Home >Backend Development >PHP Tutorial >thinkphp infinite classification implementation method
thinkphp infinite classification implementation method
- 大家讲道理Original
- 2017-02-21 10:09:044980browse
This article explains the method of implementing infinite classification under the thinkphp framework. Infinite classification is generally used in the classification menu of websites. It is a very common data structure and function. It is also very easy to implement this method in thinkphp. Okay, let's learn how to use it next.
The principle of infinite classification is to add a field (such as Sid) for differentiation. The top-level classification Sid is 0, the second-level classification Sid is the ID of the upper-level classification, and so on. When outputting, recursion is generally used.
Let’s first create a new data table with the following structure:
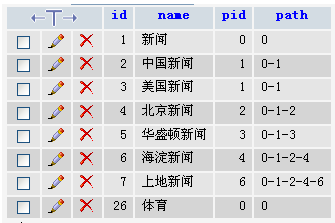
Controller: CateAction .class.php
<?php
class CateAction extends Action{
function index(){
$cate=M('Cate');
$list=$cate->field("id,name,pid,path,concat(path,'-',id) as bpath")->order('bpath')->select();
foreach($list as $key=>$value){
$list[$key]['count']=count(explode('-',$value['bpath']));
}
$this->assign('alist',$list);
$this->display();
}//添加栏目
function add(){
$cate=new CateModel();if($vo=$cate->create()){
if($cate->add()){
$this->success('添加栏目成功');
}else{
$this->error('添加栏目失败');
}
}else{
$this->error($cate->getError());
}
}}
?>Model: CateModel.class.php
<?php
class CateModel extends Model{//对应数据库中的表xp_cate
protected $_auto=array(
array('path','tclm',3,'callback'),
);function tclm(){
$pid=isset($_POST['pid'])?(int)$_POST['pid']:0;
echo ($pid);
if($pid==0){
$data=0;
}else{
$list=$this->where("id=$pid")->find();
$data=$list['path'].'-'.$list['id'];//子类的path为父类的path加上父类的id
}
return $data;
}
}
?>Template :index.html
<form action="!-URL-!/add" method="post">
请选择父级栏目:<select name="pid" size="20">
<option value="0">根栏目</option>
<volist name="alist" id="vo">
<option value="{$vo['id']}">
{:str_repeat(" ",$vo['count']-2)}
{$vo['name']}
</option>
</volist>
</select><br />
新的栏目名称:<input type="text" name="name" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="添加栏目" />
</form>The display results are as follows:

##Note:

