Home >Web Front-end >HTML Tutorial >14 new features in HTML 5.1 (with use cases)
14 new features in HTML 5.1 (with use cases)
- 高洛峰Original
- 2017-02-13 15:11:261202browse
HTML5 belongs to the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), an organization that provides standards for the entire web community and creates protocols that can be used around the world. In November 2016, the W3C updated the long-standing HTML 5 standard, its first minor update in 2 years. Many of the features originally proposed for HTML 5.1 were removed due to design flaws and lack of support from browser vendors.
Although there are some elements and feature improvements that have been brought into HTML 5.1, it is still a small update. Some of the new elements include combination tags, which now include a38fd2622755924ad24c0fc5f0b4d412, a5e9d42b316b6d06c62de0deffc36939, 631fb227578dfffda61e1fa4d04b7d25 and 9b66618b56ad8833e792d2ba7c315ba9, giving developers more ways to express their creativity and content. Space.
The W3C has also started working on the HTML 5.2 draft, which is expected to be released by the end of 2017. What we are here to present are the new features and improvements introduced in version 5.1. You don't need to use JavaScript to take advantage of these features. Not all browsers support these features, so it's a good idea to check browser support before using them in production.
14. Prevent phishing attacks
Most people who use target ='_blank' don't know an interesting fact - newly opened tabs can change window.opener.location to Some phishing pages. It will execute some malicious JavaScript code on your behalf on the open page. Because users trust that the page they open is safe, they have no doubts.
To completely eliminate this problem, HTML 5.1 has standardized the use of the rel="noopener" attribute by isolating the browser context. rel="noopener" can be used in 3499910bf9dac5ae3c52d5ede7383485 and 03fc64e1e502d5ba947b3a9af06d2d2a tags.
<a href="#" target="_blank" rel="noopener"> The link won't make trouble anymore </a>
13. Handle picture titles flexibly
614eb9dc63b3fb809437a716aa228d24 tag represents the title or legend associated with the 24203f2f45e6606542ba09fd2181843a element, usually as a container for visual elements such as pictures, charts, illustrations, etc. . In earlier versions of HTML, 614eb9dc63b3fb809437a716aa228d24 could only be used as a child tag of the first or last 24203f2f45e6606542ba09fd2181843a. HTML5.1 has relaxed this restriction so that you can now use 614eb9dc63b3fb809437a716aa228d24 anywhere within a 24203f2f45e6606542ba09fd2181843a container.
<article>
<h1>The Headline of todays news </h1>
<figure>
<img src="petrolimage.jpeg" alt="Petrol price drops">
<figcaption>A man fueling up his car at petrol station</figcaption>
</figure>
<p>This is the forth hike in petrol prices in two month and the third in case of diesel in one fortnight.</p>
</article>12. Spellcheck
spellcheck is an enumeration property whose values can be empty string, true and false. Specifying its status as true means that the element will be checked for spelling and grammar.
element.forceSpellCheck() will force user agents to report checked spelling and grammatical errors on text elements, even if the user never focused input on that element.
<p spellcheck="true"> <label>Name: <input spellcheck=" false" id="textbox"></label> </p>
11. Empty option
The new version of HTML allows you to create an empty 5a07473c87748fb1bf73f23d45547ab8 element. It can be a child element of an 5b7a15bed8615d1b843806256bebea72, fc86e7b705049fc9d4fccc89a2e80ee3 or 221f08282418e2996498697df914ce4e element. You may find this feature helpful when designing user-friendly forms.
10. Full screen support for Frame
The Boolean variable allowfullscreen attribute developed for Frame allows you to control whether content can be displayed in full screen by using the requestFullscreen() method. For example, let's use an iframe embedded in a YouTube player. The allowfullscreen attribute needs to be set to allow the player to display the video in full screen.
<article> <header> <p><img src="/usericons/16235"> <b>Fred Flintstone</b></p> <p><a href="/posts/30934" rel=bookmark>12:44</a> — <a href="#acl-503439551">Private Post</a></p> </header> <main> <p>Check out my new video!</p> <iframe title="Video" src="https://youtube.com/?id=92469812" allowfullscreen></iframe> </main> </article>
9. Embedding header and footer
HTML5.1 allows you to embed header and footer inside another header. You can add a header or footer to the header element if they contain themselves within paragraph content. This feature becomes useful if you want to add elaboration tags such as 2f8332c8dcfd5c7dec030a070bf652c3 and 23c3de37f2f9ebcb477c4a90aac6fffd to semantic paragraph elements.
<article>
<header>
<h2>Lesson: How to cook chicken</h2>
<aside>
<header>
<h2>About the author: Tom Hank</h2>
<p><a href="./tomhank/">Contact him!</a></p>
</header>
<p>Expert in nothing but Cooking. The cookbook sideshow.</p>
</aside>
</header>
<p><ins>Pour the marinade into the zip-top bag with the chicken and seal it.
Remove as much air as possible from the bag and seal it. </ins></p>
</article>8. Zero-width images
<img src="theimagefile.jpg" width="0" height="0" alt="">7. Validating forms
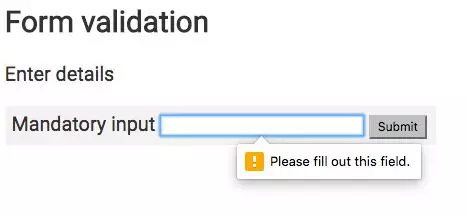
<h2>Form validation</h2>
<p>Enter details</p>
<form>
<label>
Mandatory input <input type="password" name="password" required />
</label>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
<script>
document.querySelector('form').reportValidity()
</script>6. Browser context menu
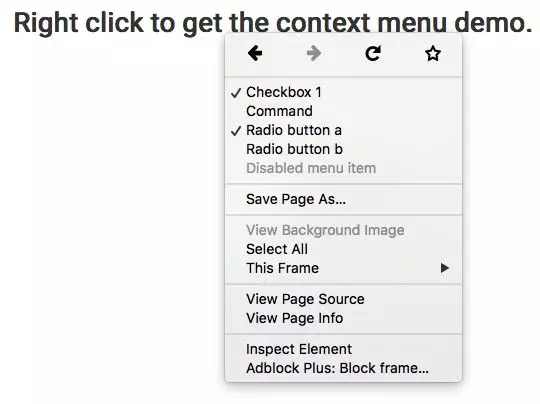
在 HTML 5.1 中, 你可以使用 5c0e96d12fc7501cef2ae2efde646ee0 标记来定义菜单,里面包含了一个或者多个 9b8d7b889acba92c978f783c55ba01dc 元素, 然后利用 contextmenu 属性将其绑定到任何元素上。 5c0e96d12fc7501cef2ae2efde646ee0 元素的 id 取值应该与我们想要为其添加上下文菜单的元素的 contextmenu 属性取值保持一致。
每一个 9b8d7b889acba92c978f783c55ba01dc 都可以有如下三个表单项中的一个:
radio – 从一个分组中获取选项;
checkbox – 选择或者取消选择一个选项;
command – 在点击时执行一个动作。
<h2 contextmenu="popup-menu"> Right click to get the context menu demo. </h2> <menu type="context" id="popup-menu"> <menuitem type="checkbox" checked="true">Checkbox 1 </menuitem> <menuitem type="command" label="Command" onclick="alert('WARNING')">Checkbox 2</menuitem> <menuitem type="radio" name="group1">Radio button a</menuitem> <menuitem type="radio" name="group1" checked="true">Radio button b</menuitem> <menuitem type="checkbox" disabled>Disabled menu item</menuitem> </menu>
5. 在脚本和样式上使用加密随机数
加密随机数(cryptographic nonce )是一个随机生成的数字,只能被使用一次, 而且针对每一次页面请求,它都得被生成出来。这个 nonce 属性可以被使用在 3f1c4e4b6b16bbbd69b2ee476dc4f83a 和 c9ccee2e6ea535a969eb3f532ad9fe89 元素中。
它一般被用在一个网站的内容安全策略之中,以决定一个特定的样式和脚本是否应该在页面上被实现。在下面所提供的代码中,这个 value 是硬编码的,不过在实际的使用场景中,这个值是随机生成的。
<script nonce='d3ne7uWP43Bhr0e'> The JavaScript Code </script>
4、反序链接关系
rev 属性在 HTML4 里有定义,但是它并没出现在 HTML5 里。W3C 决定在 3499910bf9dac5ae3c52d5ede7383485 和 2cdf5bf648cf2f33323966d7f58a7f3f 元素里重新包含 rev 属性。rev 属性标识当前和反向的链接文档的关系。它已经被包含来支持广泛使用数据结构标记格式,RDFa。
让我们用两个文档来举个例子,每个包含一课程,在它们之间的链接可以使用如下 rel 和 rev 的属性来定义。
//Document with URL "chapter1.html" <link href="Lesson2.html" rel="next" rev="prev"> //Document with URL "chapter2.html" <link href="Lesson1.html" rel="prev" rev="next"> <link href="Lesson3.html" rel="next" rev="prev">
3. 显示/隐藏信息
新的 a5e9d42b316b6d06c62de0deffc36939 和 631fb227578dfffda61e1fa4d04b7d25 元素允许您向一段内容添加扩展信息。您可以通过单击元素来显示或隐藏一个附加信息块。 默认情况下是隐藏附加信息的。
在代码中,您应该将 631fb227578dfffda61e1fa4d04b7d25 标记放在 a5e9d42b316b6d06c62de0deffc36939 标记内,如下所示。 631fb227578dfffda61e1fa4d04b7d25 标签之后,你可以添加要隐藏的其他内容。
<section>
<h3>Error Message</h3>
<details>
<summary>This file hasn't been download due to network error.</summary>
<dl>
<dt>File name:</dt><dd>Passcode.txt</dd>
<dt>File size:</dt><dd>8 KB</dd>
<dt>Error code:</dt><dd>342a</dd>
</dl>
</details>
</section>2. 更多的输入项类型
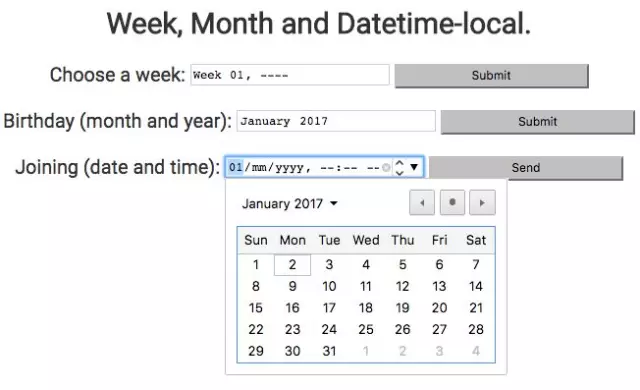
HTML 输入项元素扩充了三个输入类型 – week, month 以及 datetime-local。
正如其名称所表明的,头两个元素可以让用户选择一个星期值和一个月份值。根据浏览器的支持情况不同,它们俩都会被渲染成一个下拉显示的日历,让你可以选择一年中一个特定的星期或者月份。
datatime-local 表示的是一个日期和时间的输入域, 不过没有时区设置。其数据可以采用跟 month 或者 week 输入项类似的方法来选定, 而时间可以单独输入。
<section>
<h2>
Week, Month and Datetime-local
</h2>
<form action="action_page.php">
Choose a week:
<input type="week" name="year_week">
<input type="submit">
</form>
<form action="action_page.php">
Birthday (month and year):
<input type="month" name="bdaymonth">
<input type="submit">
</form>
<form action="action_page.php">
Joining (date and time):
<input type="datetime-local" name="bdaytime">
<input type="submit" value="Send">
</form>
</section>1. 响应式图像
W3C 引入了一些功能特性,无需使用 CSS 就可以实现响应式图像。它们是 …
srcset 图像属性
srcset 属性让你可以指定一个多个可选的图像来源,对应于不同的像素分辨率。它将允许浏览器根据用户设备的不同选择合适质量的实现来进行显示。例如,对于使用网络比较慢的移动设备的用户,显示一张低分辨率的图片会比较好。
你可以使用 srcset 属性并且带上它自有的 x 修饰符来描述每一个图片的像素比例, 如果用户的像素比例等于 3,就会显示 high-res 这张图片。
<img src="clicks/low-res.jpg" srcset=" clicks/low-res.jpg 1x, clicks/medium-res.jpg 2x, clicks/high-res.jpg 3x" >
除了像素比例之外,你也可以选择使用 w 修饰符来指定不同尺寸大小的图片。在如下示例中,high-res 图片被定义成在宽度为 1600px 时显示。
<img src="clicks/low-res.jpg" srcset=" clicks/low-res.jpg 500w, clicks/medium-res.jpg 1000w, clicks/high-res.jpg 1600w" >
sizes 图像属性
大多数时候创作者们都喜欢针对不同的屏幕尺寸显示不同的图片。这个可以用 sizes 属性做到。它让你可以针对分配给图像显示的空间大小来对宽度做出调整, 然后使用 srcset 属性来挑选合适的图片来显示。例如…
<img src="clicks/low-res.jpg" sizes="(max-width: 25em) 60vw, 100vw" srcset="clicks/low-res.jpg 500w, clicks/medium-res.jpg 1000w, clicks/high-res.jpg 1600w" >
在这里, sizes 属性定义了在视窗大于 25 em 时图像宽度为视窗宽度的 100%,或者在小于等于 25em 时为视图宽度的 60%。
picture 元素
picture 元素让你可以针对不同的屏幕尺寸声明图片。这个可以通过用 9b66618b56ad8833e792d2ba7c315ba9 元素封装 a1f02c36ba31691bcfe87b2722de723b ,并且描述多个 e02da388656c3265154666b7c71a8ddc 子元素来实现。
9b66618b56ad8833e792d2ba7c315ba9 标记单独使用并不会显示任何东西。你已经被假定会声明默认的图像来源作为 src 属性的取值,而可选的图像来源则会放在 scrset 属性之中,如下所示:
<picture>
<source media="(max-width: 25em)" srcset="
clicks/small/low-res.jpg 1x,
clicks/small/medium-res.jpg 2x,
clicks/small/high-res.jpg 3x
">
<source media="(max-width: 60em)" srcset="
clicks/large/low-res.jpg 1x,
clicks/large/medium-res.jpg 2x,
clicks/large/high-res.jpg 3x
">
<img src="clicks/default/medium-res.jpg">
</picture>更多HTML 5.1 的 14 个新特性(含使用案例)相关文章请关注PHP中文网!

