Home >Backend Development >C#.Net Tutorial >C# Advanced Programming (3) - Detailed explanation of objects and types
C# Advanced Programming (3) - Detailed explanation of objects and types
- 黄舟Original
- 2017-03-20 13:33:141292browse
3.2 Classes and Structures
The difference between classes and structures is their storage method,Access methods (similar to reference types stored on the heap, while structures are value types stored on the stack) and their some characteristics .
Syntactically, classes are very similar to structures. The main difference is that structures use keywords struct is declared instead of class .
3.3 Class members
3.3.1 Data members
Data members contain class data —Fields, Constant, and Eventa member of.
3.3.2 FunctionMember
## Function members provide certain functions for operating data in the class, includingMethods, Properties, Constructor and Destructor Functions (terminators) , operators, and indexers.
method
The difference between ref and #out :
ref must have been initialized before passing, out is not required.
The essence of ref is to pass the value type by reference, and out is To increase the return value.
Named parameters: In the process of passing parameters, you can specify their name, the format is MethodName (ParameterName : Value)
Params Keyword: must be at the end of the method parameters.
Overloading of methods: There cannot be a difference only in the return type, nor based solely on the declaration ref , Distinguish between out or params .
Attributes
Concept: A property is a method or a pair of methods. From the perspective of the client code, it (they) is a field.
The get accessor takes no parameters and returns the type declared by the property.
The set accessor takes a value parameter whose type is the same as the declared type.
Attribute access modifier: In the get and set accessors, there must be an access level with the attribute.
Constructor
Declaration of construction means declaring a method with the same name as the containing class, but the method has no return value.
If a constructor with parameters is provided, the compiler will not automatically provide a default constructor. (1) Static constructor Initialize these fields and properties from an external source before using the class for the first time.
The .NET runtime library does not ensure when to execute the static constructor, so it should not be required to execute the code in the static constructor at a specific time. But what is guaranteed is that it will only be called once before all references.
The parameterless constructor can be defined in the same class as the static constructor.
(2) Call other constructors from the constructor
ung 2)Calling other constructors from the constructor to other constructors
base
和this Keywords 3.3.3 Read-only fields
The difference between readonly
and const :
readonlycan be assigned in the constructor, And const cannot be assigned anywhere, only initialized. 3.4 Anonymous types
var
and new keywords can be used together to create anonymous types, for example. static void Main(string[] args)
2
3
4 {
5
6
7 var test = new { Name = "Earl Jones", Age = 17 };
8
9
10 Console.WriteLine(test.ToString());
11
12
13 Console.WriteLine(test.Name.GetType().ToString());
14
15
16 Console.WriteLine(test.Age.GetType().ToString());
17
18
19 Console.ReadKey();
20
21
22 }
复制代码 The output is as follows:
We don’t know this The type of object, the compiler "fake" a name for it, but only the compiler can use it, we cannot and should not use any type reflection on the new object, because this will not give consistent results .
The type of object, the compiler "fake" a name for it, but only the compiler can use it, we cannot and should not use any type reflection on the new object, because this will not give consistent results .
Structure is a value type, not a reference type, its
Lifecycle- The restrictions are the same as those of simple
- data types
, and the ref keyword can be used to reduce performance losses when passing structures. The
structure is generally used to express simple combined data. -
Structures do not support
inheritance , but all structures inherit from System.ValueType, which in turn inherits from System.Object. # Using structures, you can specify how fields are laid out in memory.
For structures, the compiler always provides a default no-argument constructor, which is not allowed to be replaced, and cannot provide initial values for fields in the structure. It must Provided in the constructor.
# Public fields in a structure are acceptable programming methods.
在定义结构时使用new关键字只不过是用于调用其构造函数,变量的声明实际上才是为结构分配空间,所以以下代码不被报错。
1 MyStruct myStruct /*= new MyStruct()*/; 2 myStruct.Name = "Earl Jones"; 3 myStruct.Age = 17;
覆盖结构默认的构造函数会报错:
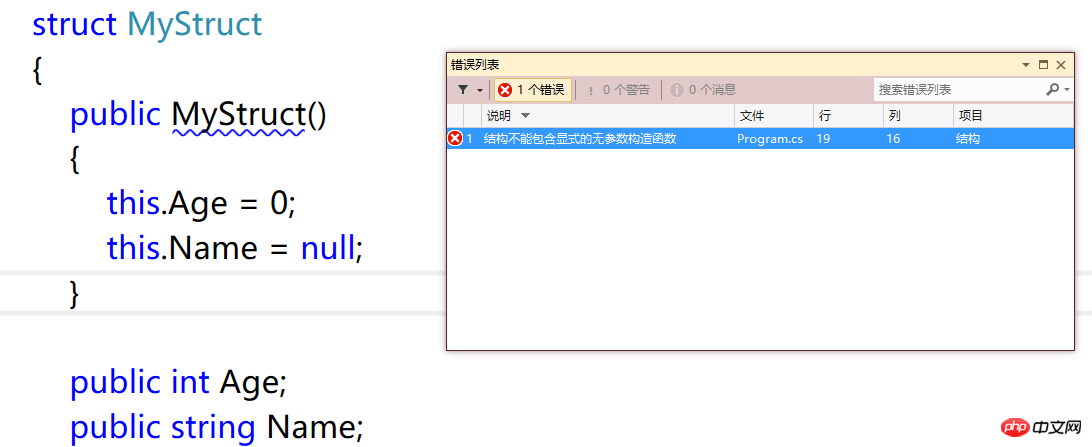
3.6 弱引用
在代码中实例化一个类或结构时,只要有代码引用它,就会形成强引用。
强引用和弱引用的区别是,强引用只要有引用就不会被GC回收,而弱引用随时都可能被GC回收,所以使用它的时候必须确定其是否存活。如:
<span style="font-family: 'Microsoft YaHei';"><span style="color: #008080;">1</span> <span style="color: #000000;"> MyClass myClass;<br/></span><span style="color: #008080;">2</span> WeakReference weakMyClass = <span style="color: #0000ff;">new</span> WeakReference(<span style="color: #0000ff;">new</span><span style="color: #000000;"> MyClass());<br/></span><span style="color: #008080;">3</span> <span style="color: #0000ff;"><a href="http://www.php.cn/wiki/109.html" target="_blank">if</a></span><span style="color: #000000;"> (weakMyClass.IsAlive)<br/></span><span style="color: #008080;">4</span> <span style="color: #000000;"> {<br/></span><span style="color: #008080;">5</span> myClass = weakMyClass.Target <span style="color: #0000ff;">as</span><span style="color: #000000;"> MyClass;<br/></span><span style="color: #008080;">6</span> <span style="color: #000000;"> Console.WriteLine(myClass.value); <br/></span><span style="color: #008080;">7</span> <span style="color: #000000;"> } </span></span>3.7 部分类
Partial关键字可以允许把类、结构、方法或结构放在多个文件中。
如果声明类似使用了下面的关键字,这些关键字就必须应用于同一个类的所有部分:
访问修饰符
abstract
sealed
new
一般约束
3.9 Object类
所有类都继承自System.Object类。
方法:
ToString();
GetHashCode();
Equals();这里有三个比较三个用于比较对象相等性的方法。
Finalize();
GetType();
GMemberwiseClone();
3.10 扩展方法
扩展方法用于在某些不能直接修改源代码中的类中添加方法。
1 using System;
2
3 namespace 扩展方法
4 {
5 class Program
6 {
7 static void Main(string[] args)
8 {
9 MyClass myClass1 = new MyClass();
10 myClass1.SayHiToSomeone();
11 myClass1.SayHi();
12 Console.ReadKey();
13 }
14 }
15
16 class MyClass
17 {
18 public void SayHi()
19 {
20 Console.WriteLine("我是最原始的方法");
21 }
22 }
23
24 static class AddMyClass
25 {
26 static public void SayHiToSomeone(this MyClass myClass)27 {
28 Console.WriteLine("我是一个扩展方法");
29 }
30
31 static public void SayHi(this MyClass myClass)
32 {
33 Console.WriteLine("我是扩展方法SayHi");
34 }
35 }
36 }输出的结果:
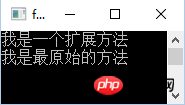
由上得出:
扩展方法必须定义在一个静态类中。
扩展方法的第一个参数为放在 this 后的类,这个方法就是这个类的一部分。
即是扩展方法是一个静态方法,也要使用调用实例方法的语法经行调用。
如果扩展方法与类中某个方法同名,就从来不会调用扩展方法。
The above is the detailed content of C# Advanced Programming (3) - Detailed explanation of objects and types. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

