 Web Front-end
Web Front-end H5 Tutorial
H5 Tutorial HTML5 geographical positioning Geolocation-API and Haversine geospatial distance algorithm (graphics and text)
HTML5 geographical positioning Geolocation-API and Haversine geospatial distance algorithm (graphics and text) HTML5 provides Geolocation-API that allows us to obtain geographical location coordinates
However, it will only be used for specific needs
For example, map applications

Generally still rarely used
Geolocation-API
The method used is also very simple
API exists on the prototype of the navigator.geolocation object

The core methods are getCurrentPostion and watchPosition
getCurrentPosition
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition method has three parameters
success Get Callback function for successful location information (required)
error Callback function for failure to obtain location information
options Configuration information parameter object
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(function(pos){
console.log(pos);//获取位置信息对象Geoposition});At this time the browser will initiate a query
Because after all location information is also considered private information

Here we click to allow sharing location information That’s it
Then Chrome will send the local network information to Google location service
(Since Google is blocked in China, we can only get the location information by overcoming the wall〒▽〒)

The location information that can be returned to us in the console
coord coordinates
accuracy Positioning accuracy (unit m)
altitude Altitude
altitudeAccuracy Altitude accuracy (unit m)
heading direction
latitude latitude
longitude longitude
speed speed
timestamp timestamp
<br/>
However, this coordinate is not very accurate (especially on PC)
It may originate from IP address, GPS, Wifi positioning, etc.
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(function(pos){
console.log(pos);
},function(err){
console.log(err);
});We can set the second parameter to do some processing when obtaining the geographical location information error
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(function(pos){
console.log(pos);
},function(err){
console.log(err); //获取错误对象PositionError});For example I'm refusing to share my location now

code = 1 means user refuses
code = 2 means unable Get
code = 3 indicates connection timeout
The third parameter is used to set configuration information
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(function(pos){
console.log(pos);
},function(err){
console.log(err);
},{
enableHighAccuracy: true,
timeout: 5000,
maximumAge: 3000});enableHighAccuracy Whether high-precision location is required, the default is false
timeout Set the request timeout (unit ms) The default infinity has no time limit
maximumAge Location information expiration time (unit ms) Default 0: Unconditionally obtain new geographical location information
When repeatedly obtaining the geographical location watchPosition, this parameter specifies how long it takes Get the position again
watchPosition
The watchPosition and getCurrentPosition parameters are the same
The difference is that watchPosition continuously obtains position information
For example The positioning software we use
When our position keeps changing while running, we need to constantly redraw the positioning
In this way, every time the coordinates change, the success callback function
will be called and watchPosiiton will return a watchID
We can cancel monitoring through clearWatch(warchID)
Similar to canceling the timer
var ID = navigator.geolocation.watchPosition(function(pos){ ...},function(err){ ...},{ ...});
navigator.geolocation.clearWatch(ID);If clearWatch does not take parameters
, clear all watchPosition
Haversine algorithm
Sometimes we
may need to get the distance between two points
For example, for example, to get nearby businesses from a food ordering APP
At this time we can use the Haversine algorithm to calculate
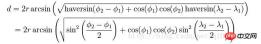
function toRadians(degree) {
return degree * Math.PI / 180;
}function haversine(latitude1, longitude1, latitude2, longitude2) {
var R = 6371; var deltaLatitude = toRadians(latitude2-latitude1);
var deltaLongitude = toRadians(longitude2-longitude1);
latitude1 = toRadians(latitude1);
latitude2 = toRadians(latitude2);
var a = Math.sin(deltaLatitude/2) * Math.sin(deltaLatitude/2) +
Math.cos(latitude1) * Math.cos(latitude2) *
Math.sin(deltaLongitude/2) * Math.sin(deltaLongitude/2);
var c = 2 * Math.atan2(Math.sqrt(a), Math.sqrt(1-a));
var d = R * c; return d;
} Pass in the coordinates of two points to get the geographical spatial distance
wherevar R = 6371; is the radius of the earth 6371km
Of course there are also some other algorithms
Varies in timing and accuracy
The above is the detailed content of HTML5 geographical positioning Geolocation-API and Haversine geospatial distance algorithm (graphics and text). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Mastering Microdata: A Step-by-Step Guide for HTML5May 14, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Mastering Microdata: A Step-by-Step Guide for HTML5May 14, 2025 am 12:07 AMMicrodatainHTML5enhancesSEOanduserexperiencebyprovidingstructureddatatosearchengines.1)Useitemscope,itemtype,anditempropattributestomarkupcontentlikeproductsorevents.2)TestmicrodatawithtoolslikeGoogle'sStructuredDataTestingTool.3)ConsiderusingJSON-LD
 What's New in HTML5 Forms? Exploring the New Input TypesMay 13, 2025 pm 03:45 PM
What's New in HTML5 Forms? Exploring the New Input TypesMay 13, 2025 pm 03:45 PMHTML5introducesnewinputtypesthatenhanceuserexperience,simplifydevelopment,andimproveaccessibility.1)automaticallyvalidatesemailformat.2)optimizesformobilewithanumerickeypad.3)andsimplifydateandtimeinputs,reducingtheneedforcustomsolutions.
 Understanding H5: The Meaning and SignificanceMay 11, 2025 am 12:19 AM
Understanding H5: The Meaning and SignificanceMay 11, 2025 am 12:19 AMH5 is HTML5, the fifth version of HTML. HTML5 improves the expressiveness and interactivity of web pages, introduces new features such as semantic tags, multimedia support, offline storage and Canvas drawing, and promotes the development of Web technology.
 H5: Accessibility and Web Standards ComplianceMay 10, 2025 am 12:21 AM
H5: Accessibility and Web Standards ComplianceMay 10, 2025 am 12:21 AMAccessibility and compliance with network standards are essential to the website. 1) Accessibility ensures that all users have equal access to the website, 2) Network standards follow to improve accessibility and consistency of the website, 3) Accessibility requires the use of semantic HTML, keyboard navigation, color contrast and alternative text, 4) Following these principles is not only a moral and legal requirement, but also amplifying user base.
 What is the H5 tag in HTML?May 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
What is the H5 tag in HTML?May 09, 2025 am 12:11 AMThe H5 tag in HTML is a fifth-level title that is used to tag smaller titles or sub-titles. 1) The H5 tag helps refine content hierarchy and improve readability and SEO. 2) Combined with CSS, you can customize the style to enhance the visual effect. 3) Use H5 tags reasonably to avoid abuse and ensure the logical content structure.
 H5 Code: A Beginner's Guide to Web StructureMay 08, 2025 am 12:15 AM
H5 Code: A Beginner's Guide to Web StructureMay 08, 2025 am 12:15 AMThe methods of building a website in HTML5 include: 1. Use semantic tags to define the web page structure, such as, , etc.; 2. Embed multimedia content, use and tags; 3. Apply advanced functions such as form verification and local storage. Through these steps, you can create a modern web page with clear structure and rich features.
 H5 Code Structure: Organizing Content for ReadabilityMay 07, 2025 am 12:06 AM
H5 Code Structure: Organizing Content for ReadabilityMay 07, 2025 am 12:06 AMA reasonable H5 code structure allows the page to stand out among a lot of content. 1) Use semantic labels such as, etc. to organize content to make the structure clear. 2) Control the rendering effect of pages on different devices through CSS layout such as Flexbox or Grid. 3) Implement responsive design to ensure that the page adapts to different screen sizes.
 H5 vs. Older HTML Versions: A ComparisonMay 06, 2025 am 12:09 AM
H5 vs. Older HTML Versions: A ComparisonMay 06, 2025 am 12:09 AMThe main differences between HTML5 (H5) and older versions of HTML include: 1) H5 introduces semantic tags, 2) supports multimedia content, and 3) provides offline storage functions. H5 enhances the functionality and expressiveness of web pages through new tags and APIs, such as and tags, improving user experience and SEO effects, but need to pay attention to compatibility issues.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools






