Home >Backend Development >XML/RSS Tutorial >Apache Commons Configuration reads xml configuration
Apache Commons Configuration reads xml configuration
- 黄舟Original
- 2017-02-17 15:33:201981browse
Recent project is to write a string connection pool by hand. Because the environments are different, there are development versions, test versions, and online versions, and the database used by each version is also different. Therefore, it is necessary to flexibly switch database connections. Of course this can be solved using maven. The Apache Commons Configuration framework is mainly used to parse database connection strings.
The following introduces the common parts of the Apache Commons Configuration framework.
1) Apache Commons Configuration framework uses
**
# to download the jar package http://www.php.cn/ or http: //www.php.cn/ Search and download
in maven to study the use of api.
Benefits of use
·When the xml structure changes greatly, there is no need to modify the code for parsing xml too much
Users only need to modify their own parsing syntax tree.
Customers only need to modify the syntax tree framework for parsing. The starting point for thinking is whether it is similar to the interpreter pattern in the design pattern. Build abstract syntax trees and interpret execution.
Users only need to care about and modify their own parsing syntax tree.
Users do not need to worry about how to parse, they only need to configure the corresponding parsing grammar rules.
-
Simplify the program and significantly modify the code after the xml configuration structure changes.
First configure Maven.
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-configuration</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-configuration</artifactId>
<version>1.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-beanutils</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-beanutils</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-jxpath</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-jxpath</artifactId>
<version>1.3</version>
</dependency>Define a springok1.xml with the following content 
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!-- springok1.xml --><config>
<database>
<url>127.0.0.1</url>
<port>3306</port>
<login>admin</login>
<password></password>
</database></config>The parsing code begins
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
XMLConfiguration conf=new XMLConfiguration("springok1.xml");
System.out.println(conf.getString("database.url"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("database.port"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("database.login"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("database.password"));
} The output is as follows: It means that the xml has been successfully parsed.
127.0.0.1
3306
admin
Acquisition methods There are many more detailed acquisition methods that can be found in the AbstractConfiguration method.
The above configuration is the connection information of one database. If the connection information of many databases is configured, how to parse and switch the connection information. Modify the information of springok1.xml to configure multiple connections as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!-- springok1.xml --><config><databases>
<database>
<url>127.0.0.1</url>
<port>3306</port>
<login>admin</login>
<password></password>
</database>
<database>
<url>127.0.0.1</url>
<port>3302</port>
<login>admin</login>
<password>admin</password>
</database></databases></config>Now assume that we want to obtain two configuration database connection information, the program is as follows:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
XMLConfiguration conf=new XMLConfiguration("springok1.xml");
System.out.println(conf.getString("databases.database(0).url"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("databases.database(0).port"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("databases.database(0).login"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("databases.database(0).password"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("databases.database(1).url"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("databases.database(1).port"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("databases.database(1).login"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("databases.database(1).password"));
}Output:
127.0. 0.1
3306
admin
127.0.0.1
3302
admin
admin
Parsing is ok,
Combined with the previous configuration file example In actual combat, we found that if there are multiple identical tags, the index starts from 0.
XPath expression uses the
point access method. The above method is no problem. For some complex configurations, we may need to use the XPath expression language. The main advantage here is that, using XML's advanced queries, the program still looks relatively simple and easy to understand. High understandability. 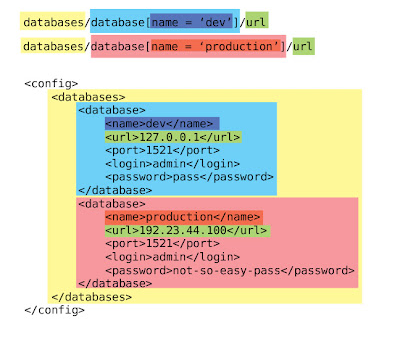
Or parse the springok.xml file above. The code is as follows:
XMLConfiguration conf=new XMLConfiguration("springok1.xml");
conf.setExpressionEngine(new XPathExpressionEngine());
System.out.println(conf.getString("databases/database[port='3306']/url"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("databases/database[port='3302']/port"));Output:
127.0.0.1
3302
Test ok.
Access environment variables
EnvironmentConfiguration conf=new EnvironmentConfiguration();
System.out.println(conf.getMap());How to implement source code analysis:
public EnvironmentConfiguration()
{ super(new HashMap<String, Object>(System.getenv()));
}Joint configuration
Combining two methods, 1 and 2, can we define a database string key that needs to be connected in the system variable, and obtain dynamic loading during parsing? ?
public String getDbUrl() throws ConfigurationException {
EnvironmentConfiguration envConfig =new EnvironmentConfiguration(); String env = envConfig.getString("ENV_TYPE"); if("dev".equals(env) ||"production".equals(env)) {
XMLConfiguration xmlConfig =new XMLConfiguration("springok1.xml");
xmlConfig.setExpressionEngine(new XPathExpressionEngine()); String xpath ="databases/database[name = '"+ env +"']/url"; return xmlConfig.getString(xpath);
}else{ String msg ="ENV_TYPE environment variable is "+
"not properly set";
throw new IllegalStateException(msg);
}
}The test is ok, no problem.
Unified management modularity
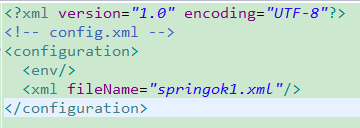
xml configuration is as shown below:
public String getDbUrl()throws ConfigurationException {
DefaultConfigurationBuilder builder =
new DefaultConfigurationBuilder(“config.xml”);
boolean load =true;
CombinedConfiguration config = builder.getConfiguration(load);
config.setExpressionEngine(new XPathExpressionEngine());
String env = config.getString("ENV_TYPE");
if(“dev”.equals(env) ||”production”.equals(env)) {
String xpath =”databases/database[name = ‘”+ env +”’]/url”;
Return config.getString(xpath);
}else{
String msg =”ENV_TYPE environment variable is “+
“not properly set”;
Throw new IllegalStateException(msg);
}
}
Automatic reload
Automatically load when the file-based configuration changes, because we can set the loading strategy. The framework polls the configuration file, and when the file's contents change, the configuration object is refreshed. You can use program control:
XMLConfiguration config =new XMLConfiguration("springok1.xml");
ReloadingStrategy strategy =new FileChangedReloadingStrategy();
((FileChangedReloadingStrategy) strategy).setRefreshDelay(5000);
config.setReloadingStrategy(strategy);or control during configuration:
<?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?><!-- config.xml --><configuration>
<env/>
<xmlfileName="const.xml">
<reloadingStrategyrefreshDelay="5000" config-class="org.apache.commons.configuration.reloading.FileChangedReloadingStrategy"/>
</xml></configuration>下面是dom和sax方式的手动解析方式可参考使用。
java语言中xml解析有很多种方式,最流行的方式有sax和dom两种。
1. dom是把所有的解析内容一次性加入内存所以xml内容大的话性能不好。
2. sax是驱动解析。所以内存不会占用太多。(spring用的就是sax解析方式)
需要什么包自己到网上找下吧?
xml文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="GB2312"?> <RESULT> <VALUE> <NO>springok1</NO> <ADDR>springok</ADDR> </VALUE> <VALUE> <NO>springok2</NO> <ADDR>springok</ADDR> </VALUE> </RESULT>
1)DOM(JAXP Crimson解析器)
DOM是用与平台和语言无关的方式表示XML文档的官方W3C标准。DOM是以层次结构组织的节点或信息片断的集合。这个层次结构允许开发人员在树中寻找特定信息。分析该结构通常需要加载整个文档和构造层次结构,然后才能做任何工作。由于它是基于信息层次的,因而DOM被认为是基于树或基于对象的。DOM以及广义的基于树的处理具有几个优点。首先,由于树在内存中是持久的,因此可以修改它以便应用程序能对数据和结构作出更改。它还可以在任何时候在树中上下导航,而不是像SAX那样是一次性的处理。DOM使用起来也要简单得多。
import java.io.*; import java.util.*; import org.w3c.dom.*; import javax.xml.parsers.*; public class MyXMLReader{
public static void main(String arge[]){
long lasting =System.currentTimeMillis(); try{
File f=new File("data_10k.xml"); DocumentBuilderFactory factory=DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance(); DocumentBuilder builder=factory.newDocumentBuilder(); Document doc = builder.parse(f); NodeList nl = doc.getElementsByTagName("VALUE"); for (int i=0;i<nl.getLength();i++){ System.out.print("车牌号码:" + doc.getElementsByTagName("NO").item(i).getFirstChild().getNodeValue()); System.out.println("车主地址:" + doc.getElementsByTagName("ADDR").item(i).getFirstChild().getNodeValue()); }
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace(); }2)SAX
SAX处理的优点非常类似于流媒体的优点。分析能够立即开始,而不是等待所有的数据被处理。而且,由于应用程序只是在读取数据时检查数据,因此不需要将数据存储在内存中。这对于大型文档来说是个巨大的优点。事实上,应用程序甚至不必解析整个文档;它可以在某个条件得到满足时停止解析。一般来说,SAX还比它的替代者DOM快许多。 选择DOM还是选择SAX? 对于需要自己编写代码来处理XML文档的开发人员来说, 选择DOM还是SAX解析模型是一个非常重要的设计决策。 DOM采用建立树形结构的方式访问XML文档,而SAX采用的事件模型。 DOM解析器把XML文档转化为一个包含其内容的树,并可以对树进行遍历。用DOM解析模型的优点是编程容易,开发人员只需要调用建树的指令,然后利用navigation APIs访问所需的树节点来完成任务。可以很容易的添加和修改树中的元素。然而由于使用DOM解析器的时候需要处理整个XML文档,所以对性能和内存的要求比较高,尤其是遇到很大的XML文件的时候。由于它的遍历能力,DOM解析器常用于XML文档需要频繁的改变的服务中。 SAX解析器采用了基于事件的模型,它在解析XML文档的时候可以触发一系列的事件,当发现给定的tag的时候,它可以激活一个回调方法,告诉该方法制定的标签已经找到。SAX对内存的要求通常会比较低,因为它让开发人员自己来决定所要处理的tag.特别是当开发人员只需要处理文档中所包含的部分数据时,SAX这种扩展能力得到了更好的体现。但用SAX解析器的时候编码工作会比较困难,而且很难同时访问同一个文档中的多处不同数据。
import org.xml.sax.*;
import org.xml.sax.helpers.*;
import javax.xml.parsers.*;
public class MyXMLReader extends DefaultHandler { java.util.Stack tags = new java.util.Stack();
public MyXMLReader() {
super();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
long lasting = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
SAXParserFactory sf = SAXParserFactory.newInstance();
SAXParser sp = sf.newSAXParser();
MyXMLReader reader = new MyXMLReader();
sp.parse(new InputSource("data_10k.xml"), reader);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("运行时间:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - lasting) + "毫秒");}
public void characters(char ch[], int start, int length) throws SAXException {
String tag = (String) tags.peek();
if (tag.equals("NO")) {
System.out.print("车牌号码:" + new String(ch, start, length));
}
if (tag.equals("ADDR")) {
System.out.println("地址:" + new String(ch, start, length));
}
}
public void startElement(String uri,String localName,String qName,Attributes attrs) {
tags.push(qName);}
}**
总结:个人喜欢这个框架,支持定时刷新、xpath、import方式。
近期项目自己手写一个字符串连接池。因为环境不同有开发版本、测试版本、上线版本、每一个版本用到的数据库也是不一样的。所以需要能灵活的切换数据库连接。当然这个用maven就解决了。Apache Commons Configuration 框架用的主要是解析数据库连接字符串。
下面介绍Apache Commons Configuration 框架的常用部分。
1)Apache Commons Configuration framework框架使用
**
下载jar包http://www.php.cn/或者http://www.php.cn/ maven中搜索下载
研究api的使用。
使用好处
·当xml结构大变化的时候不用过多的修改解析xml的代码
用户只需要修改自己的解析语法树即可。
客户只需要修改语法树框架去解析,思考的起点是不是跟设计模式中的解释器模式类似。构建抽象语法树并解释执行。
用户只需要关心和修改自己的解析语法树即可。
用户不用关系如何解析只需要配置对应的解析语法规则即可。
-
简化程序xml配置结构变化后大幅度的修改代码。
首先先配置一下Maven。
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-configuration</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-configuration</artifactId>
<version>1.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-beanutils</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-beanutils</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-jxpath</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-jxpath</artifactId>
<version>1.3</version>
</dependency>定义一个springok1.xml内容如下 
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!-- springok1.xml --><config>
<database>
<url>127.0.0.1</url>
<port>3306</port>
<login>admin</login>
<password></password>
</database></config>解析代码开始了
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
XMLConfiguration conf=new XMLConfiguration("springok1.xml");
System.out.println(conf.getString("database.url"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("database.port"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("database.login"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("database.password"));
}输出如下:说明已经成功解析xml了。
127.0.0.1
3306
admin
获取的方法有很多种更详细的获取方法可以从AbstractConfiguration方法中对应找到。
上面配置的是一个数据库的连接信息,如果配置很多数据库的连接信息,怎么解析连接信息切换呢。修改springok1.xml的信息为多个连接配置如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!-- springok1.xml --><config><databases>
<database>
<url>127.0.0.1</url>
<port>3306</port>
<login>admin</login>
<password></password>
</database>
<database>
<url>127.0.0.1</url>
<port>3302</port>
<login>admin</login>
<password>admin</password>
</database></databases></config>现在假设我们要获取两个的配置数据库连接信息,程序如下:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
XMLConfiguration conf=new XMLConfiguration("springok1.xml");
System.out.println(conf.getString("databases.database(0).url"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("databases.database(0).port"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("databases.database(0).login"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("databases.database(0).password"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("databases.database(1).url"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("databases.database(1).port"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("databases.database(1).login"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("databases.database(1).password"));
}输出:
127.0.0.1
3306
admin
127.0.0.1
3302
admin
admin
解析ok,
结合前面的配置文件的例子跟实战我们发现多个相同的标签的话索引是从0开始的。
XPath表达式使用
点的访问方式上面的那种方式是没问题,对于一些复杂的配置来讲,我们可能需要使用XPath表达式语言。这里的主要优点是,使用了XML的高级查询,程序看起来仍然比较简洁易懂。可理解性高。 
还是解析上面的springok.xml文件。代码如下:
XMLConfiguration conf=new XMLConfiguration("springok1.xml");
conf.setExpressionEngine(new XPathExpressionEngine());
System.out.println(conf.getString("databases/database[port='3306']/url"));
System.out.println(conf.getString("databases/database[port='3302']/port"));输出:
127.0.0.1
3302
测试ok.
访问环境变量
EnvironmentConfiguration conf=new EnvironmentConfiguration();
System.out.println(conf.getMap());源码分析如何实现:
public EnvironmentConfiguration()
{ super(new HashMap<String, Object>(System.getenv()));
}联合配置
联合一和2两种方式,是不是我们可以再系统变量中定义一个需要连接的数据库字符串key,解析的时候获取动态加载呢?
public String getDbUrl() throws ConfigurationException {
EnvironmentConfiguration envConfig =new EnvironmentConfiguration(); String env = envConfig.getString("ENV_TYPE"); if("dev".equals(env) ||"production".equals(env)) {
XMLConfiguration xmlConfig =new XMLConfiguration("springok1.xml");
xmlConfig.setExpressionEngine(new XPathExpressionEngine()); String xpath ="databases/database[name = '"+ env +"']/url"; return xmlConfig.getString(xpath);
}else{ String msg ="ENV_TYPE environment variable is "+
"not properly set";
throw new IllegalStateException(msg);
}
}测试ok没问题。
统一管理模块化
xml配置如下图:

public String getDbUrl()throws ConfigurationException {
DefaultConfigurationBuilder builder =
new DefaultConfigurationBuilder(“config.xml”);
boolean load =true;
CombinedConfiguration config = builder.getConfiguration(load);
config.setExpressionEngine(new XPathExpressionEngine());
String env = config.getString(“ENV_TYPE”);
if(“dev”.equals(env) ||”production”.equals(env)) {
String xpath =”databases/database[name = ‘”+ env +”’]/url”;
return config.getString(xpath);
}else{
String msg =”ENV_TYPE environment variable is “+
“not properly set”;
throw new IllegalStateException(msg);
}
}
自动重新加载
当基于文件的配置变化的时候自动加载,因为我们可以设置加载策略。框架会轮询配置文件,当文件的内容发生改变时,配置对象也会刷新。你可以用程序控制:
XMLConfiguration config =new XMLConfiguration("springok1.xml");
ReloadingStrategy strategy =new FileChangedReloadingStrategy();
((FileChangedReloadingStrategy) strategy).setRefreshDelay(5000);
config.setReloadingStrategy(strategy);或者配置的时候控制:
<?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?><!-- config.xml --><configuration>
<env/>
<xmlfileName="const.xml">
<reloadingStrategyrefreshDelay="5000" config-class="org.apache.commons.configuration.reloading.FileChangedReloadingStrategy"/>
</xml></configuration>下面是dom和sax方式的手动解析方式可参考使用。
java语言中xml解析有很多种方式,最流行的方式有sax和dom两种。
1. dom是把所有的解析内容一次性加入内存所以xml内容大的话性能不好。
2. sax是驱动解析。所以内存不会占用太多。(spring用的就是sax解析方式)
需要什么包自己到网上找下吧?
xml文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="GB2312"?> <RESULT> <VALUE> <NO>springok1</NO> <ADDR>springok</ADDR> </VALUE> <VALUE> <NO>springok2</NO> <ADDR>springok</ADDR> </VALUE> </RESULT>
1)DOM(JAXP Crimson解析器)
DOM是用与平台和语言无关的方式表示XML文档的官方W3C标准。DOM是以层次结构组织的节点或信息片断的集合。这个层次结构允许开发人员在树中寻找特定信息。分析该结构通常需要加载整个文档和构造层次结构,然后才能做任何工作。由于它是基于信息层次的,因而DOM被认为是基于树或基于对象的。DOM以及广义的基于树的处理具有几个优点。首先,由于树在内存中是持久的,因此可以修改它以便应用程序能对数据和结构作出更改。它还可以在任何时候在树中上下导航,而不是像SAX那样是一次性的处理。DOM使用起来也要简单得多。
import java.io.*; import java.util.*; import org.w3c.dom.*; import javax.xml.parsers.*; public class MyXMLReader{
public static void main(String arge[]){
long lasting =System.currentTimeMillis(); try{
File f=new File("data_10k.xml"); DocumentBuilderFactory factory=DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance(); DocumentBuilder builder=factory.newDocumentBuilder(); Document doc = builder.parse(f); NodeList nl = doc.getElementsByTagName("VALUE"); for (int i=0;i<nl.getLength();i++){ System.out.print("车牌号码:" + doc.getElementsByTagName("NO").item(i).getFirstChild().getNodeValue()); System.out.println("车主地址:" + doc.getElementsByTagName("ADDR").item(i).getFirstChild().getNodeValue()); }
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace(); }2)SAX
SAX处理的优点非常类似于流媒体的优点。分析能够立即开始,而不是等待所有的数据被处理。而且,由于应用程序只是在读取数据时检查数据,因此不需要将数据存储在内存中。这对于大型文档来说是个巨大的优点。事实上,应用程序甚至不必解析整个文档;它可以在某个条件得到满足时停止解析。一般来说,SAX还比它的替代者DOM快许多。 选择DOM还是选择SAX? 对于需要自己编写代码来处理XML文档的开发人员来说, 选择DOM还是SAX解析模型是一个非常重要的设计决策。 DOM采用建立树形结构的方式访问XML文档,而SAX采用的事件模型。 DOM解析器把XML文档转化为一个包含其内容的树,并可以对树进行遍历。用DOM解析模型的优点是编程容易,开发人员只需要调用建树的指令,然后利用navigation APIs访问所需的树节点来完成任务。可以很容易的添加和修改树中的元素。然而由于使用DOM解析器的时候需要处理整个XML文档,所以对性能和内存的要求比较高,尤其是遇到很大的XML文件的时候。由于它的遍历能力,DOM解析器常用于XML文档需要频繁的改变的服务中。 SAX解析器采用了基于事件的模型,它在解析XML文档的时候可以触发一系列的事件,当发现给定的tag的时候,它可以激活一个回调方法,告诉该方法制定的标签已经找到。SAX对内存的要求通常会比较低,因为它让开发人员自己来决定所要处理的tag.特别是当开发人员只需要处理文档中所包含的部分数据时,SAX这种扩展能力得到了更好的体现。但用SAX解析器的时候编码工作会比较困难,而且很难同时访问同一个文档中的多处不同数据。
import org.xml.sax.*;
import org.xml.sax.helpers.*;
import javax.xml.parsers.*;
public class MyXMLReader extends DefaultHandler { java.util.Stack tags = new java.util.Stack();
public MyXMLReader() {
super();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
long lasting = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
SAXParserFactory sf = SAXParserFactory.newInstance();
SAXParser sp = sf.newSAXParser();
MyXMLReader reader = new MyXMLReader();
sp.parse(new InputSource("data_10k.xml"), reader);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("运行时间:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - lasting) + "毫秒");}
public void characters(char ch[], int start, int length) throws SAXException {
String tag = (String) tags.peek();
if (tag.equals("NO")) {
System.out.print("车牌号码:" + new String(ch, start, length));
}
if (tag.equals("ADDR")) {
System.out.println("地址:" + new String(ch, start, length));
}
}
public void startElement(String uri,String localName,String qName,Attributes attrs) {
tags.push(qName);}
}**
总结:个人喜欢这个框架,支持定时刷新、xpath、import方式。
以上就是Apache Commons Configuration读取xml配置的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(www.php.cn)!

