Set up an FTP server in Linux
- 高洛峰Original
- 2016-12-20 09:33:461385browse
Set up an ftp server in Linux for two working groups to store files. Disable anonymity. The first team uses the ftp account: ftp1, and the working directory is: /var/ftp/ftp1; the second team uses ftp2, and the working directory is: /var/ftp/ftp2.
The two groups cannot access each other’s files, and users need to be restricted from leaving their working directories.
【Implementation steps】
1. Check the installation of vsftpd server
After entering the terminal as root (if you enter the terminal with other accounts, you can use su root to enter the password and enter root mode). After that, enter the following command in the terminal command window. Verification: # rpm –qa | grep vsftpd. If the result displays "vsftpd-1.1.3-8", it means that the vsftpd server has been installed on the system. If there is no reply, it means it is not installed in the system.

The system CD of version 2.rhel contains the vsftpd installation package, so the next step is to mount the system CD to /media for easy retrieval.
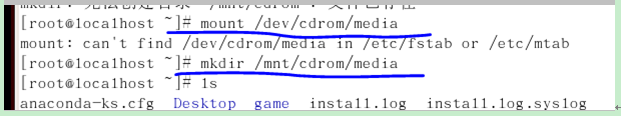
3. The above screenshot shows that the vsftpd server is not installed in this system, so use the rpm command to install it.
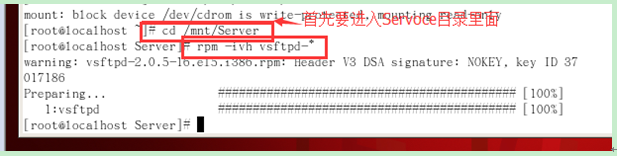
The command to install vsftpd in the terminal command window: #rpm -ivh vsftpd-1.1.3-8.i386.rpm.
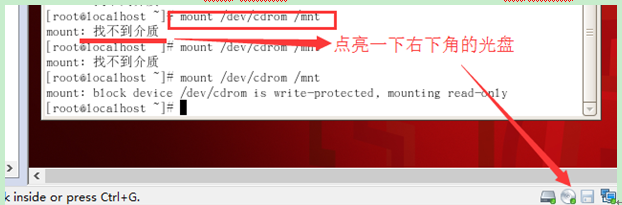
(1) First mount the optical drive, there is rpm in the /mnt/cdrom/Server directory, rpm -ivh vsftpd*
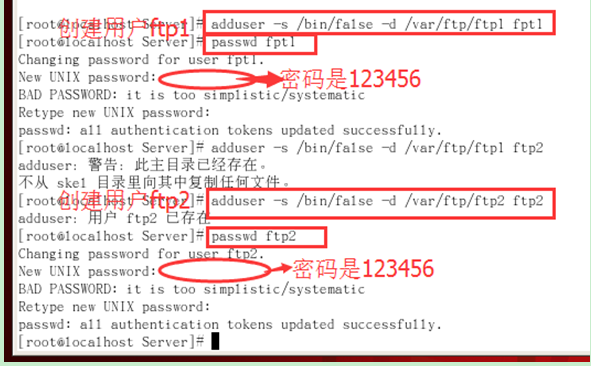
4. Create a user
(1) First start the service
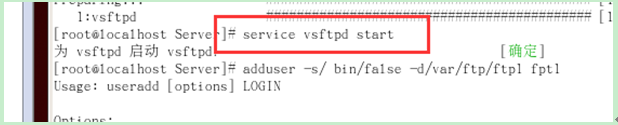
(2) Create two users
5.vsftpd configuration
After installation, there will be three configuration files in the /etc/vsftpd/ path.
vsftpd.conf: Main configuration file
ftpusers: Specify which users cannot access the FTP server. The users here include some important users including root.
user_list: Whether the specified user can access the ftp server, determine whether the user in the configuration can access the userlist_deny configuration in the vsftpd.conf file, userlist_enable=YES, userlist_deny=YES, userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd/user_list This Three configurations allow users in the file to access FTP.
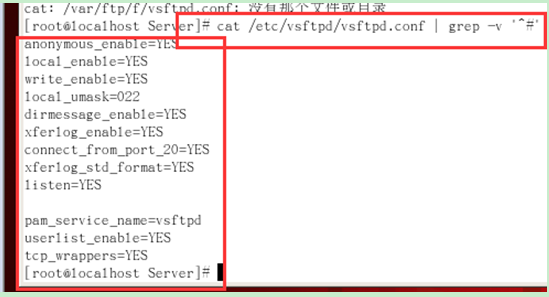
(1) View the default configuration of the main configuration file:
(Use: cat /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf | grep -v '^#';)
(2) Modify the configuration file:
After logging in to ftp, you will find that the user can access other directories and has the permissions of the mpsp group. This is not allowed. We need to control the user's access scope to his home directory. The method is as follows:
a. vi /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf Enter the ftp configuration file directory and edit this file,
b.
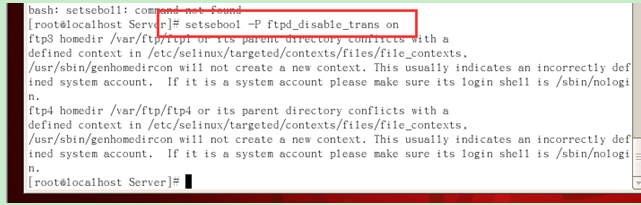
Find #chroot_list_enable=YES, delete the # sign in front, which means it is enabled This restricted function;
Find chroot_list_file: chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd/chroot_list, delete the # sign in front, indicating that this restricted function is enabled; add chroot_local_use=NO
(press i after entering the edit box to start editing)
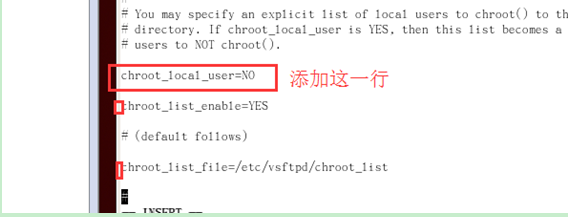
c. After entering the configuration file, add the following three lines at the end:
① userlist_enable=YES
.
d. Ban anonymous users Login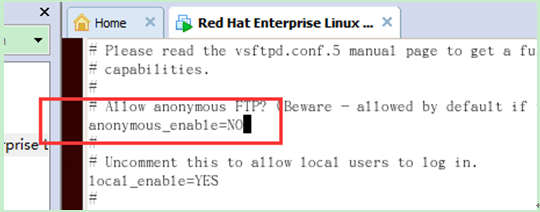
(After editing, press esc and use ":wq" to save and exit)
e. Edit some files
① Find the vsftpd.chroot_list file in the etc directory and enter the editing state
Add what you want Restricted user names, one user per line, such as ftp2
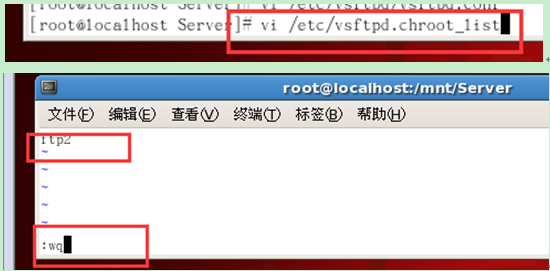
(After editing, press esc and use ":wq" to save and exit)
② Enter the vsftpd directory, find vsftpd.user_list, type ftp11, which means ftp11 is allowed Log in to the ftp server
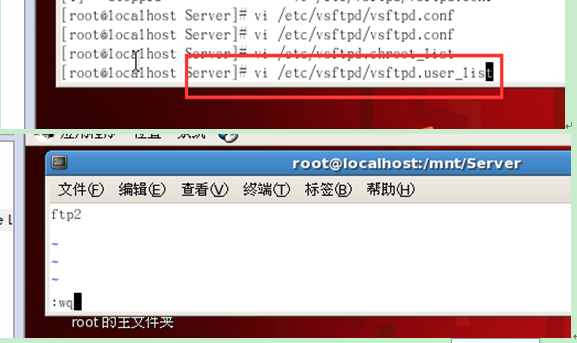
(After editing, press esc and use ":wq" to save and exit)
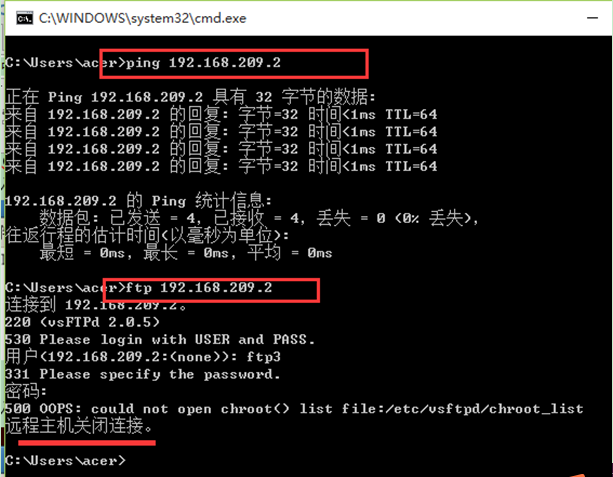
Then on this machine, through the console, use ftp1 to access the system through ftp, the user successfully logged in, and successfully Are restricted to their own home directory and cannot access other directories.
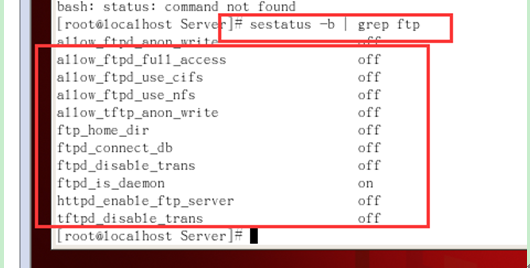
Create 2 users, ftp1 and ftp2 in this order. P t View FTP status seastatus -b | GREP FTP:
Then enter: