Home >Java >javaTutorial >Detailed explanation of http communication using JAVA
Detailed explanation of http communication using JAVA
- 高洛峰Original
- 2017-01-05 14:26:032350browse
Http Communication Overview
Http communication mainly has two methods: POST method and GET method. The former sends data to the server through Http message entities, which has high security and no limit on data transmission size. The latter passes the query string of the URL to the server parameters and displays them in the browser address bar in plain text. It has poor confidentiality and can transmit up to 2048 characters. . But GET requests are not useless - GET requests are mostly used for querying (reading resources) and are highly efficient. POST requests are used for registration, login and other operations with high security and writing data to the database.
In addition to POST and GET, there are other ways of http communication! Please see the http request method
Preparation before encoding
Before encoding, we first create a Servlet that receives the client's parameters (name and age) and responds to the client.
@WebServlet(urlPatterns={"/demo.do"})
public class DemoServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String age = request.getParameter("age");
PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter();
pw.print("您使用GET方式请求该Servlet。<br />" + "name = " + name + ",age = " + age);
pw.flush();
pw.close();
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String age = request.getParameter("age");
PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter();
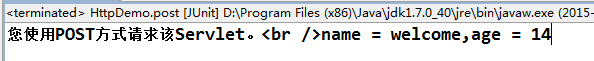
pw.print("您使用POST方式请求该Servlet。<br />" + "name = " + name + ",age = " + age);
pw.flush();
pw.close();
}
}Use JDK to implement http communication
Use URLConnection to implement GET request
Instantiate a java.net.URL object;
Through the openConnection() method of the URL object Get a java.net.URLConnection;
Get the input stream through the getInputStream() method of the URLConnection object;
Read the input stream;
Close the resource.
public void get() throws Exception{
URL url = new URL("http://127.0.0.1/http/demo.do?name=Jack&age=10");
URLConnection urlConnection = url.openConnection(); // 打开连接
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(urlConnection.getInputStream(),"utf-8")); // 获取输入流
String line = null;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(line + "\n");
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
Use HttpURLConnection to implement POST requests
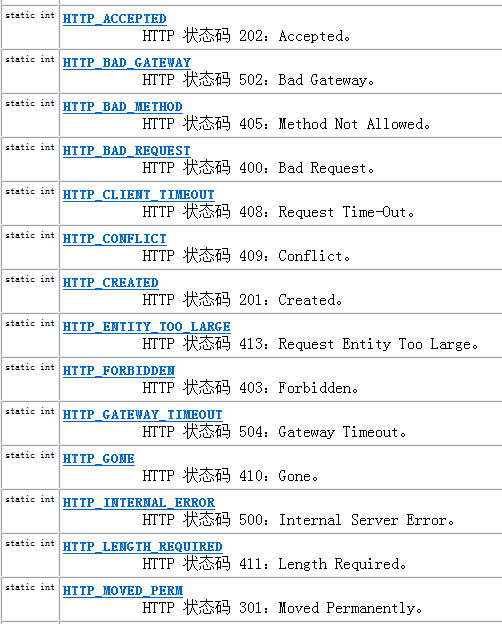
java.net.HttpURLConnection is a subclass of java.net.URL, providing more information about http Operations (getXXX and setXXX methods). This class defines a series of HTTP status codes:
public void post() throws IOException{
URL url = new URL("http://127.0.0.1/http/demo.do");
HttpURLConnection httpURLConnection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
httpURLConnection.setDoInput(true);
httpURLConnection.setDoOutput(true); // 设置该连接是可以输出的
httpURLConnection.setRequestMethod("POST"); // 设置请求方式
httpURLConnection.setRequestProperty("charset", "utf-8");
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(httpURLConnection.getOutputStream()));
pw.write("name=welcome"); // 向连接中输出数据(相当于发送数据给服务器)
pw.write("&age=14");
pw.flush();
pw.close();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(httpURLConnection.getInputStream(),"utf-8"));
String line = null;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { // 读取数据
sb.append(line + "\n");
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId> <artifactId>httpclient</artifactId> <version>4.3.6</version> </dependency>GET request
public void httpclientGet() throws Exception{
// 创建HttpClient对象
HttpClient client = HttpClients.createDefault();
// 创建GET请求(在构造器中传入URL字符串即可)
HttpGet get = new HttpGet("http://127.0.0.1/http/demo.do?name=admin&age=40");
// 调用HttpClient对象的execute方法获得响应
HttpResponse response = client.execute(get);
// 调用HttpResponse对象的getEntity方法得到响应实体
HttpEntity httpEntity = response.getEntity();
// 使用EntityUtils工具类得到响应的字符串表示
String result = EntityUtils.toString(httpEntity,"utf-8");
System.out.println(result);
}
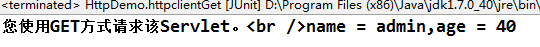
public void httpclientPost() throws Exception{
// 创建HttpClient对象
HttpClient client = HttpClients.createDefault();
// 创建POST请求
HttpPost post = new HttpPost("http://127.0.0.1/http/demo.do");
// 创建一个List容器,用于存放基本键值对(基本键值对即:参数名-参数值)
List<BasicNameValuePair> parameters = new ArrayList<>();
parameters.add(new BasicNameValuePair("name", "张三"));
parameters.add(new BasicNameValuePair("age", "25"));
// 向POST请求中添加消息实体
post.setEntity(new UrlEncodedFormEntity(parameters, "utf-8"));
// 得到响应并转化成字符串
HttpResponse response = client.execute(post);
HttpEntity httpEntity = response.getEntity();
String result = EntityUtils.toString(httpEntity,"utf-8");
System.out.println(result);
}


