Home >Java >javaTutorial >Regaining the basics of Java (11): Summary of three common methods of Eclipse and bean objects
Regaining the basics of Java (11): Summary of three common methods of Eclipse and bean objects
- 黄舟Original
- 2017-01-16 09:53:482003browse
Regain the basics of java (11): Summary of three common methods of Eclipse and bean objects
1. Introduction to Eclipse
1. Eclipse is a multifunctional and powerful Java and other language development software jointly developed by IBM and OTI.
2. Installation and use of Eclipse
1. Changing the working path for the first time*Person class, used to define basic information about people*@author author*@version version informationFile|Switch Workpace
3. Common shortcut keys for Eclipse
1. Shortcut keys Ctrl + Shift + f*Get the value of the name attribute *@return the value of the name attribute*Set the value of the age attribute*@param age age & code formatting Ctrl + Shift + O&&& included Import Ctrl + F11&&&&&&& Compile and run Ctrl + d& Delete a line of code Ctrl + /&&Add/Cancel single line comment Crtl + Shift + /&Multiple Line comment (first select the code to be commented) Crtl + Shift + /& Cancel multi-line comment (first select the code to be uncommented) Generate main method: write main first and then alt + / Finally Enter to generate the output statement: write first syso then alt + / automatically generate (right-click Source menu) getter/setter method construction method
4. Documentation comments
& /**& #&*/&&/**&*//**&*/1. Stronger function: you can extract the content in the comments to generate a help document (instruction manual)
3. Write documentation comments in Java source files& a. Can only be written above (immediately next to) the class or method& b./**&*/& c. Generally, the first line is an overall introduction to the class or method
4. How to extract and generate help documentation& javadoc xxx.java -d doc
5. Breakpoint debugging
-
Troubleshooting (logical errors)
2. Steps a. Add breakpoints b. To debug Mode running program& c. Single-step code execution& d. Observe Variables, console and other views
6. Use of Object class
& 1. Our customized class will automatically inherit the Object class
2. The non-private methods of this class will be automatically inherited by other classes and can also be overridden
3. Functional method&&getClass(), obtain the type of an object (runtime type)&&equals(), "equality" judgment between objects (reference types)&&hashCode (), returns the hash code of the object&&toString(), returns the string representation of the object
## 7. equals method
- If you want to compare the values of basic data types for equality, use ==
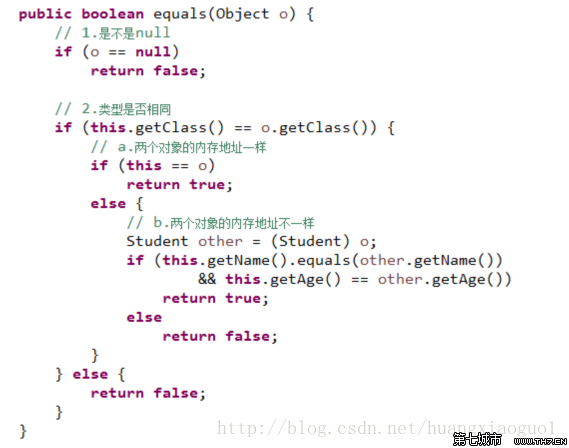
- A master :Hash& invented an algorithm that can convert a hexadecimal memory address into a number. This number is called a hash value
- 2. Memory addresses of two objects Different, the hash value is different, the memory address is the same, the hash value is the same
3. By overriding the hashCode method to generate a hash value based on the content, the efficiency of comparison can be improved
4. Adding attribute values
 ##9. toString() method
##9. toString() method
cannot be output directly An object
- 2. When we directly output an object, the toString() method will be automatically called

