JavaWeb learning summary_Servlet development
- 高洛峰Original
- 2016-12-02 16:25:532084browse
1. Introduction to Servlet
2. The running process of Servlet
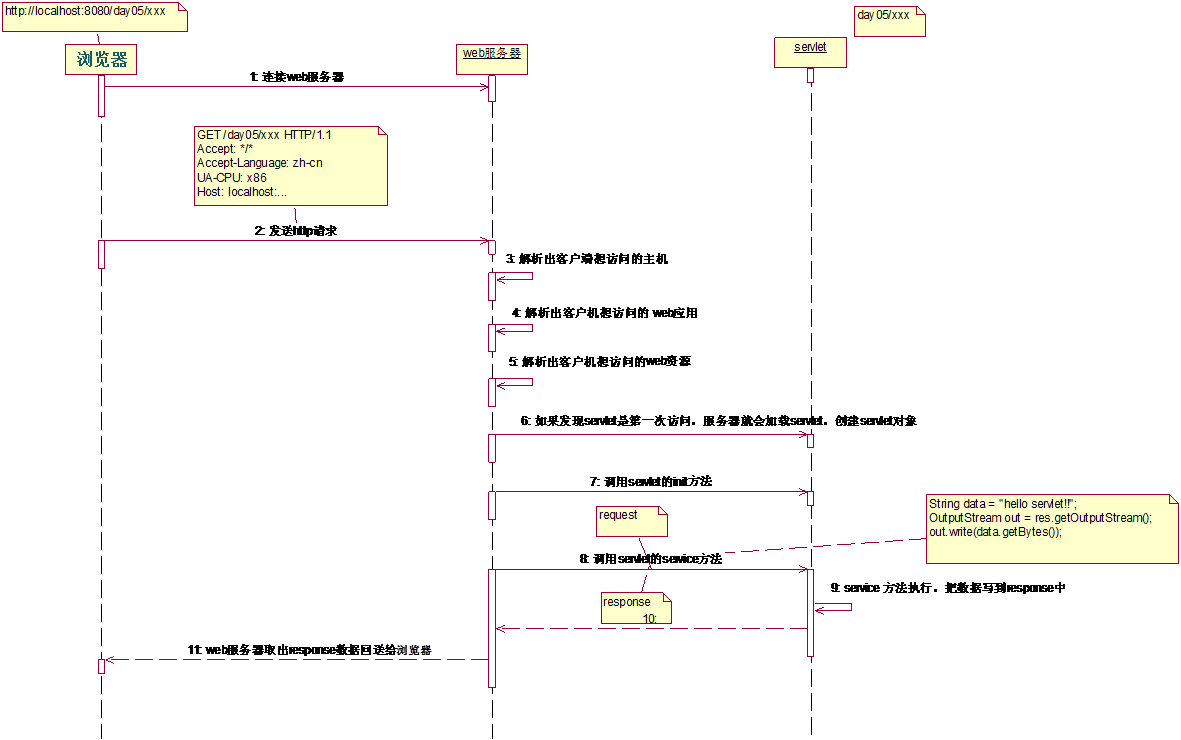
The Servlet program is called by the Web server. After the web server receives the client's Servlet access request:
The WEB server first checks whether it has been loaded and created an instance of the Servlet object. If yes, go to step 4 directly, otherwise go to step 2.
Load and create the init() method of the Servlet instance object
Call the init() method of the Servlet instance object
Create an HttpServletRequest object used to encapsulate the HTTP request message and an HttpServletResponse object representing the Http corresponding message, and then call Servlet's service() method, and the request and response objects are passed in as parameters.
Before the Web application is stopped or restarted, the Servlet engine will uninstall the Servlet and call the Servlet's destroy() method
3. Servlet call graph
4. Servlet access URL mapping configuration
Same Servlet Can be mapped to multiple URLs, that is, the setting value of the
<servlet>
<description></description>
<display-name>ServletDemo1</display-name>
<servlet-name>ServletDemo1</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.atguigu.servlet.ServletDemo1</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<!-- 同一个servlet可以映射到多个url -->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ServletDemo1</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/servletDemo1</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ServletDemo1</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/1.html</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ServletDemo1</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/2.htm</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ServletDemo1</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/3.htm</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
