Home >Java >javaTutorial >Writing serial communication tools based on Java
Writing serial communication tools based on Java
- 高洛峰Original
- 2017-01-05 14:40:462397browse
A recent course required writing a host computer serial communication tool. I wrote a simple serial communication tool with a graphical interface based on Java. The process is described in detail below for your reference^_^
1:
First of all, you need to download an additional jar package that supports Java serial port communication operations. Since java.comm is relatively old and does not support 64-bit systems, the Rxtx jar package is recommended here (32-bit/ 64-bit supported).
Official download address: http://fizzed.com/oss/rxtx-for-java (Note: FQ may be required to download)
Children's shoes that cannot be FQ can be downloaded here:
http://xiazai.jb51.net/201612/yuanma/javamfzrxtx(jb51.net).rar(32-bit)
http://xiazai.jb51.net/201612/ yuanma/javamfzrxtx(jb51.net).rar (64-bit)
Two:
Download and decompress the jar package and introduce it under Java Build Path:
Capture

Note: If a java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError error is thrown during operation, please copy the rxtxParallel.dll and rxtxSerial.dll files in the rxtx decompression package to C:\ This error can be solved by going to the Windows\System32 directory.
Three:
Regarding the use of this jar package, I wrote a SerialTool.java class, which provides simple services related to serial port communication. The code is as follows (note that this class is located in the serialPort package ):
package serialPort;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.TooManyListenersException;
import gnu.io.CommPort;
import gnu.io.CommPortIdentifier;
import gnu.io.NoSuchPortException;
import gnu.io.PortInUseException;
import gnu.io.SerialPort;
import gnu.io.SerialPortEventListener;
import gnu.io.UnsupportedCommOperationException;
import serialException.*;
/**
* 串口服务类,提供打开、关闭串口,读取、发送串口数据等服务(采用单例设计模式)
* @author zhong
*
*/
public class SerialTool {
private static SerialTool serialTool = null;
static {
//在该类被ClassLoader加载时就初始化一个SerialTool对象
if (serialTool == null) {
serialTool = new SerialTool();
}
}
//私有化SerialTool类的构造方法,不允许其他类生成SerialTool对象
private SerialTool() {}
/**
* 获取提供服务的SerialTool对象
* @return serialTool
*/
public static SerialTool getSerialTool() {
if (serialTool == null) {
serialTool = new SerialTool();
}
return serialTool;
}
/**
* 查找所有可用端口
* @return 可用端口名称列表
*/
public static final ArrayList<String> findPort() {
//获得当前所有可用串口
Enumeration<CommPortIdentifier> portList = CommPortIdentifier.getPortIdentifiers();
ArrayList<String> portNameList = new ArrayList<>();
//将可用串口名添加到List并返回该List
while (portList.hasMoreElements()) {
String portName = portList.nextElement().getName();
portNameList.add(portName);
}
return portNameList;
}
/**
* 打开串口
* @param portName 端口名称
* @param baudrate 波特率
* @return 串口对象
* @throws SerialPortParameterFailure 设置串口参数失败
* @throws NotASerialPort 端口指向设备不是串口类型
* @throws NoSuchPort 没有该端口对应的串口设备
* @throws PortInUse 端口已被占用
*/
public static final SerialPort openPort(String portName, int baudrate) throws SerialPortParameterFailure, NotASerialPort, NoSuchPort, PortInUse {
try {
//通过端口名识别端口
CommPortIdentifier portIdentifier = CommPortIdentifier.getPortIdentifier(portName);
//打开端口,并给端口名字和一个timeout(打开操作的超时时间)
CommPort commPort = portIdentifier.open(portName, 2000);
//判断是不是串口
if (commPort instanceof SerialPort) {
SerialPort serialPort = (SerialPort) commPort;
try {
//设置一下串口的波特率等参数
serialPort.setSerialPortParams(baudrate, SerialPort.DATABITS_8, SerialPort.STOPBITS_1, SerialPort.PARITY_NONE);
} catch (UnsupportedCommOperationException e) {
throw new SerialPortParameterFailure();
}
//System.out.println("Open " + portName + " sucessfully !");
return serialPort;
}
else {
//不是串口
throw new NotASerialPort();
}
} catch (NoSuchPortException e1) {
throw new NoSuchPort();
} catch (PortInUseException e2) {
throw new PortInUse();
}
}
/**
* 关闭串口
* @param serialport 待关闭的串口对象
*/
public static void closePort(SerialPort serialPort) {
if (serialPort != null) {
serialPort.close();
serialPort = null;
}
}
/**
* 往串口发送数据
* @param serialPort 串口对象
* @param order 待发送数据
* @throws SendDataToSerialPortFailure 向串口发送数据失败
* @throws SerialPortOutputStreamCloseFailure 关闭串口对象的输出流出错
*/
public static void sendToPort(SerialPort serialPort, byte[] order) throws SendDataToSerialPortFailure, SerialPortOutputStreamCloseFailure {
OutputStream out = null;
try {
out = serialPort.getOutputStream();
out.write(order);
out.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new SendDataToSerialPortFailure();
} finally {
try {
if (out != null) {
out.close();
out = null;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new SerialPortOutputStreamCloseFailure();
}
}
}
/**
* 从串口读取数据
* @param serialPort 当前已建立连接的SerialPort对象
* @return 读取到的数据
* @throws ReadDataFromSerialPortFailure 从串口读取数据时出错
* @throws SerialPortInputStreamCloseFailure 关闭串口对象输入流出错
*/
public static byte[] readFromPort(SerialPort serialPort) throws ReadDataFromSerialPortFailure, SerialPortInputStreamCloseFailure {
InputStream in = null;
byte[] bytes = null;
try {
in = serialPort.getInputStream();
int bufflenth = in.available(); //获取buffer里的数据长度
while (bufflenth != 0) {
bytes = new byte[bufflenth]; //初始化byte数组为buffer中数据的长度
in.read(bytes);
bufflenth = in.available();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ReadDataFromSerialPortFailure();
} finally {
try {
if (in != null) {
in.close();
in = null;
}
} catch(IOException e) {
throw new SerialPortInputStreamCloseFailure();
}
}
return bytes;
}
/**
* 添加监听器
* @param port 串口对象
* @param listener 串口监听器
* @throws TooManyListeners 监听类对象过多
*/
public static void addListener(SerialPort port, SerialPortEventListener listener) throws TooManyListeners {
try {
//给串口添加监听器
port.addEventListener(listener);
//设置当有数据到达时唤醒监听接收线程
port.notifyOnDataAvailable(true);
//设置当通信中断时唤醒中断线程
port.notifyOnBreakInterrupt(true);
} catch (TooManyListenersException e) {
throw new TooManyListeners();
}
}
}Note: The Exceptions thrown in this class of methods are all my custom Exceptions. The reason for doing this is to facilitate corresponding processing in the main program. One of the Exceptions is posted below for everyone. Make the following explanation:
(Note that all my custom Exceptions are placed in the serialException package)
package serialException;
public class SerialPortParameterFailure extends Exception {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public SerialPortParameterFailure() {}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "设置串口参数失败!打开串口操作未完成!";
}
}I have overridden its toString() method for each custom Exception class. , so that the main program can print the corresponding error message after catching the Exception
There is also a class in the serialException package that specifically extracts the error information in the received Exception object, converts it into a string, and returns it. The code is as follows:
package serialException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.StringWriter;
/**
* 负责将传入的Exception中的错误信息提取出来并转换成字符串;
* @author zhong
*
*/
public class ExceptionWriter {
/**
* 将Exception中的错误信息封装到字符串中并返回该字符串
* @param e 包含错误的Exception
* @return 错误信息字符串
*/
public static String getErrorInfoFromException(Exception e) {
StringWriter sw = null;
PrintWriter pw = null;
try {
sw = new StringWriter();
pw = new PrintWriter(sw);
e.printStackTrace(pw);
return "\r\n" + sw.toString() + "\r\n";
} catch (Exception e2) {
return "出错啦!未获取到错误信息,请检查后重试!";
} finally {
try {
if (pw != null) {
pw.close();
}
if (sw != null) {
sw.close();
}
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}Four:
Usage of the main program class. Client.java contains the entry address of the program (main method). Its function is to display a welcome interface and call DataView. This java class performs actual serial port data display.
Client.java code is as follows:
package serialPort;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.Font;
import java.awt.Frame;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.GridLayout;
import java.awt.Image;
import java.awt.Label;
import java.awt.Panel;
import java.awt.Toolkit;
import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
import serialException.ExceptionWriter;
/**
* 主程序
* @author zhong
*
*/
public class Client extends Frame{
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* 程序界面宽度
*/
public static final int WIDTH = 800;
/**
* 程序界面高度
*/
public static final int HEIGHT = 620;
/**
* 程序界面出现位置(横坐标)
*/
public static final int LOC_X = 200;
/**
* 程序界面出现位置(纵坐标)
*/
public static final int LOC_Y = 70;
Color color = Color.WHITE;
Image offScreen = null; //用于双缓冲
//设置window的icon(这里我自定义了一下Windows窗口的icon图标,因为实在觉得哪个小咖啡图标不好看 = =)
Toolkit toolKit = getToolkit();
Image icon = toolKit.getImage(Client.class.getResource("computer.png"));
//持有其他类
DataView dataview = new DataView(this); //主界面类(显示监控数据主面板)
/**
* 主方法
* @param args //
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Client().launchFrame();
}
/**
* 显示主界面
*/
public void launchFrame() {
this.setBounds(LOC_X, LOC_Y, WIDTH, HEIGHT); //设定程序在桌面出现的位置
this.setTitle("CDIO工程项目"); //设置程序标题
this.setIconImage(icon);
this.setBackground(Color.white); //设置背景色
this.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
//添加对窗口状态的监听
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent arg0) {
//当窗口关闭时
System.exit(0); //退出程序
}
});
this.addKeyListener(new KeyMonitor()); //添加键盘监听器
this.setResizable(false); //窗口大小不可更改
this.setVisible(true); //显示窗口
new Thread(new RepaintThread()).start(); //开启重画线程
}
/**
* 画出程序界面各组件元素
*/
public void paint(Graphics g) {
Color c = g.getColor();
g.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑", Font.BOLD, 40));
g.setColor(Color.black);
g.drawString("欢迎使用上位机实时监控系统", 45, 190);
g.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑", Font.ITALIC, 26));
g.setColor(Color.BLACK);
g.drawString("Version:1.0 Powered By:ZhongLei", 280, 260);
g.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑", Font.BOLD, 30));
g.setColor(color);
g.drawString("————点击Enter键进入主界面————", 100, 480);
//使文字 "————点击Enter键进入主界面————" 黑白闪烁
if (color == Color.WHITE) color = Color.black;
else if (color == color.BLACK) color = Color.white;
}
/**
* 双缓冲方式重画界面各元素组件
*/
public void update(Graphics g) {
if (offScreen == null) offScreen = this.createImage(WIDTH, HEIGHT);
Graphics gOffScreen = offScreen.getGraphics();
Color c = gOffScreen.getColor();
gOffScreen.setColor(Color.white);
gOffScreen.fillRect(0, 0, WIDTH, HEIGHT); //重画背景画布
this.paint(gOffScreen); //重画界面元素
gOffScreen.setColor(c);
g.drawImage(offScreen, 0, 0, null); //将新画好的画布“贴”在原画布上
}
/*
* 内部类形式实现对键盘事件的监听
*/
private class KeyMonitor extends KeyAdapter {
public void keyReleased(KeyEvent e) {
int keyCode = e.getKeyCode();
if (keyCode == KeyEvent.VK_ENTER) { //当监听到用户敲击键盘enter键后执行下面的操作
setVisible(false); //隐去欢迎界面
dataview.setVisible(true); //显示监测界面
dataview.dataFrame(); //初始化监测界面
}
}
}
/*
* 重画线程(每隔250毫秒重画一次)
*/
private class RepaintThread implements Runnable {
public void run() {
while(true) {
repaint();
try {
Thread.sleep(250);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
//重画线程出错抛出异常时创建一个Dialog并显示异常详细信息
String err = ExceptionWriter.getErrorInfoFromException(e);
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, err, "错误", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE);
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
}
}Running screenshot:
Note: During the actual running process, the bottom "Click the Enter key to enter the main interface" has a flash and a flash. The effect of flickering (is achieved by redrawing the interface every once in a while, so that this sentence appears alternately in white and black). The double buffering method is helpful to solve the problem of interface flickering during redrawing (if the double buffering method is not used It is equivalent to drawing new things bit by bit on the old interface every time you redraw, while double buffering essentially draws a new interface picture directly in the memory, and then directly overwrites it with the new interface at once. Remove the old interface)

DataView.java code is as follows: (This class is used to display serial port data in real time)
Simple description:
The hardware device sends data to the computer through the serial port at regular intervals. After the serial port tool is successfully connected to the hardware device and adds monitoring, it will parse the data and update the interface each time it receives data;
You are using The requirements may be different from mine. This class is for reference only. In actual use, you may need to re-create the data display interface and data analysis method
package serialPort;
import java.awt.Button;
import java.awt.Choice;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Font;
import java.awt.Frame;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Image;
import java.awt.Label;
import java.awt.Toolkit;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.TooManyListenersException;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
import gnu.io.SerialPort;
import gnu.io.SerialPortEvent;
import gnu.io.SerialPortEventListener;
import serialException.*;
/**
* 监测数据显示类
* @author Zhong
*
*/
public class DataView extends Frame {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
Client client = null;
private List<String> commList = null; //保存可用端口号
private SerialPort serialPort = null; //保存串口对象
private Font font = new Font("微软雅黑", Font.BOLD, 25);
private Label tem = new Label("暂无数据", Label.CENTER); //温度
private Label hum = new Label("暂无数据", Label.CENTER); //湿度
private Label pa = new Label("暂无数据", Label.CENTER); //压强
private Label rain = new Label("暂无数据", Label.CENTER); //雨量
private Label win_sp = new Label("暂无数据", Label.CENTER); //风速
private Label win_dir = new Label("暂无数据", Label.CENTER); //风向
private Choice commChoice = new Choice(); //串口选择(下拉框)
private Choice bpsChoice = new Choice(); //波特率选择
private Button openSerialButton = new Button("打开串口");
Image offScreen = null; //重画时的画布
//设置window的icon
Toolkit toolKit = getToolkit();
Image icon = toolKit.getImage(DataView.class.getResource("computer.png"));
/**
* 类的构造方法
* @param client
*/
public DataView(Client client) {
this.client = client;
commList = SerialTool.findPort(); //程序初始化时就扫描一次有效串口
}
/**
* 主菜单窗口显示;
* 添加Label、按钮、下拉条及相关事件监听;
*/
public void dataFrame() {
this.setBounds(client.LOC_X, client.LOC_Y, client.WIDTH, client.HEIGHT);
this.setTitle("CDIO工程项目");
this.setIconImage(icon);
this.setBackground(Color.white);
this.setLayout(null);
this.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent arg0) {
if (serialPort != null) {
//程序退出时关闭串口释放资源
SerialTool.closePort(serialPort);
}
System.exit(0);
}
});
tem.setBounds(140, 103, 225, 50);
tem.setBackground(Color.black);
tem.setFont(font);
tem.setForeground(Color.white);
add(tem);
hum.setBounds(520, 103, 225, 50);
hum.setBackground(Color.black);
hum.setFont(font);
hum.setForeground(Color.white);
add(hum);
pa.setBounds(140, 193, 225, 50);
pa.setBackground(Color.black);
pa.setFont(font);
pa.setForeground(Color.white);
add(pa);
rain.setBounds(520, 193, 225, 50);
rain.setBackground(Color.black);
rain.setFont(font);
rain.setForeground(Color.white);
add(rain);
win_sp.setBounds(140, 283, 225, 50);
win_sp.setBackground(Color.black);
win_sp.setFont(font);
win_sp.setForeground(Color.white);
add(win_sp);
win_dir.setBounds(520, 283, 225, 50);
win_dir.setBackground(Color.black);
win_dir.setFont(font);
win_dir.setForeground(Color.white);
add(win_dir);
//添加串口选择选项
commChoice.setBounds(160, 397, 200, 200);
//检查是否有可用串口,有则加入选项中
if (commList == null || commList.size()<1) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "没有搜索到有效串口!", "错误", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE);
}
else {
for (String s : commList) {
commChoice.add(s);
}
}
add(commChoice);
//添加波特率选项
bpsChoice.setBounds(526, 396, 200, 200);
bpsChoice.add("1200");
bpsChoice.add("2400");
bpsChoice.add("4800");
bpsChoice.add("9600");
bpsChoice.add("14400");
bpsChoice.add("19200");
bpsChoice.add("115200");
add(bpsChoice);
//添加打开串口按钮
openSerialButton.setBounds(250, 490, 300, 50);
openSerialButton.setBackground(Color.lightGray);
openSerialButton.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑", Font.BOLD, 20));
openSerialButton.setForeground(Color.darkGray);
add(openSerialButton);
//添加打开串口按钮的事件监听
openSerialButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
//获取串口名称
String commName = commChoice.getSelectedItem();
//获取波特率
String bpsStr = bpsChoice.getSelectedItem();
//检查串口名称是否获取正确
if (commName == null || commName.equals("")) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "没有搜索到有效串口!", "错误", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE);
}
else {
//检查波特率是否获取正确
if (bpsStr == null || bpsStr.equals("")) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "波特率获取错误!", "错误", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE);
}
else {
//串口名、波特率均获取正确时
int bps = Integer.parseInt(bpsStr);
try {
//获取指定端口名及波特率的串口对象
serialPort = SerialTool.openPort(commName, bps);
//在该串口对象上添加监听器
SerialTool.addListener(serialPort, new SerialListener());
//监听成功进行提示
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "监听成功,稍后将显示监测数据!", "提示", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE);
} catch (SerialPortParameterFailure | NotASerialPort | NoSuchPort | PortInUse | TooManyListeners e1) {
//发生错误时使用一个Dialog提示具体的错误信息
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, e1, "错误", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE);
}
}
}
}
});
this.setResizable(false);
new Thread(new RepaintThread()).start(); //启动重画线程
}
/**
* 画出主界面组件元素
*/
public void paint(Graphics g) {
Color c = g.getColor();
g.setColor(Color.black);
g.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑", Font.BOLD, 25));
g.drawString(" 温度: ", 45, 130);
g.setColor(Color.black);
g.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑", Font.BOLD, 25));
g.drawString(" 湿度: ", 425, 130);
g.setColor(Color.black);
g.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑", Font.BOLD, 25));
g.drawString(" 压强: ", 45, 220);
g.setColor(Color.black);
g.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑", Font.BOLD, 25));
g.drawString(" 雨量: ", 425, 220);
g.setColor(Color.black);
g.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑", Font.BOLD, 25));
g.drawString(" 风速: ", 45, 310);
g.setColor(Color.black);
g.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑", Font.BOLD, 25));
g.drawString(" 风向: ", 425, 310);
g.setColor(Color.gray);
g.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑", Font.BOLD, 20));
g.drawString(" 串口选择: ", 45, 410);
g.setColor(Color.gray);
g.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑", Font.BOLD, 20));
g.drawString(" 波特率: ", 425, 410);
}
/**
* 双缓冲方式重画界面各元素组件
*/
public void update(Graphics g) {
if (offScreen == null) offScreen = this.createImage(Client.WIDTH, Client.HEIGHT);
Graphics gOffScreen = offScreen.getGraphics();
Color c = gOffScreen.getColor();
gOffScreen.setColor(Color.white);
gOffScreen.fillRect(0, 0, Client.WIDTH, Client.HEIGHT); //重画背景画布
this.paint(gOffScreen); //重画界面元素
gOffScreen.setColor(c);
g.drawImage(offScreen, 0, 0, null); //将新画好的画布“贴”在原画布上
}
/*
* 重画线程(每隔30毫秒重画一次)
*/
private class RepaintThread implements Runnable {
public void run() {
while(true) {
//调用重画方法
repaint();
//扫描可用串口
commList = SerialTool.findPort();
if (commList != null && commList.size()>0) {
//添加新扫描到的可用串口
for (String s : commList) {
//该串口名是否已存在,初始默认为不存在(在commList里存在但在commChoice里不存在,则新添加)
boolean commExist = false;
for (int i=0; i<commChoice.getItemCount(); i++) {
if (s.equals(commChoice.getItem(i))) {
//当前扫描到的串口名已经在初始扫描时存在
commExist = true;
break;
}
}
if (commExist) {
//当前扫描到的串口名已经在初始扫描时存在,直接进入下一次循环
continue;
}
else {
//若不存在则添加新串口名至可用串口下拉列表
commChoice.add(s);
}
}
//移除已经不可用的串口
for (int i=0; i<commChoice.getItemCount(); i++) {
//该串口是否已失效,初始默认为已经失效(在commChoice里存在但在commList里不存在,则已经失效)
boolean commNotExist = true;
for (String s : commList) {
if (s.equals(commChoice.getItem(i))) {
commNotExist = false;
break;
}
}
if (commNotExist) {
//System.out.println("remove" + commChoice.getItem(i));
commChoice.remove(i);
}
else {
continue;
}
}
}
else {
//如果扫描到的commList为空,则移除所有已有串口
commChoice.removeAll();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(30);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
String err = ExceptionWriter.getErrorInfoFromException(e);
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, err, "错误", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE);
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 以内部类形式创建一个串口监听类
* @author zhong
*
*/
private class SerialListener implements SerialPortEventListener {
/**
* 处理监控到的串口事件
*/
public void serialEvent(SerialPortEvent serialPortEvent) {
switch (serialPortEvent.getEventType()) {
case SerialPortEvent.BI: // 10 通讯中断
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "与串口设备通讯中断", "错误", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE);
break;
case SerialPortEvent.OE: // 7 溢位(溢出)错误
case SerialPortEvent.FE: // 9 帧错误
case SerialPortEvent.PE: // 8 奇偶校验错误
case SerialPortEvent.CD: // 6 载波检测
case SerialPortEvent.CTS: // 3 清除待发送数据
case SerialPortEvent.DSR: // 4 待发送数据准备好了
case SerialPortEvent.RI: // 5 振铃指示
case SerialPortEvent.OUTPUT_BUFFER_EMPTY: // 2 输出缓冲区已清空
break;
case SerialPortEvent.DATA_AVAILABLE: // 1 串口存在可用数据
//System.out.println("found data");
byte[] data = null;
try {
if (serialPort == null) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "串口对象为空!监听失败!", "错误", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE);
}
else {
data = SerialTool.readFromPort(serialPort); //读取数据,存入字节数组
//System.out.println(new String(data));
// 自定义解析过程,你在实际使用过程中可以按照自己的需求在接收到数据后对数据进行解析
if (data == null || data.length < 1) { //检查数据是否读取正确
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "读取数据过程中未获取到有效数据!请检查设备或程序!", "错误", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE);
System.exit(0);
}
else {
String dataOriginal = new String(data); //将字节数组数据转换位为保存了原始数据的字符串
String dataValid = ""; //有效数据(用来保存原始数据字符串去除最开头*号以后的字符串)
String[] elements = null; //用来保存按空格拆分原始字符串后得到的字符串数组
//解析数据
if (dataOriginal.charAt(0) == '*') { //当数据的第一个字符是*号时表示数据接收完成,开始解析
dataValid = dataOriginal.substring(1);
elements = dataValid.split(" ");
if (elements == null || elements.length < 1) { //检查数据是否解析正确
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "数据解析过程出错,请检查设备或程序!", "错误", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE);
System.exit(0);
}
else {
try {
//更新界面Label值
/*for (int i=0; i<elements.length; i++) {
System.out.println(elements[i]);
}*/
//System.out.println("win_dir: " + elements[5]);
tem.setText(elements[0] + " ℃");
hum.setText(elements[1] + " %");
pa.setText(elements[2] + " hPa");
rain.setText(elements[3] + " mm");
win_sp.setText(elements[4] + " m/s");
win_dir.setText(elements[5] + " °");
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "数据解析过程出错,更新界面数据失败!请检查设备或程序!", "错误", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE);
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
}
}
} catch (ReadDataFromSerialPortFailure | SerialPortInputStreamCloseFailure e) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, e, "错误", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE);
System.exit(0); //发生读取错误时显示错误信息后退出系统
}
break;
}
}
}
}Run screenshot:
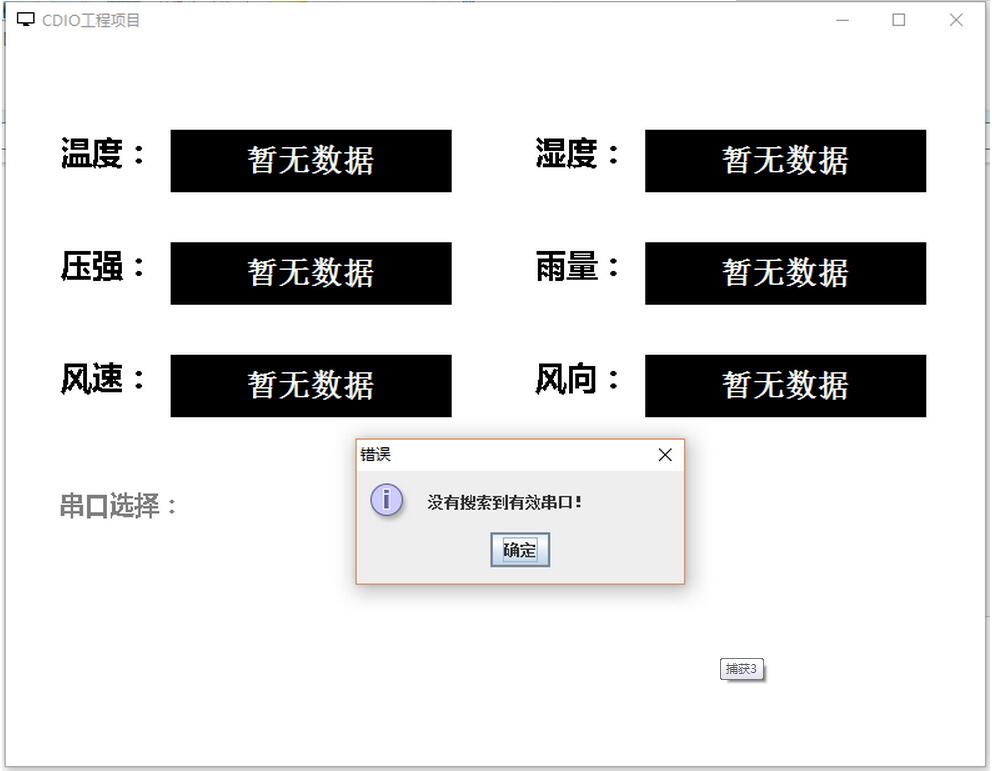
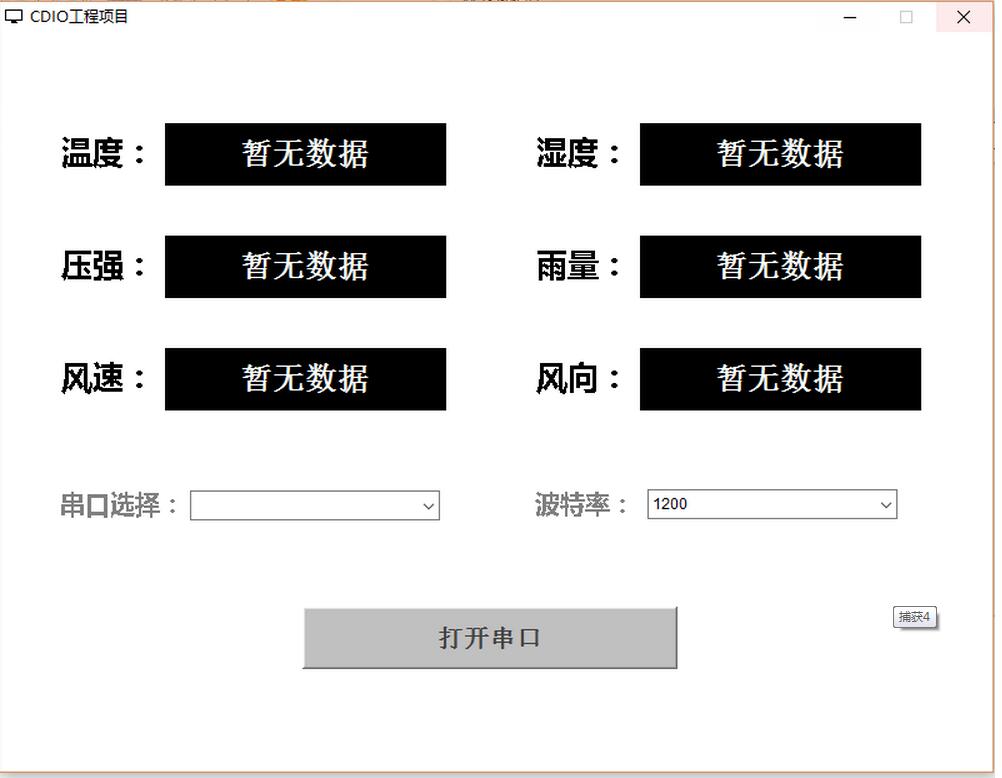
The above is the entire content of this article. I hope it will be helpful to everyone's learning. I also hope that everyone will support the PHP Chinese website.
For more articles related to writing serial communication tools based on Java, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- How to Inject Dependencies into Self-Instantiated Objects in Spring?
- Where Should You Place Your JFrames?
- Implicit vs. Explicit Waits in Selenium-WebDriver: Which Should You Choose?
- How to Dynamically Add Files to the Java Classpath at Runtime?
- API Debugging: Best Practices for Fetching Test Data from a Database

