Home >Backend Development >Python Tutorial >Detailed explanation of python using djingo to develop helloword in pychram
Detailed explanation of python using djingo to develop helloword in pychram
- 高洛峰Original
- 2017-03-10 16:54:332319browse
This article explains in detail how python uses djingo to develop helloword in pychram
First install pycheam, python, and djingo.
Create a new djingo project in pychram
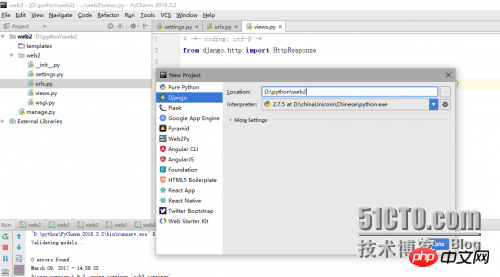
Create a new views.py file in the web2 directory, the directory is as follows:
Next, write the helloworld code in the views.py file:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*
from django.http import HttpResponse
def hello(request):
return HttpResponse("Hello world! This is my first trial. [笔记]")You also need to configure the urls.py file to complete the mapping
from django.conf.urls import patterns, include, url
from web2.views import hello
from django.contrib import admin
from django.conf.urls import *
admin.autodiscover()
urlpatterns = patterns('',
# Examples:
# url(r'^$', 'web2.views.home', name='home'),
# url(r'^blog/', include('blog.urls')),
url(r'^admin/', include(admin.site.urls)),
('^hello/$', hello),
)Be sure to import hello first
from web2.views import hello
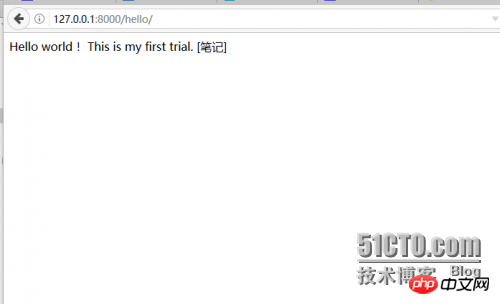
Then start the project and open it in the browser
http://127.0.0.1:8000/hello/
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of python using djingo to develop helloword in pychram. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

