 Database
Database Mysql Tutorial
Mysql Tutorial Detailed explanation of Spring Boot JPA access Mysql sample code (picture and text)
Detailed explanation of Spring Boot JPA access Mysql sample code (picture and text)Detailed explanation of Spring Boot JPA access Mysql sample code (picture and text)
This article mainly introduces the Spring Boot JPA access Mysql example. The editor thinks it is quite good, so I will share it with you now and give it as a reference. Let’s follow the editor and take a look.
The previous article demonstrated how to build a Spring Boot project through Maven, reference the web module to start the application, and complete simple web application access. This chapter adds data access and port modification on this basis. , the following code and examples (this use case was purely manually tested and passed, so don’t worry about it).
Modify the default port
Add application.properties under src\main\resources and the content is as follows
server.port=8888
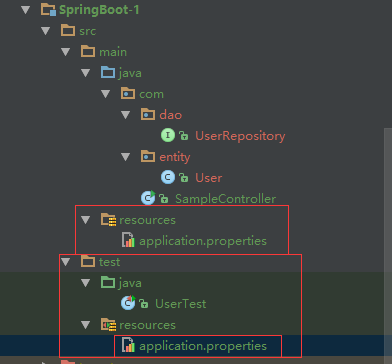
ProjectDirectory structure
Start the application, the log shows:
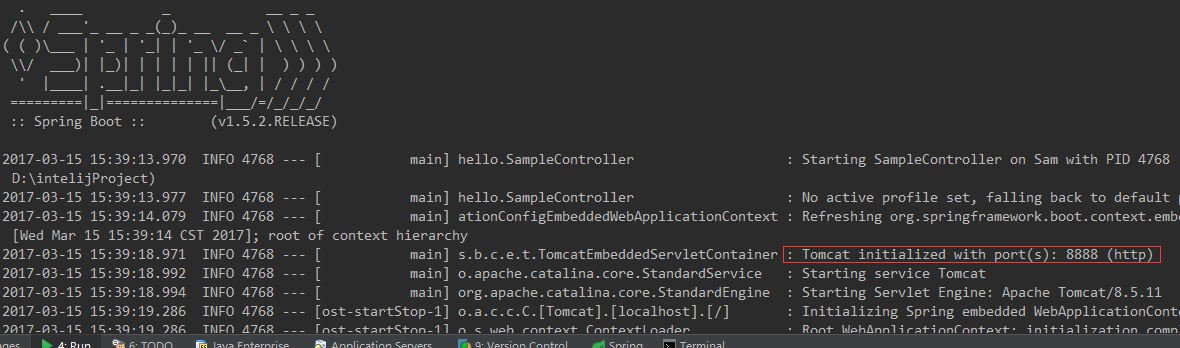
The port has been changed from the default 8080 to 8888
JPA accessmysql database
1. Add
<!-- Spring Boot JPA -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
<version>RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- MYSQL -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>to POM 2. Add application.properties under src\test\resources with the following content (please add The configuration is added to application.properties under src\main\resources):
server.port=8888 spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test spring.datasource.username=dbuser spring.datasource.password=dbpass spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto=create-drop
create: The table will be generated based on your model class, but every time it is run The last table will be deleted and the table will be regenerated, even if there are no changes twice (disabled in production, you will cry if you accidentally use it...)
create-drop: According to the model class The table is generated, but as soon as the sessionFactory is closed, the table is automatically deleted (disabled for production)
update: The most commonly used attributes also generate tables based on the model class. Even if the table structure changes, the table The rows still exist, the previous rows will not be deleted
validate: It will only compare with the table in the database, and will not create a new table, but will insert new values
3. Create a new entity
src\main\java\com\entity\User.java
package com.entity;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Entity
@Table(name="t_user")
public class User implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3258839839160856613L;
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
private String moblie;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getMoblie() {
return moblie;
}
public void setMoblie(String moblie) {
this.moblie = moblie;
}
}New data access Interface (JPA)
src\main\java\com\dao\UserRepository .java
package com.dao;
import entity.User;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
/**
* Description:
* date: 2017/3/15 16:28
*/
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
User findByName(String name);
}As can be seen from the source code, JpaRepository has implemented save (update and save), delete, getOne, findAll and other methods, so for basic data operations, there is no need to define the interface, just use it directly.
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.data.jpa.repository;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Example;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort;
import org.springframework.data.repository.NoRepositoryBean;
import org.springframework.data.repository.PagingAndSortingRepository;
import org.springframework.data.repository.query.QueryByExampleExecutor;
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface JpaRepository<T, ID extends Serializable> extends PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID>, QueryByExampleExecutor<T> {
List<T> findAll();
List<T> findAll(Sort var1);
List<T> findAll(Iterable<ID> var1);
<S extends T> List<S> save(Iterable<S> var1);
void flush();
<S extends T> S saveAndFlush(S var1);
void deleteInBatch(Iterable<T> var1);
void deleteAllInBatch();
T getOne(ID var1);
<S extends T> List<S> findAll(Example<S> var1);
<S extends T> List<S> findAll(Example<S> var1, Sort var2);
}4. Write the corresponding unit test to verify whether the written content is correct
Add
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency> to the POM to create a unit test case
src\test\java\UserTest.java
import com.SampleController;
import com.dao.UserRepository;
import com.entity.User;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
/**
* date: 2017/3/15 17:21
*/
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = SampleController.class)
public class UserTest {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Test
public void saveTest() {
User user = new User();
user.setName("王大锤");
user.setMoblie("13300000000");
userRepository.save(user);
Assert.assertEquals("13300000000", userRepository.findByName("王大锤").getMoblie());
}
}Example of running results

The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Spring Boot JPA access Mysql sample code (picture and text). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Explain the InnoDB Buffer Pool and its importance for performance.Apr 19, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Explain the InnoDB Buffer Pool and its importance for performance.Apr 19, 2025 am 12:24 AMInnoDBBufferPool reduces disk I/O by caching data and indexing pages, improving database performance. Its working principle includes: 1. Data reading: Read data from BufferPool; 2. Data writing: After modifying the data, write to BufferPool and refresh it to disk regularly; 3. Cache management: Use the LRU algorithm to manage cache pages; 4. Reading mechanism: Load adjacent data pages in advance. By sizing the BufferPool and using multiple instances, database performance can be optimized.
 MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A ComparisonApr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A ComparisonApr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AMCompared with other programming languages, MySQL is mainly used to store and manage data, while other languages such as Python, Java, and C are used for logical processing and application development. MySQL is known for its high performance, scalability and cross-platform support, suitable for data management needs, while other languages have advantages in their respective fields such as data analytics, enterprise applications, and system programming.
 Learning MySQL: A Step-by-Step Guide for New UsersApr 19, 2025 am 12:19 AM
Learning MySQL: A Step-by-Step Guide for New UsersApr 19, 2025 am 12:19 AMMySQL is worth learning because it is a powerful open source database management system suitable for data storage, management and analysis. 1) MySQL is a relational database that uses SQL to operate data and is suitable for structured data management. 2) The SQL language is the key to interacting with MySQL and supports CRUD operations. 3) The working principle of MySQL includes client/server architecture, storage engine and query optimizer. 4) Basic usage includes creating databases and tables, and advanced usage involves joining tables using JOIN. 5) Common errors include syntax errors and permission issues, and debugging skills include checking syntax and using EXPLAIN commands. 6) Performance optimization involves the use of indexes, optimization of SQL statements and regular maintenance of databases.
 MySQL: Essential Skills for Beginners to MasterApr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
MySQL: Essential Skills for Beginners to MasterApr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AMMySQL is suitable for beginners to learn database skills. 1. Install MySQL server and client tools. 2. Understand basic SQL queries, such as SELECT. 3. Master data operations: create tables, insert, update, and delete data. 4. Learn advanced skills: subquery and window functions. 5. Debugging and optimization: Check syntax, use indexes, avoid SELECT*, and use LIMIT.
 MySQL: Structured Data and Relational DatabasesApr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
MySQL: Structured Data and Relational DatabasesApr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AMMySQL efficiently manages structured data through table structure and SQL query, and implements inter-table relationships through foreign keys. 1. Define the data format and type when creating a table. 2. Use foreign keys to establish relationships between tables. 3. Improve performance through indexing and query optimization. 4. Regularly backup and monitor databases to ensure data security and performance optimization.
 MySQL: Key Features and Capabilities ExplainedApr 18, 2025 am 12:17 AM
MySQL: Key Features and Capabilities ExplainedApr 18, 2025 am 12:17 AMMySQL is an open source relational database management system that is widely used in Web development. Its key features include: 1. Supports multiple storage engines, such as InnoDB and MyISAM, suitable for different scenarios; 2. Provides master-slave replication functions to facilitate load balancing and data backup; 3. Improve query efficiency through query optimization and index use.
 The Purpose of SQL: Interacting with MySQL DatabasesApr 18, 2025 am 12:12 AM
The Purpose of SQL: Interacting with MySQL DatabasesApr 18, 2025 am 12:12 AMSQL is used to interact with MySQL database to realize data addition, deletion, modification, inspection and database design. 1) SQL performs data operations through SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE statements; 2) Use CREATE, ALTER, DROP statements for database design and management; 3) Complex queries and data analysis are implemented through SQL to improve business decision-making efficiency.
 MySQL for Beginners: Getting Started with Database ManagementApr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
MySQL for Beginners: Getting Started with Database ManagementApr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AMThe basic operations of MySQL include creating databases, tables, and using SQL to perform CRUD operations on data. 1. Create a database: CREATEDATABASEmy_first_db; 2. Create a table: CREATETABLEbooks(idINTAUTO_INCREMENTPRIMARYKEY, titleVARCHAR(100)NOTNULL, authorVARCHAR(100)NOTNULL, published_yearINT); 3. Insert data: INSERTINTObooks(title, author, published_year)VA


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment




