Home >Web Front-end >HTML Tutorial >Compilation of front-end HTML knowledge points
Compilation of front-end HTML knowledge points
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOriginal
- 2016-08-22 10:13:58916browse
1. html overview
htyper text markup language is hypertext markup language
Hypertext: It means that the page can contain pictures, links, and even non-text elements such as music and programs.
Markup language: A language composed of marks (labels).
Web page == HTML document, parsed by the browser and used for display
Static web pages: static resources, such as xxx.html
Dynamic web pages: HTML code is dynamically generated by a certain development language based on user requests
The following is the tree structure diagram of the html file
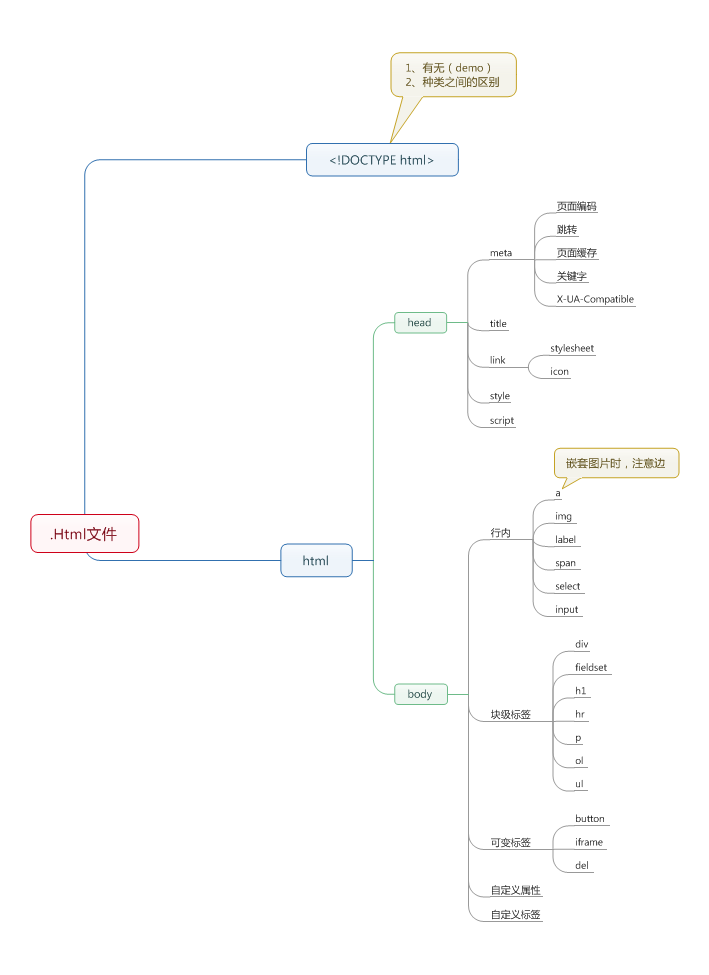
The concept of tags:
- is composed of a pair of words wrapped in angle brackets. For example: *The words in all tags cannot start with a number.
- Tags are not case-sensitive. and . Lowercase is recommended.
- The tag is divided into two parts: the start tag and the end tag . The part between the two tags is called the tag body.
- Some tag functions are relatively simple. Just use one tag. This kind of tag is called a self-closing tag. For example:
- Tags can be nested. But they cannot be cross-nested.
Tag attributes:
- Usually appears in the form of key-value pairs. For example, name="alex"
- Attributes can only appear in opening tags or self-closing tags.
- Attribute names are all lowercase. *Attribute values must be wrapped in double quotes or single quotes, for example name="alex"
- If the attribute value and attribute name are exactly the same, just write the attribute name directly. For example, readonly
2. Introduction to the main tags of head
- The composition of the meta tag: The meta tag has two attributes, which are the http-equiv attribute and the name attribute. Different attributes have different parameter values. These different parameter values realize different web page functions. .
1 The name attribute is mainly used to describe web pages, and the corresponding attribute value is content. The content in content is mainly used by search engine robots to find information and classify information.
2 http-equiv, as the name suggests, is equivalent to the file header function of http. It can return some useful information to the browser to help display the web page content correctly and accurately. The corresponding attribute value is content, and the content in content In fact, it is the variable value of each parameter.
//(note the quotation marks at the end, in front of the seconds and after the URL)
Oldboy
3. Body tag
Basic tags:
: Paragraph tag. The wrapped content is wrapped. There is also a blank line between the upper and lower content.
: bold label.
: Add a center line to the text.
: The text becomes italic.
and : superscript and subscript.
: Line break.
: Horizontal line
块级标签和内联标签
块级标签:

