Home >Web Front-end >CSS Tutorial >Summary of text-align in css common text attributes
Summary of text-align in css common text attributes
- 高洛峰Original
- 2017-03-14 15:38:002622browse
This article introduces the text-align in css commonly used text attributes Summary description
The text-indent attribute mentioned earlier, Used to achieve text indentation, today's text-align usage rate is much higher than text indentation. Taking the project I am currently working on as an example, horizontal centering and vertical centering are probably used the most, so let’s take a look at its syntax first!
text-align
Allowed valuesleft| center | right | justify |
The initial value is related to the user agent
Can it be Inherited Yes
Applicable to block-level elements
text-align is another one that is only applicable to block level Property of the element, if you want to center a link or image in a row, regardless of the alignment of the rest of the row that won't work. Let’s first feel the effect of text-align through the overall picture
below.
Here are the four attribute value display pictures of text-align
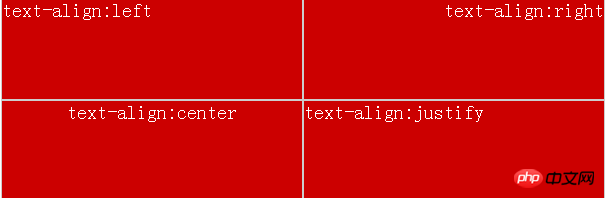
The above display shows the attribute rules of text-align very intuitively. The last attribute, text-align:justify, does not behave consistently in each browser. Personally, I feel that there are not many application scenarios for justice.
Application scenarios:
1. Text alignment Method: It depends on how the UI diagram is designed. In a word, just follow the design.
2. Center alignment of images: Using text-align on img alone has no effect. Don’t forget, text-align can only be used for block-level elements, not for inline elements and non-replaced elements. of. So if we want to center the image, we need to modify the scheme:
That’s it for the superficial discussion about text-align, please try it yourself.
The above is the detailed content of Summary of text-align in css common text attributes. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

