A module is an independent software unit, consisting of models, views, controllers and other supporting components. End users can access the controllers of installed modules in the application body. The module is treated as a small application body, which is different from the application body. The important thing is that modules cannot be deployed individually and must belong to an application subject.
Create module
The module is organized into a directory called [[yiibaseModule::basePath|base path]]. In this directory, there are subdirectories such as controllers, models, and views for corresponding controllers, models, views, and The rest of the code is very similar to the application. The following example shows the directory structure of a model:
forum/
Module.php 模块类文件
controllers/ 包含控制器类文件
DefaultController.php default 控制器类文件
models/ 包含模型类文件
views/ 包含控制器视图文件和布局文件
layouts/ 包含布局文件
default/ 包含DefaultController控制器视图文件
index.php index视图文件Module class
Each module has a module class that inherits [[yiibaseModule]], and this class file is placed directly in the module's [[yiibaseModule::basePath|base path] ] directory and can be loaded automatically. When a module is accessed, a unique instance of the module class is created similar to the application body instance. The module instance is used to help the code within the module share data and components.
The following example roughly defines a module class:
namespace app\modules\forum; class Module extends \yii\base\Module { public function init() { parent::init(); $this->params['foo'] = 'bar';
// ... 其他初始化代码 ... } }If the init() method contains a lot of code to initialize module properties, they can be saved in the configuration and loaded using the following code in init():
public function init() { parent::init(); // 从config.php加载配置来初始化模块 \Yii::configure($this, require(__DIR__ . '/config.php')); }config.php configuration file It may contain the following content, similar to the application main configuration.
<?php return [ 'components' => [ // list of component configurations ], 'params' => [ // list of parameters ], ];
Controllers in modules
When creating a module's controller, the convention is to place the controller class in the controllers sub-namespace of the module class namespace, which also means Place the controller class files in the controllers subdirectory in the module [[yiibaseModule::basePath|base path]] directory. For example, to create a post controller in the forum module in the previous section, you should declare the controller class as follows:
namespace app\modules\forum\controllers; use yii\web\Controller; class PostController extends Controller { // ... }You can configure the [[yiibaseModule::controllerNamespace]] attribute to customize the namespace of the controller class. If some controllers No longer in this namespace, you can configure the [[yiibaseModule::controllerMap]] attribute to make them accessible, similar to what is done in the application body configuration.
Views in the module
The views should be placed in the views directory under the directory corresponding to [[yiibaseModule::basePath|base path]] of the module. The view files corresponding to the controllers in the module should be placed under the views/ControllerID directory. Where ControllerID corresponds to the controller ID. For example, if For example, assuming that the controller class is PostController, the directory corresponds to the views/post directory under the module [[yiibaseModule::basePath|base path]] directory.
Modules can specify layout, which is used in the module's controller view rendering. The layout file is placed in the views/layouts directory by default. You can configure the [[yiibaseModule::layout]] attribute to specify the layout name. If the layout attribute name is not configured, the application layout will be used by default.
Using modules
To use modules in an application, you only need to add the module to the list of [[yiibaseApplication::modules|modules]] attributes of the application body configuration. The application body configuration of the following code uses the forum module:
[ 'modules' => [ 'forum' => [ 'class' => 'app\modules\forum\Module', // ... 模块其他配置 ... ], ], ]The
[[yiibaseApplication::modules|modules]] attribute uses a module configuration array. Each array key is the module ID, which identifies the unique module in the application. The value of the array is the configuration used to create the module.
Routing
Similar to accessing application controllers, routing is also used to address the controller in the module. The route for the controller in the module must start with the module ID, followed by the controller ID and operation ID. For example, assuming that the application uses a module named forum, the route forum/post/index represents the index operation of the post controller in the module. If the route only contains the module ID, the default [[yiibaseModule::defaultRoute]] attribute is used to determine the use. Which controller/action, that is, the routing forum may represent the default controller of the forum module.
Access module
In a module, you may often need to obtain an instance of a module class to access module ID, module parameters, module components, etc. You can use the following statement to obtain it:
$module = MyModuleClass::getInstance();
where MyModuleClass corresponds to the module class you want, The getInstance() method returns the currently requested module class instance. If the module is not requested, this method will return null. Note that there is no need to manually create a module class, because the manually created one is different from the one automatically created when Yii processes the request.
Supplement: When developing a module, you cannot assume that the module uses a fixed ID, because in the application or other modules, the module may correspond to any ID. In order to obtain the module ID, you should use the above code to obtain the module instance, and then Get the module ID through $module->id.
You can also access module instances using the following methods:
// 获取ID为 "forum" 的模块 $module = \Yii::$app->getModule('forum'); // 获取处理当前请求控制器所属的模块 $module = \Yii::$app->controller->module;
第一种方式仅在你知道模块ID的情况下有效,第二种方式在你知道处理请求的控制器下使用。
一旦获取到模块实例,可访问注册到模块的参数和组件,例如:
$maxPostCount = $module->params['maxPostCount'];
引导启动模块
有些模块在每个请求下都有运行, [[yii\debug\Module|debug]] 模块就是这种, 为此将这种模块加入到应用主体的 [[yii\base\Application::bootstrap|bootstrap]] 属性中。
例如,如下示例的应用主体配置会确保debug模块每次都被加载:
[ 'bootstrap' => [ 'debug', ], 'modules' => [ 'debug' => 'yii\debug\Module', ], ]
模块嵌套
模块可无限级嵌套,也就是说,模块可以包含另一个包含模块的模块,我们称前者为父模块,后者为子模块, 子模块必须在父模块的[[yii\base\Module::modules|modules]]属性中申明,例如:
namespace app\modules\forum; class Module extends \yii\base\Module { public function init() { parent::init(); $this->modules = [ 'admin' => [
// 此处应考虑使用一个更短的命名空间 'class' => 'app\modules\forum\modules\admin\Module', ], ]; } }在嵌套模块中的控制器,它的路由应包含它所有祖先模块的ID,例如forum/admin/dashboard/index代表 在模块forum中子模块admin中dashboard控制器的index操作。
最佳实践
模块在大型项目中常备使用,这些项目的特性可分组,每个组包含一些强相关的特性, 每个特性组可以做成一个模块由特定的开发人员和开发组来开发和维护。
在特性组上,使用模块也是重用代码的好方式,一些常用特性,如用户管理,评论管理,可以开发成模块, 这样在相关项目中非常容易被重用。
 如何使用PHP框架Yii开发一个高可用的云备份系统Jun 27, 2023 am 09:04 AM
如何使用PHP框架Yii开发一个高可用的云备份系统Jun 27, 2023 am 09:04 AM随着云计算技术的不断发展,数据的备份已经成为了每个企业必须要做的事情。在这样的背景下,开发一款高可用的云备份系统尤为重要。而PHP框架Yii是一款功能强大的框架,可以帮助开发者快速构建高性能的Web应用程序。下面将介绍如何使用Yii框架开发一款高可用的云备份系统。设计数据库模型在Yii框架中,数据库模型是非常重要的一部分。因为数据备份系统需要用到很多的表和关
 Yii2 vs Phalcon:哪个框架更适合开发显卡渲染应用?Jun 19, 2023 am 08:09 AM
Yii2 vs Phalcon:哪个框架更适合开发显卡渲染应用?Jun 19, 2023 am 08:09 AM在当前信息时代,大数据、人工智能、云计算等技术已经成为了各大企业关注的热点。在这些技术中,显卡渲染技术作为一种高性能图形处理技术,受到了越来越多的关注。显卡渲染技术被广泛应用于游戏开发、影视特效、工程建模等领域。而对于开发者来说,选择一个适合自己项目的框架,是一个非常重要的决策。在当前的语言中,PHP是一种颇具活力的语言,一些优秀的PHP框架如Yii2、Ph
 php如何使用Yii3框架?May 31, 2023 pm 10:42 PM
php如何使用Yii3框架?May 31, 2023 pm 10:42 PM随着互联网的不断发展,Web应用程序开发的需求也越来越高。对于开发人员而言,开发应用程序需要一个稳定、高效、强大的框架,这样可以提高开发效率。Yii是一款领先的高性能PHP框架,它提供了丰富的特性和良好的性能。Yii3是Yii框架的下一代版本,它在Yii2的基础上进一步优化了性能和代码质量。在这篇文章中,我们将介绍如何使用Yii3框架来开发PHP应用程序。
 Yii框架中的数据查询:高效地访问数据Jun 21, 2023 am 11:22 AM
Yii框架中的数据查询:高效地访问数据Jun 21, 2023 am 11:22 AMYii框架是一个开源的PHPWeb应用程序框架,提供了众多的工具和组件,简化了Web应用程序开发的流程,其中数据查询是其中一个重要的组件之一。在Yii框架中,我们可以使用类似SQL的语法来访问数据库,从而高效地查询和操作数据。Yii框架的查询构建器主要包括以下几种类型:ActiveRecord查询、QueryBuilder查询、命令查询和原始SQL查询
 Symfony vs Yii2:哪个框架更适合开发大型Web应用?Jun 19, 2023 am 10:57 AM
Symfony vs Yii2:哪个框架更适合开发大型Web应用?Jun 19, 2023 am 10:57 AM随着Web应用需求的不断增长,开发者们在选择开发框架方面也越来越有选择的余地。Symfony和Yii2是两个备受欢迎的PHP框架,它们都具有强大的功能和性能,但在面对需要开发大型Web应用时,哪个框架更适合呢?接下来我们将对Symphony和Yii2进行比较分析,以帮助你更好地进行选择。基本概述Symphony是一个由PHP编写的开源Web应用框架,它是建立
 yii如何将对象转化为数组或直接输出为json格式Jan 08, 2021 am 10:13 AM
yii如何将对象转化为数组或直接输出为json格式Jan 08, 2021 am 10:13 AMyii框架:本文为大家介绍了yii将对象转化为数组或直接输出为json格式的方法,具有一定的参考价值,希望能够帮助到大家。
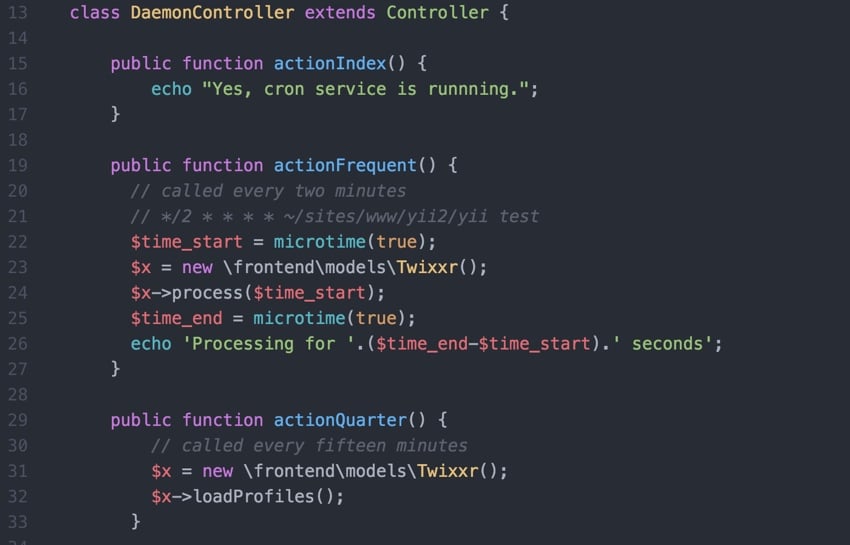 Yii2编程指南:运行Cron服务的方法Sep 01, 2023 pm 11:21 PM
Yii2编程指南:运行Cron服务的方法Sep 01, 2023 pm 11:21 PM如果您问“Yii是什么?”查看我之前的教程:Yii框架简介,其中回顾了Yii的优点,并概述了2014年10月发布的Yii2.0的新增功能。嗯>在这个使用Yii2编程系列中,我将指导读者使用Yii2PHP框架。在今天的教程中,我将与您分享如何利用Yii的控制台功能来运行cron作业。过去,我在cron作业中使用了wget—可通过Web访问的URL来运行我的后台任务。这引发了安全问题并存在一些性能问题。虽然我在我们的启动系列安全性专题中讨论了一些减轻风险的方法,但我曾希望过渡到控制台驱动的命令
 分享10个有趣且实用的Python模块,看看他们的功能吧!Feb 18, 2022 am 10:51 AM
分享10个有趣且实用的Python模块,看看他们的功能吧!Feb 18, 2022 am 10:51 AMPython程序有有许多有助于高效编程的模块和第三方包,了解这些模块的正确使用方法是很重要的,下面本篇文章就来给大家总结分享10个有趣且实用的Python模块,一起看看他们的功能吧!


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor






