1.Relative positioning and absolute positioning
// represents relative positioning. Relative positioning should be used for pages or nodes that frequently change. Search

/ means absolute positioning. When remains unchanged, you can use absolute positioning to search

2.Node
##Top node: bookstore
 Current node:“. ”
Current node:“. ”
If there are multiple current nodes, match multiple

If the current node has only 1, then match 1

Select the current node The parentnode:" ..”
For p under html/body, its parent node is body. This is done using absolute The path means that you must find the body from the html and then find p, and then match the parent node of p.

If you use a relative path to find the parent node, you can see that its absolute position is not considered starting from p, that is to say All elements starting from body that meet the conditions of the parent node will be found.
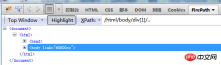
Find all elements under the current node: //book[1]/..
This is the method of node index +parent node

Positioning by label Element //book
: Find all tags namedbook


Attribute positioning1.
The element whose positioning attribute iscategory//book[@category='cooking'] '
[]' means search attribute
 2.
2.
text text attribute for precise positioning, text can also be used instead of
Find the element with the text 30.00 under//book//price

Find the element in the text in the year tag that is greater than 2004

3. Use contains for fuzzy positioning. contains means containing
Fuzzy positioning searches for elements whose text information contains Potter: //title[contains(text(),"Potter")]

Extension Exercise


4.”*” means any Attributes All attributes
Find all attributes with attribute values://@*


Find all elements with attributes in the tag:

Not to negate , means to find elements that have no attributes in the title tag , there is no one here so I didn’t find it.
@*
means all attributesnot(@*)
means no attributes
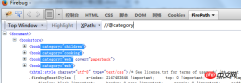
5.
Find elements with thecategory attribute//@category
Logical operators1.
Locate elements through theand operator//book[@category="web" and @cover="paperback"]
 2. Locate elements through the or operator
2. Locate elements through the or operator
 3.
3.
not operator //book[not(position()>2)]
Get the# whose position is greater than
2 in thebook tag
##//book[not(position()>2)] not negation
//year[not(.=2005) ]  means taking the year node that is not the
means taking the year node that is not the
Find the element by “>=”“operator
//price>=30 Whether there is price greater than or equal to 30 Exists returns Boolean true Does not exist Returns Boolean: false


4.Locate elements through "!"operator
//book [@category!='web' ]

6.Locate elements by node index
1.Find the first element
//book[1]: Find the first # with the label book

Position the th 3# through position ##Element//bookstore/book[position()=3]

3.
Get multiple elements throughposition//bookstore/book[position()>=2]
 4. Through last()
4. Through last()
//book[last()]
 5.
5.
last ()Function to find the penultimate element//book[last()-1]

7 .
Axis positioning
Find the parent element of
book[1]/title: //book [1]/title/parent::*

book[1]: //book[ 1]/child::*
 //book/child::price
//book/child::price
book tag with the tag price
 following-sibling
following-sibling
//bookstore/book[1]/child::title/following-sibling::*
Following-sibling represents all sibling node elements in the subsequent sequence of the current node
title

following-sibling::author
title The element named author
 preceding-sibling::* represents all sibling node elements in front of the current node
preceding-sibling::* represents all sibling node elements in front of the current node
//bookstore /book[1]/child::price/preceding-sibling::*
means to find all sibling elements in front of theprice node Find ancestor nodes including self: //book[1]/ancestor-or-self::* Find descendant nodes including self: //book[1]/descendant-or-self::* ##//book[2]//preceding::* will book[2] and book[2] nodes before Find all elements of
# #Axis summary: parent::* represents the parent node element of the current node child::* represents the current node The child elements of the node /A/descendant::* represent all descendant elements of A 


Find all elements of the current node: //book[1]/preceding::* Find all elements under the current node

self::* represent the self elements of the current node
ancestor-or-self::* represent the current node and its ancestor nodes The element
descendant-or-self::* represents the current node and their descendant elements
following-sibling::* represents the following sibling node elements of the current node
preceding-sibling::* represents All sibling node elements in front of the current node
following::* represents all elements in the following order of the current node
preceding::* represents all elements of the current node
The above is the detailed content of Summary of Xpath positioning. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Why are HTML tags important for web development?May 02, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Why are HTML tags important for web development?May 02, 2025 am 12:03 AMHTMLtagsareessentialforwebdevelopmentastheystructureandenhancewebpages.1)Theydefinelayout,semantics,andinteractivity.2)SemantictagsimproveaccessibilityandSEO.3)Properuseoftagscanoptimizeperformanceandensurecross-browsercompatibility.
 Explain the importance of using consistent coding style for HTML tags and attributes.May 01, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Explain the importance of using consistent coding style for HTML tags and attributes.May 01, 2025 am 12:01 AMA consistent HTML encoding style is important because it improves the readability, maintainability and efficiency of the code. 1) Use lowercase tags and attributes, 2) Keep consistent indentation, 3) Select and stick to single or double quotes, 4) Avoid mixing different styles in projects, 5) Use automation tools such as Prettier or ESLint to ensure consistency in styles.
 How to implement multi-project carousel in Bootstrap 4?Apr 30, 2025 pm 03:24 PM
How to implement multi-project carousel in Bootstrap 4?Apr 30, 2025 pm 03:24 PMSolution to implement multi-project carousel in Bootstrap4 Implementing multi-project carousel in Bootstrap4 is not an easy task. Although Bootstrap...
 How does deepseek official website achieve the effect of penetrating mouse scroll event?Apr 30, 2025 pm 03:21 PM
How does deepseek official website achieve the effect of penetrating mouse scroll event?Apr 30, 2025 pm 03:21 PMHow to achieve the effect of mouse scrolling event penetration? When we browse the web, we often encounter some special interaction designs. For example, on deepseek official website, �...
 How to modify the playback control style of HTML videoApr 30, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
How to modify the playback control style of HTML videoApr 30, 2025 pm 03:18 PMThe default playback control style of HTML video cannot be modified directly through CSS. 1. Create custom controls using JavaScript. 2. Beautify these controls through CSS. 3. Consider compatibility, user experience and performance, using libraries such as Video.js or Plyr can simplify the process.
 What problems will be caused by using native select on your phone?Apr 30, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
What problems will be caused by using native select on your phone?Apr 30, 2025 pm 03:15 PMPotential problems with using native select on mobile phones When developing mobile applications, we often encounter the need for selecting boxes. Normally, developers...
 What are the disadvantages of using native select on your phone?Apr 30, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
What are the disadvantages of using native select on your phone?Apr 30, 2025 pm 03:12 PMWhat are the disadvantages of using native select on your phone? When developing applications on mobile devices, it is very important to choose the right UI components. Many developers...
 How to optimize collision handling of third-person roaming in a room using Three.js and Octree?Apr 30, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to optimize collision handling of third-person roaming in a room using Three.js and Octree?Apr 30, 2025 pm 03:09 PMUse Three.js and Octree to optimize collision handling of third-person roaming in the room. Use Octree in Three.js to implement third-person roaming in the room and add collisions...


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!







