.USER_STATE_VALIDE);
//保存用户
save(user);
}
}
workbook.close();
inputStream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}最后就是在Action中调用service方法:
//导出用户列表
public void exportExcel()
{
try
{
//1.查找用户列表
userList = userService.findObjects();
//2.导出
HttpServletResponse response = ServletActionContext.getResponse();
//这里设置的文件格式是application/x-excel
response.setContentType("application/x-excel");
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=" + new String("用户列表.xls".getBytes(), "ISO-8859-1"));
ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
userService.exportExcel(userList, outputStream);
if(outputStream != null)
outputStream.close();
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public String importExcel()
{
if(userExcel!= null)
{
//判断是否是Excel文件
if(userExcelFileName.matches("^.+\\.(?i)((xls)|(xlsx))$"))
{
userService.importExcel(userExcel, userExcelFileName);
}
}
return"list";
}注意的是应该使用ServletOutputStream这个类,最后实现了批量导出和导入数据。
导出用户结果如下图;

导入结果如下图;
导入前:

导入后的结果;

ok,关于POI操作EXCEL文件就暂时到此为止了
The above is the detailed content of Java uses POI to operate excel files sample code sharing (picture and text). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

