Home >Backend Development >Python Tutorial >Detailed explanation of python's simple host batch management tool
Detailed explanation of python's simple host batch management tool
- 高洛峰Original
- 2017-02-04 15:12:411357browse
I did a very simple small project today. I felt the power of the paramiko module, and I also felt that my Linux skills were not good~~
1. Requirements

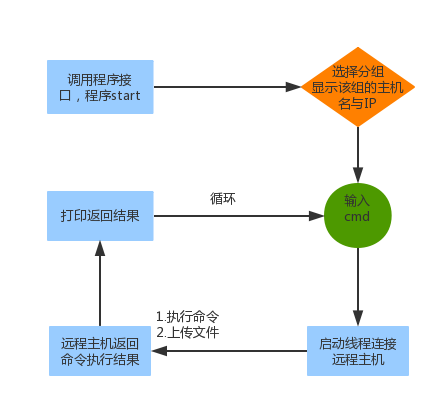
2. Simple requirements analysis and flow chart
The requirements are very small, so I will simply say:
1. Host grouping can be configured File implementation (I use a dictionary to store data).
2. The login function does not work. After selecting a group, you can view the host name and IP address of the corresponding host in the group.
3. Depends on the host) executed simultaneously)
Output:
-------------h1--------- ---
......(Data returned by the command)
-------------h2------- -----
……
 ##3. Directory structure and source code
##3. Directory structure and source code
Directory structure:
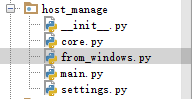 from_windows.py (file to be uploaded)
from_windows.py (file to be uploaded)
main.py (batch host management interface)
"""批量主机管理接口""" import core if __name__ == "__main__": core.run()
core.py (core code, called by the interface)
"""核心代码"""
import settings
import paramiko
import threading
import os
class REMOTE_HOST(object):
#远程操作主机
def __init__(self, host, port ,username, password, cmd):
self.host = host
self.port = port
self.username = username
self.password = password
self.cmd = cmd
def run(self):
"""起线程连接远程主机后调用"""
cmd_str = self.cmd.split()[0]
if hasattr(self, cmd_str): #反射 eg:调用put方法
getattr(self, cmd_str)()
else:
#setattr(x,'y',v)is equivalent to ``x.y=v''
setattr(self, cmd_str, self.command)
getattr(self, cmd_str)() #调用command方法,执行批量命令处理
def command(self):
"""批量命令处理"""
ssh = paramiko.SSHClient() #创建ssh对象
#允许连接不在know_hosts文件中的主机
ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
ssh.connect(hostname=self.host,port=self.port,username=self.username,password=self.password)
stdin,stdout,stderr = ssh.exec_command(self.cmd)
result = stdout.read()
print("%s".center(50, "-") % self.host)
print(result.decode())
ssh.close()
def put(self):
"""上传文件"""
filename = self.cmd.split()[1] #要上传的文件
transport = paramiko.Transport((self.host, self.port))
transport.connect(username=self.username, password=self.password)
sftp = paramiko.SFTPClient.from_transport(transport)
sftp.put(filename, filename)
print("put sucesss")
transport.close()
def show_host_list():
"""通过选择分组显示主机名与IP"""
for index, key in enumerate(settings.msg_dic):
print(index + 1, key, len(settings.msg_dic[key]))
while True:
choose_host_list = input(">>>(eg:group1)").strip()
host_dic = settings.msg_dic.get(choose_host_list)
if host_dic:
#print(host_dic)
for key in host_dic:
print(key, host_dic[key]["IP"])
return host_dic
else:
print("NO exit this group!")
def interactive(choose_host_list):
"""根据选择的分组主机起多个线程进行批量交互"""
thread_list = []
while True:
cmd = input(">>>").strip()
if cmd:
for key in choose_host_list:
host, port, username, password = choose_host_list[key]["IP"], choose_host_list[key]["port"], \
choose_host_list[key]["username"], choose_host_list[key]["password"]
func = REMOTE_HOST(host, port, username, password, cmd) # 实例化类
t = threading.Thread(target=func.run) # 起线程
t.start()
thread_list.append(t)
for t in thread_list:
t.join() # 主线程等待子线程执行完毕
else:
continue
def run():
choose_host_list = show_host_list()
interactive(choose_host_list)settings.py(configuration file)
"""配置文件"""
msg_dic = {
"group1":{ #分组1
"h1":{"IP":"192.168.1.1", "username":"11", "password":"aa", "port":22},
"h2":{"IP":"192.168.1.2", "username":"22", "password":"bb", "port":22},
"h3":{"IP":"192.168.1.3", "username":"33", "password":"cc", "port":22},
"h4":{"IP":"192.168.1.4", "username":"44", "password":"dd", "port":22},
"h5":{"IP":"192.168.1.5", "username":"55", "password":"ee", "port":22},
"h6":{"IP":"192.168.1.6", "username":"66", "password":"ff", "port":22},
},
"group2":{ #分组2
"h1":{"IP":"192.168.2.1", "username":"111", "password":"aaa", "port":22},
"h2":{"IP":"192.168.2.2", "username":"222", "password":"bbb", "port":22},
"h3":{"IP":"192.168.2.3", "username":"333", "password":"ccc", "port":22},
"h4":{"IP":"192.168.2.4", "username":"444", "password":"ddd", "port":22},
"h5":{"IP":"192.168.2.5", "username":"555", "password":"eee", "port":22},
"h6":{"IP":"192.168.2.6", "username":"666", "password":"fff", "port":22},
"h7":{"IP":"192.168.2.7", "username":"777", "password":"ggg", "port":22},
"h8":{"IP":"192.168.2.8", "username":"888", "password":"hhh", "port":22},
},
"group3":{
"h1":{"IP":"192.168.179.133", "username":"root", "password":"zcl", "port":22},
}
}Test:
Hardware Limitation, I only need to connect to one virtual machine for testing~
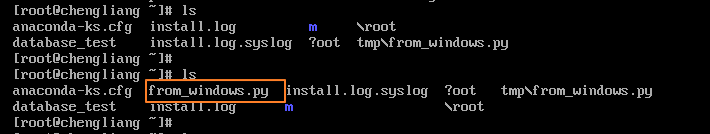
C:\Python34\python3.exe C:/Users/Administrator/PycharmProjects/laonanhai/host_manage/main.py 1 group1 6 2 group3 1 3 group2 8 >>>(eg:group1)group3 h1 192.168.179.133 >>>put from_windows.py put sucesss >>> >>>ls ------------------------192.168.179.133------------------------ anaconda-ks.cfg database_test from_windows.py install.log install.log.syslog m oot \root tmp\from_windows.py >>>
There is no from_windows.py file before uploading, but there is after uploading!
 That’s it I hope that the entire content of this article will be helpful to everyone's learning, and I also hope that everyone will support the PHP Chinese website.
That’s it I hope that the entire content of this article will be helpful to everyone's learning, and I also hope that everyone will support the PHP Chinese website.
For more detailed explanations of Python’s simple host batch management tools, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!

