Home >Backend Development >C#.Net Tutorial >C# starts using LINQ (Part 1)
C# starts using LINQ (Part 1)
- 黄舟Original
- 2017-02-06 16:36:071649browse
Introduction to LINQ
Language Integrated Query (LINQ) is an innovative feature introduced in Visual Studio 2008 and .NET Framework version 3.5.
#Traditionally, queries against data have been expressed as simple strings without compile-time type checking or IntelliSense support. In addition, you must learn a different query language for various data sources: SQL databases, XML documents, various Web services, and so on. With LINQ, you can write queries against collections of strongly typed objects using language keywords and familiar operators.
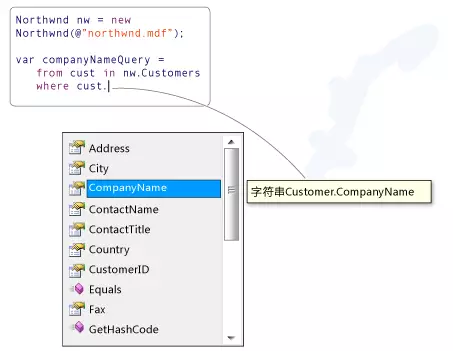
In Visual Studio, you can write LINQ queries for the following data sources: SQL Server databases, XML documents, ADO.NET datasets, and support IEnumerable or generic IEnumerable An arbitrary collection of objects of the interface.
Requirements: Project ≥ .NET Framework 3.5.
1. Introduction to LINQ query
Query is an expression that retrieves data from a data source. Over time, different languages have been developed for various data sources; for example, SQL for relational databases and XQuery for XML. As a result, developers are forced to learn new query languages for each data source or data format they must support.
#LINQ simplifies this situation by providing a consistent model for working with data across data sources and data formats. In LINQ queries, objects are always used. You can use the same encoding mode to query and transform data in XML documents, SQL databases, ADO.NET datasets, .NET collections, and any other format for which a LINQ provider is available.
1.1 Three parts of query operation
internal class Program
{
private static void Main(string[] args)
{
//1.获取数据源
var nums = new int[7] { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
//2.创建查询
var numQuery =
from num in nums
where (num % 2) == 0
select num;
//3.执行查询
foreach (var num in numQuery)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}", num);
}
}
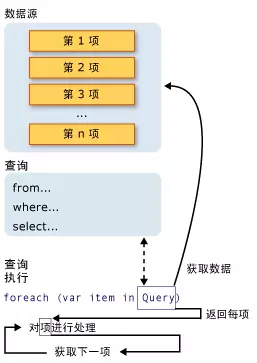
}Result:0 2 4 6The following figure shows the complete query operation. In LINQ, the execution of a query is distinct from the query itself; in other words, the query itself only creates query variables and does not retrieve any data.
##1.2 Data source
In the previous example, due to the data The source is an array, so it implicitly supports the generic IEnumerable
Queryable types can be used as LINQ data sources without modification or special processing. If the source data does not already exist in memory as a queryable type, the LINQ provider must represent the source data in this way. For example, LINQ to XML loads an XML document into a queryable XElement type:
//从 XML 中创建数据源 //using System.Xml.Linq; var contacts = XElement.Load(@"c:\xxx.xml");
In LINQ to SQL, you first need to create an object-relational mapping. Queries are written against these objects, and LINQ to SQL handles communication with the database at runtime.
var db = new Northwnd(@"c:\northwnd.mdf");
//查询在伦敦的客户
var custQuery= from cust in db.Customers
where cust.City == "London"
select cust;Customers represents a specific table in the database
1.3 查询
查询指定要从数据源中检索的信息。 查询还可以指定在返回这些信息之前如何对其进行排序、分组和结构化。 查询存储在查询变量中,并用查询表达式进行初始化。
之前的示例中的查询是从整数数组中返回所有的偶数。 该查询表达式包含三个子句:from、where 和 select。(如果您熟悉 SQL,您会注意到这些子句的顺序与 SQL 中的顺序相反。)from 子句指定数据源,where 子句指定应用筛选器,select 子句指定返回的元素的类型。 目前需要注意的是,在 LINQ 中,查询变量本身不执行任何操作并且不返回任何数据。 它只是存储在以后某个时刻执行查询时为生成结果而必需的信息。
1.4 查询执行
1.延迟执行
如前所述,查询变量本身只是存储查询命令。 实际的查询执行会延迟到在 foreach 语句中循环访问查询变量时发生。 此概念称为“延迟执行”。
2.强制立即执行
对一系列源元素执行聚合函数的查询必须首先循环访问这些元素。Count、Max、Average 和 First 就属于此类查询。由于查询本身必须使用 foreach 以便返回结果,因此这些查询在执行时不使用显式 foreach 语句。另外还要注意,这些类型的查询返回单个值,而不是 IEnumerable 集合。
var numbers = new int[7] { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
var evenNumQuery =
from num in numbers
where (num % 2) == 0
select num;
var evenNumCount = evenNumQuery.Count();结果:
4
若要强制立即执行任意查询并缓存其结果,可以调用 ToList
var numQuery2 =(from num in numbers
where (num % 2) == 0
select num).ToList();
var numQuery3 =(from num in numbers
where (num % 2) == 0
select num).ToArray();此外,还可以通过在紧跟查询表达式之后的位置放置一个 foreach 循环来强制执行查询。但是,通过调用 ToList 或 ToArray,也可以将所有数据缓存在单个集合对象中。
二、基本 LINQ 查询操作
2.1 获取数据源:from
在 LINQ 查询中,第一步是指定数据源。像在大多数编程语言中一样,必须先声明变量,才能使用它。在 LINQ 查询中,最先使用 from 子句的目的是引入数据源和范围变量。
//queryAllCustomers 是 IEnumerable<Cutsomer> 类型
//数据源 (customers) 和范围变量 (cust)
var queryAllCustomers = from cust in customers
select cust;范围变量类似于 foreach 循环中的迭代变量,但在查询表达式中,实际上不发生迭代。执行查询时,范围变量将用作对 customers 中的每个后续元素的引用。因为编译器可以推断 cust 的类型,所以您不必显式指定此类型。
2.2 筛选:where
也许最常用的查询操作是应用布尔表达式形式的筛选器。此筛选器使查询只返回那些表达式结果为 true 的元素。使用 where 子句生成结果。实际上,筛选器指定从源序列中排除哪些元素。
var queryLondonCustomers = from cust in customers
where cust.City = "London"
select cust;您可以使用熟悉的 C# 逻辑 AND(&&)和 OR(||) 运算符来根据需要在 where 子句中应用任意数量的筛选表达式。
where cust.City = "London" && cust.Name = "Devon" where cust.City = "London" || cust.Name = "Paris"
2.3 排序:orderby
通常可以很方便地将返回的数据进行排序。orderby 子句将使返回的序列中的元素按照被排序的类型的默认比较器进行排序。
var queryLondonCustomers = from cust in customers
where cust.City = "London"
orderby cust.Name descending
select cust;因为 Name 是一个字符串,所以默认比较器执行从 A 到 Z 的字母排序。若要按相反顺序(从 Z 到 A)对结果进行排序,请使用 orderby…descending 子句。
2.4 分组:group
使用 group 子句,您可以按指定的键分组结果。
var queryLondonCustomers = from cust in customers
group cust by cust.City;
foreach (var queryLondonCustomer in queryLondonCustomers)
{
Console.WriteLine(queryLondonCustomer.Key);
foreach (var cust in queryLondonCustomer)
{
Console.WriteLine(cust.Name);
}
}您可以指定结果应按 City 分组,以便位于伦敦或巴黎的所有客户位于各自组中。
在本例中,cust.City 是键。
在使用 group 子句结束查询时,结果采用列表的列表形式。列表中的每个元素是一个具有 Key 成员及根据该键分组的元素列表的对象。在循环访问生成组序列的查询时,您必须使用嵌套的 foreach 循环。外部循环用于循环访问每个组,内部循环用于循环访问每个组的成员。
如果您必须引用组操作的结果,可以使用 into 关键字来创建可进一步查询的标识符。
//custQuery 是 IEnumable<IGrouping<string, Customer>> 类型
var custQuery = from cust in customers
group cust by cust.City
into custGroup
where custGroup.Count() > 2
orderby custGroup.Key
select custGroup;这里的查询只返回那些包含两个以上的客户的组。
2.5 联接:join
联接运算创建数据源中没有显式建模的序列之间的关联。例如,您可以执行联接来查找位于同一地点的所有客户和经销商。在 LINQ 中,join 子句始终针对对象集合而非直接针对数据库表运行。
var innerJoinQuery = from cust in customers
join dist in distributors on cust.City equals dist.City
select new {CustomerName = cust.Name, DistributorName = dist.Name};在 LINQ 中,join 子句始终针对对象集合而非直接针对数据库表运行。
在 LINQ 中,您不必像在 SQL 中那样频繁使用 join,因为 LINQ 中的外键在对象模型中表示为包含项集合的属性。
from order in Customer.Orders...
2.6 选择(投影):select
select 子句生成查询结果并指定每个返回的元素的“形状”或类型。
例如,您可以指定结果包含的是整个 Customer 对象、仅一个成员、成员的子集,还是某个基于计算或新对象创建的完全不同的结果类型。当 select 子句生成除源元素副本以外的内容时,该操作称为“投影”。
三、使用 LINQ 进行数据转换
语言集成查询 (LINQ) 不仅可用于检索数据,而且还是一个功能强大的数据转换工具。通过使用 LINQ 查询,您可以将源序列用作输入,并采用多种方式修改它以创建新的输出序列。您可以通过排序和分组来修改该序列,而不必修改元素本身。但是,LINQ 查询的最强大的功能是能够创建新类型。这一功能在 select 子句中实现。 例如,可以执行下列任务:
3.1 将多个输入联接到一个输出序列
class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public string City { get; set; }
public List<int> Scores { get; set; }
}
class Teacher
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public string City { get; set; }
}学生和老师两个类
internal class Program
{
private static void Main(string[] args)
{
//创建第一个数据源
var students = new List<Student>()
{
new Student()
{
Age = 23,
City = "广州",
Name = "小C",
Scores = new List<int>(){85,88,83,97}
},
new Student()
{
Age = 18,
City = "广西",
Name = "小明",
Scores = new List<int>(){86,78,85,90}
},
new Student()
{
Age = 33,
City = "梦里",
Name = "小叁",
Scores = new List<int>(){86,68,73,97}
}
};
//创建第二个数据源
var teachers = new List<Teacher>()
{
new Teacher()
{
Age = 35,
City = "梦里",
Name = "啵哆"
},
new Teacher()
{
Age = 28,
City = "云南",
Name = "小红"
},
new Teacher()
{
Age = 38,
City = "河南",
Name = "丽丽"
}
};
//创建查询
var peopleInDreams = (from student in students
where student.City == "梦里"
select student.Name)
.Concat(from teacher in teachers
where teacher.City == "梦里"
select teacher.Name);
//执行查询
foreach (var person in peopleInDreams)
{
Console.WriteLine(person);
}
Console.Read();
}
}以上就是C#开始使用 LINQ (上)的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(www.php.cn)!

