Home >Web Front-end >HTML Tutorial >Research on CSS3 selectors
Research on CSS3 selectors
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOriginal
- 2016-09-15 11:15:141044browse
Attribute selector
[title]: Select elements with title attributes
[title='hello']: Select the element whose attribute is title and whose value is hello
[title~='hello']: Select the element whose attribute is title and part of the value is hello. hello needs to be a separate value, separated by spaces
[title*='hello']: The selected attribute is title and it contains the element of hello
[title|='hello']: The selected attribute is title and the value starts with hello and any character followed by - is allowed
[title^='hello']: Any character whose attribute starts with hello
[title$='hello']: Any character whose attribute ends with hello
[title^='hello'][title$='.py']: Select elements whose attributes start with hello and end with .py
Connector
h1~p: Select all p elements of the same level behind the h1 element
p~p: Select all p elements of the same level after the p element, except the first p element
h1+p: Select the first sibling p element after the h1 element
Pseudo class selector
nth series, numbers
nth-child(): Count according to position
nth-of-type(): Count according to type
nth-last-child(): Count from the end according to the position
nth-last-of-type(): Count from the end by type
Use (-n+number) to specify the first few elements to select
-n will increase in the direction of negative numbers, starting from 0, -1, -2, -3...
Use :nth-child(odd) or :nth-child(even) to achieve interlaced color change.
Single selection
first-child: Select the first element, by position
first-of-type: Select the first element, by type
Last-child: Select the last element, by position
Last-of-type: Select the last element, by type
only-child: It will be selected when there are no other sibling elements
only-of-type: There can be sibling elements but they must be of different types
Using only-of-type allows you to select an element from other types of elements, whereas only-child requires the element to exist alone. This must be of great use, yet to be discovered.
Pseudo class
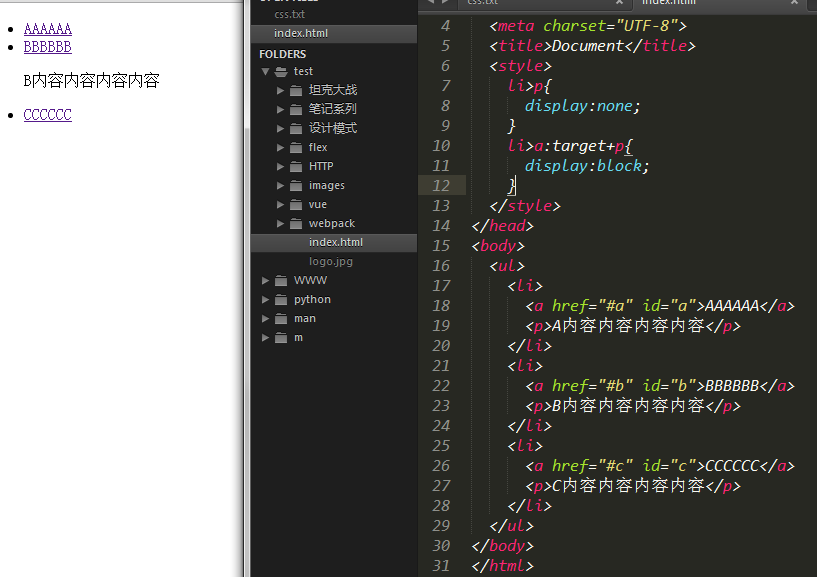
:target
- Use :target to simulate click events
- Use target to realize tab bar switching
- Using the target pseudo-class, you can easily highlight the comments that users want to read
Use the tab switching made by target. Of course, it still has many flaws, but you can expand it through it.
:empty
Select elements that have no child elements and no text nodes
:root
Select the root element. In HTML, root is always the html element
:not
Parameters support passing an element or even other pseudo-class selectors, but do not support passing connectors and pseudo-elements
Select any element except the specified parameters
Element status pseudo-class
:checked
When checkbox is selected
:disabled
When the element is disabled
:enabled
When the element is not disabled
Pseudo elements
::first-line
Select the first line of text
::first-letter
Select the first letter
::after
Add a pseudo element at the end of the element
::before
Add a pseudo element at the beginning of the element
::selection
Apply to selected text
Proper use of these selectors can help you solve many problems. It is still under research and the content of this article will be updated in the long term.

