<span>location</span> / <span>{</span>
proxy_pass <span>http</span>://localhost:<span>8000</span><span>;</span>
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP <span>$remote_addr</span><span>;</span><span>}</span>
proxy_bind 192.168.1.1<span>;</span>
server
location
This directive set the buffer size, into which will be read the first part of the response, obtained from the proxied server.
server
location
This directive activate response buffering of the proxied server.
server
location
This directive sets the number and the size of buffers, into which will be read the answer, obtained from the proxied server. By default, the size of one buffer is equal to the size of page. Depending on platform this is either 4K or 8K.
server
location
server
location
This directive sets name of zone for caching. The same zone can be used in multiple places.
server
location
The directive specifies the conditions under which the answer will not be taken from the cache. If at least one of a string variable is not empty and not equal to "0", the answer is not taken from the cache:
proxy_cache_bypass <span>$cookie_nocache</span><span>$arg_nocache</span><span>$arg_comment</span><span>;</span> proxy_cache_bypass <span>$http_pragma</span><span>$http_authorization</span><span>;</span>
proxy_cache_bypass <span>$http_my_secret_header</span><span>;</span>
server
location
The directive specifies what information is included in the key for caching, for example
proxy_cache_key <span>"$host$request_uri$cookie_user"</span><span>;</span>
proxy_cache_key <span>"$scheme$host$request_uri"</span><span>;</span>
server
location
server
location
proxy_cache_methods POST<span>;</span>
server
location
Number of queries, after which reply will be cached.
This directive sets the cache path and other cache parameters. Cached data is stored in files. An MD5 hash of the proxied URL is used as the key for the cache entry, and is also used as the filename in the cache path for the response contents and metadata. The levels parameter sets the number of subdirectory levels in cache. For example:
proxy_cache_path /data/nginx/cache/one levels<span>=</span><span>1</span>:<span>2</span> keys_zone<span>=</span>one:10m<span>;</span>
<span>/</span>data<span>/</span>nginx<span>/</span>cache<span>/</span>c<span>/</span><span>29</span><span>/</span>b7f54b2df7773722d382f4809d65029c
proxy_cache_path /data/nginx/cache/one levels<span>=</span><span>1</span> keys_zone<span>=</span>one:10m<span>;</span> proxy_cache_path /data/nginx/cache/two levels<span>=</span><span>2</span>:<span>2</span> keys_zone<span>=</span>two:100m<span>;</span> proxy_cache_path /data/nginx/cache/three levels<span>=</span><span>1</span>:<span>1</span>:<span>2</span> keys_zone<span>=</span>three:1000m<span>;</span>
server
location
This directive tells Nginx when to serve a stale item from the proxy cache. The parameters for this directive are similar to proxy_next_upstream with the addition of 'updating'.
server
location
This directive sets the time for caching different replies. Example:
proxy_cache_valid <span>200</span><span>302</span> 10m<span>;</span> proxy_cache_valid <span>404</span> 1m<span>;</span>
proxy_cache_valid 5m<span>;</span>
proxy_cache_valid <span>200</span><span>302</span> 10m<span>;</span> proxy_cache_valid <span>301</span> 1h<span>;</span> proxy_cache_valid any 1m<span>;</span>
proxy_ignore_headers X-Accel-Expires Expires Cache-Control<span>;</span>
server
location
This directive assigns a timeout for the connection to the upstream server. It is necessary to keep in mind that this time out cannot be more than 75 seconds.
proxy_cookie_domain domain replacement
server
location
proxy_cookie_path path replacement
server
location
This determines the limit of the header name. If you use header names longer than 64 characters then increase this.
Should not be smaller than the amount of headers your back-end is setting.
server
location
nginx does not transfer the "Date", "Server", "X-Pad" and "X-Accel-..." header lines from the proxied server response. The
<span>location</span> / <span>{</span>
proxy_hide_header X-AspNet-Version<span>;</span>
proxy_hide_header MicrosoftOfficeWebServer<span>;</span><span>}</span>
<span>location</span> / <span>{</span>
proxy_pass <span>http</span>://backend_servers<span>;</span><span>}</span>
<span>location</span> /files/ <span>{</span>
proxy_pass <span>http</span>://fileserver<span>;</span>
proxy_hide_header Content-Type<span>;</span><span>}</span>
server
location
server
location
Prevents aborting request to proxy in case the client itself aborts the request.
server
location
Prohibits the processing of the header lines from the proxy server's response.
server
location
This directive decides if nginx will intercept responses with HTTP status codes of 400 and higher.
server
location
The maximum size of a temporary file when the content is larger than the proxy buffer. If file is larger than this size, it will be served synchronously from upstream server rather than buffered to disk.
proxy_method POST<span>;</span>
server
location
Directive determines in what cases the request will be transmitted to the next server:
server
location
Specifies in what cases a response will not be cached, e.g.
proxy_no_cache <span>$cookie_nocache</span><span>$arg_nocache</span><span>$arg_comment</span><span>;</span> proxy_no_cache <span>$http_pragma</span><span>$http_authorization</span><span>;</span>
if in location
limit_except
This directive sets the address of the proxied server and the URI to which location will be mapped. Address may be given as hostname or address and port, for example,
proxy_pass <span>http</span>://localhost:<span>8000</span>/uri/<span>;</span>
proxy_pass <span>http</span>://unix:/path/to/backend.socket:/uri/<span>;</span>
proxy_set_header Host <span>$host</span><span>;</span>
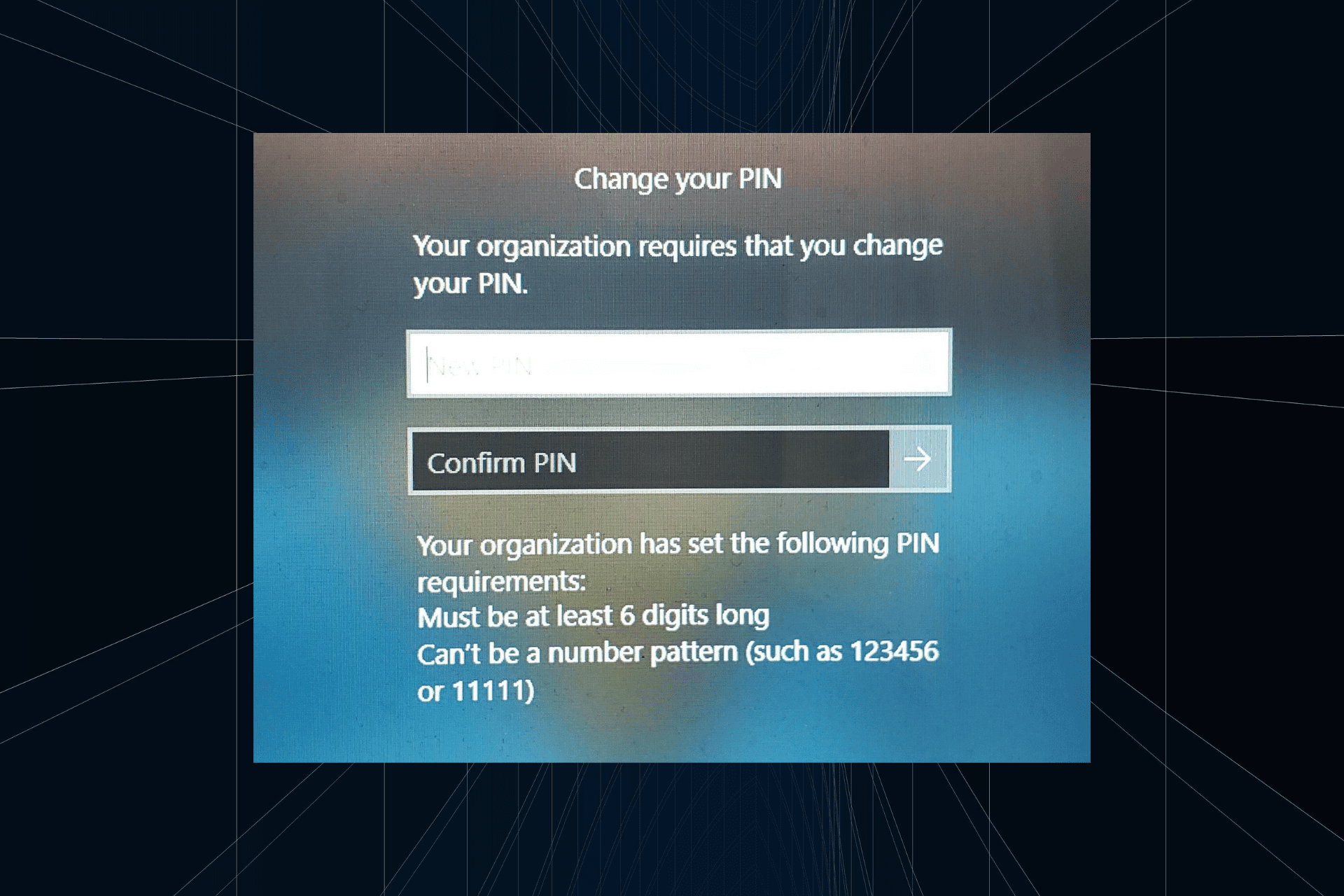 解决方法:您的组织要求您更改 PIN 码Oct 04, 2023 pm 05:45 PM
解决方法:您的组织要求您更改 PIN 码Oct 04, 2023 pm 05:45 PM“你的组织要求你更改PIN消息”将显示在登录屏幕上。当在使用基于组织的帐户设置的电脑上达到PIN过期限制时,就会发生这种情况,在该电脑上,他们可以控制个人设备。但是,如果您使用个人帐户设置了Windows,则理想情况下不应显示错误消息。虽然情况并非总是如此。大多数遇到错误的用户使用个人帐户报告。为什么我的组织要求我在Windows11上更改我的PIN?可能是您的帐户与组织相关联,您的主要方法应该是验证这一点。联系域管理员会有所帮助!此外,配置错误的本地策略设置或不正确的注册表项也可能导致错误。即
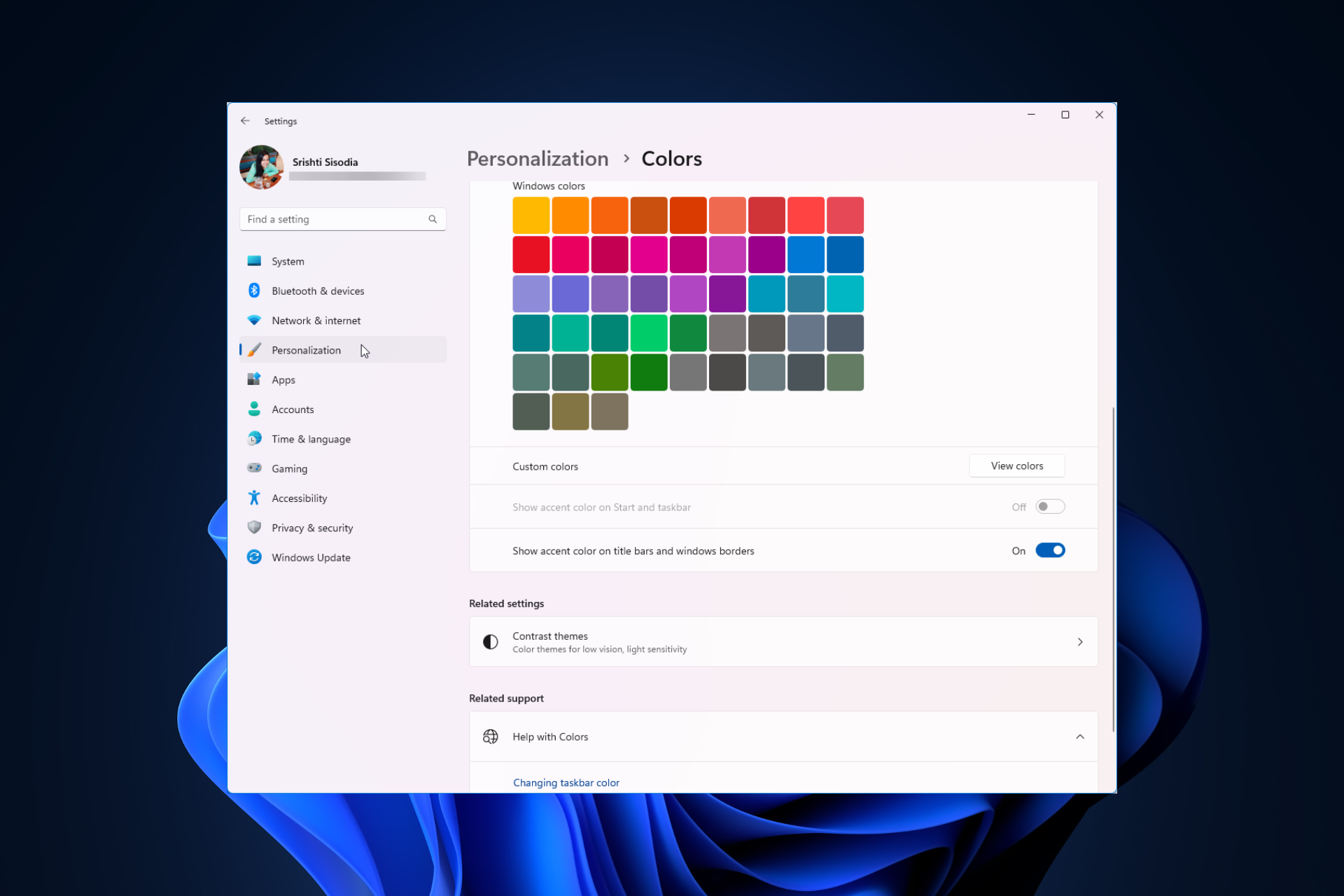 Windows 11 上调整窗口边框设置的方法:更改颜色和大小Sep 22, 2023 am 11:37 AM
Windows 11 上调整窗口边框设置的方法:更改颜色和大小Sep 22, 2023 am 11:37 AMWindows11将清新优雅的设计带到了最前沿;现代界面允许您个性化和更改最精细的细节,例如窗口边框。在本指南中,我们将讨论分步说明,以帮助您在Windows操作系统中创建反映您的风格的环境。如何更改窗口边框设置?按+打开“设置”应用。WindowsI转到个性化,然后单击颜色设置。颜色更改窗口边框设置窗口11“宽度=”643“高度=”500“>找到在标题栏和窗口边框上显示强调色选项,然后切换它旁边的开关。若要在“开始”菜单和任务栏上显示主题色,请打开“在开始”菜单和任务栏上显示主题
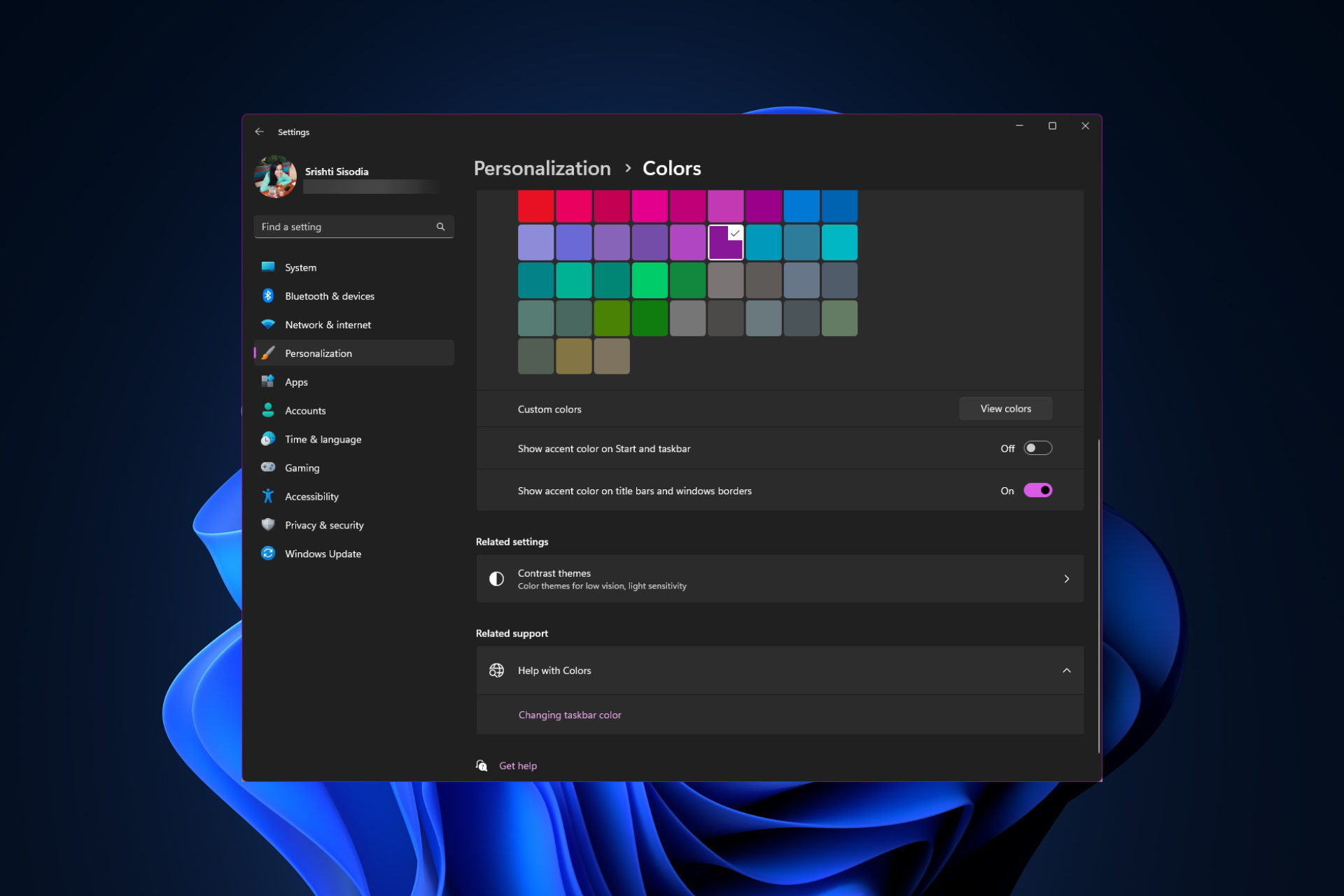 如何在 Windows 11 上更改标题栏颜色?Sep 14, 2023 pm 03:33 PM
如何在 Windows 11 上更改标题栏颜色?Sep 14, 2023 pm 03:33 PM默认情况下,Windows11上的标题栏颜色取决于您选择的深色/浅色主题。但是,您可以将其更改为所需的任何颜色。在本指南中,我们将讨论三种方法的分步说明,以更改它并个性化您的桌面体验,使其具有视觉吸引力。是否可以更改活动和非活动窗口的标题栏颜色?是的,您可以使用“设置”应用更改活动窗口的标题栏颜色,也可以使用注册表编辑器更改非活动窗口的标题栏颜色。若要了解这些步骤,请转到下一部分。如何在Windows11中更改标题栏的颜色?1.使用“设置”应用按+打开设置窗口。WindowsI前往“个性化”,然
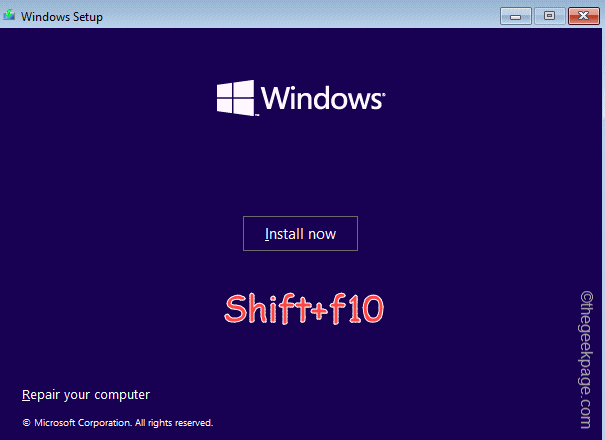 OOBELANGUAGE错误Windows 11 / 10修复中出现问题的问题Jul 16, 2023 pm 03:29 PM
OOBELANGUAGE错误Windows 11 / 10修复中出现问题的问题Jul 16, 2023 pm 03:29 PM您是否在Windows安装程序页面上看到“出现问题”以及“OOBELANGUAGE”语句?Windows的安装有时会因此类错误而停止。OOBE表示开箱即用的体验。正如错误提示所表示的那样,这是与OOBE语言选择相关的问题。没有什么可担心的,你可以通过OOBE屏幕本身的漂亮注册表编辑来解决这个问题。快速修复–1.单击OOBE应用底部的“重试”按钮。这将继续进行该过程,而不会再打嗝。2.使用电源按钮强制关闭系统。系统重新启动后,OOBE应继续。3.断开系统与互联网的连接。在脱机模式下完成OOBE的所
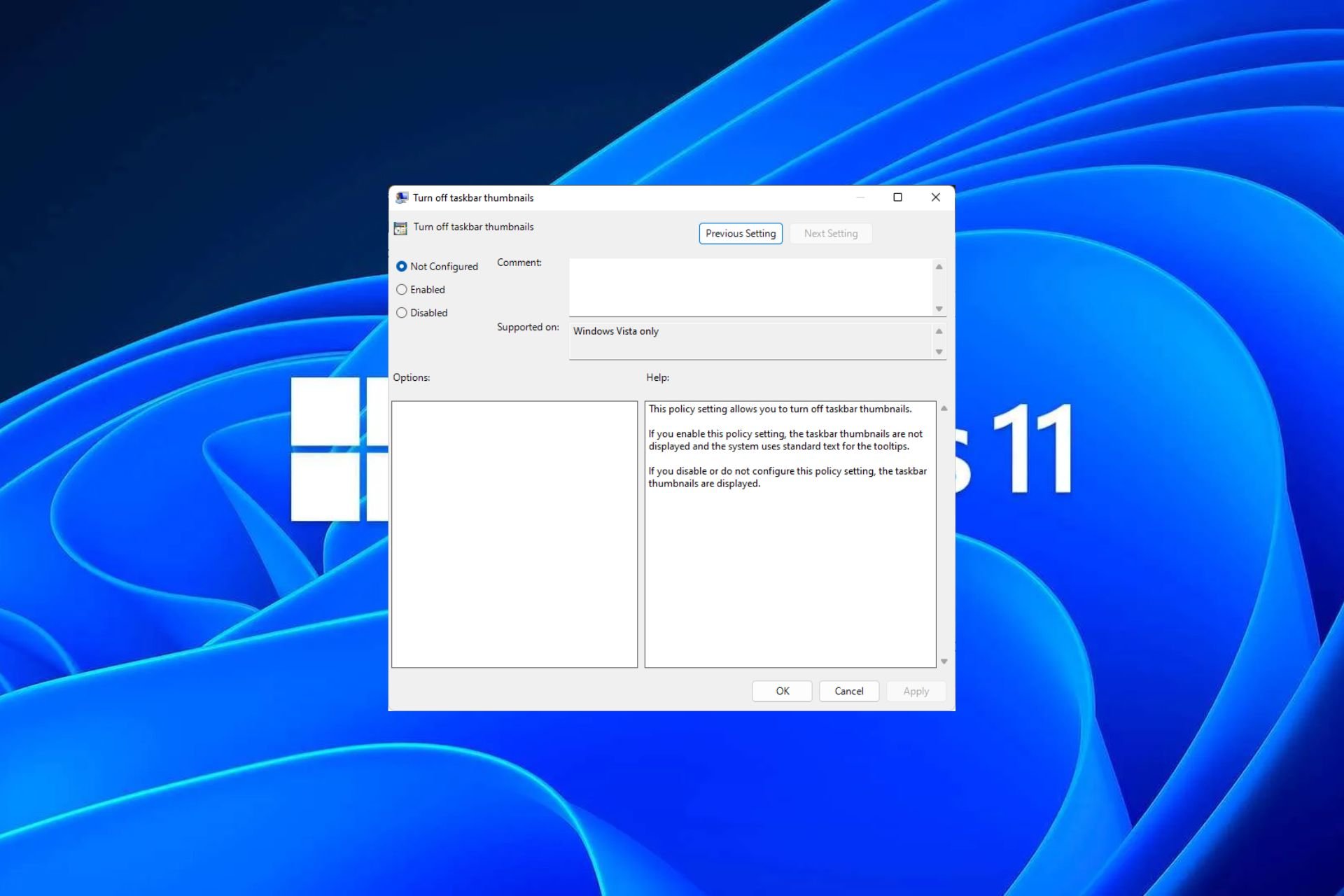 Windows 11 上启用或禁用任务栏缩略图预览的方法Sep 15, 2023 pm 03:57 PM
Windows 11 上启用或禁用任务栏缩略图预览的方法Sep 15, 2023 pm 03:57 PM任务栏缩略图可能很有趣,但它们也可能分散注意力或烦人。考虑到您将鼠标悬停在该区域的频率,您可能无意中关闭了重要窗口几次。另一个缺点是它使用更多的系统资源,因此,如果您一直在寻找一种提高资源效率的方法,我们将向您展示如何禁用它。不过,如果您的硬件规格可以处理它并且您喜欢预览版,则可以启用它。如何在Windows11中启用任务栏缩略图预览?1.使用“设置”应用点击键并单击设置。Windows单击系统,然后选择关于。点击高级系统设置。导航到“高级”选项卡,然后选择“性能”下的“设置”。在“视觉效果”选
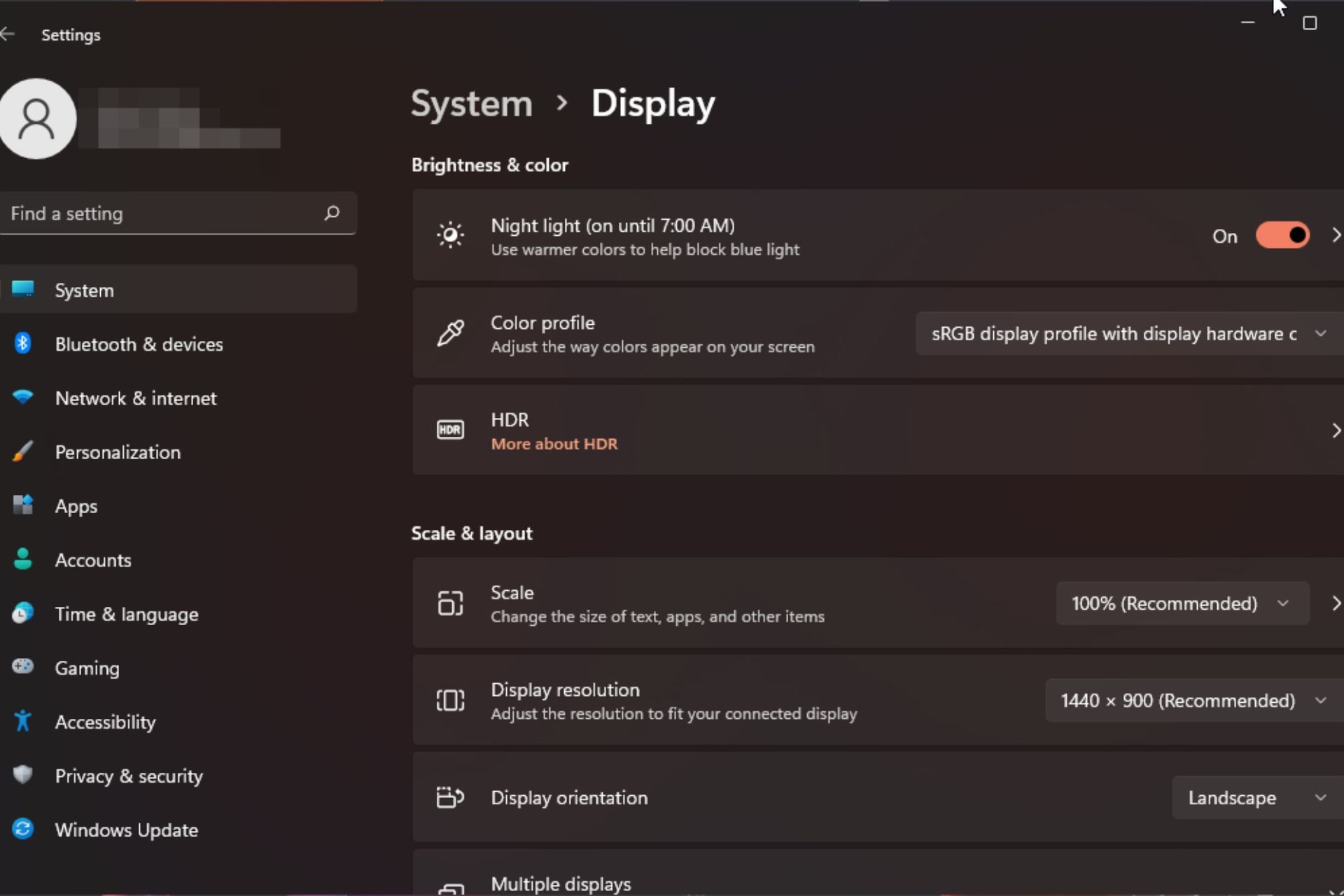 Windows 11 上的显示缩放比例调整指南Sep 19, 2023 pm 06:45 PM
Windows 11 上的显示缩放比例调整指南Sep 19, 2023 pm 06:45 PM在Windows11上的显示缩放方面,我们都有不同的偏好。有些人喜欢大图标,有些人喜欢小图标。但是,我们都同意拥有正确的缩放比例很重要。字体缩放不良或图像过度缩放可能是工作时真正的生产力杀手,因此您需要知道如何对其进行自定义以充分利用系统功能。自定义缩放的优点:对于难以阅读屏幕上的文本的人来说,这是一个有用的功能。它可以帮助您一次在屏幕上查看更多内容。您可以创建仅适用于某些监视器和应用程序的自定义扩展配置文件。可以帮助提高低端硬件的性能。它使您可以更好地控制屏幕上的内容。如何在Windows11
 10种在 Windows 11 上调整亮度的方法Dec 18, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
10种在 Windows 11 上调整亮度的方法Dec 18, 2023 pm 02:21 PM屏幕亮度是使用现代计算设备不可或缺的一部分,尤其是当您长时间注视屏幕时。它可以帮助您减轻眼睛疲劳,提高易读性,并轻松有效地查看内容。但是,根据您的设置,有时很难管理亮度,尤其是在具有新UI更改的Windows11上。如果您在调整亮度时遇到问题,以下是在Windows11上管理亮度的所有方法。如何在Windows11上更改亮度[10种方式解释]单显示器用户可以使用以下方法在Windows11上调整亮度。这包括使用单个显示器的台式机系统以及笔记本电脑。让我们开始吧。方法1:使用操作中心操作中心是访问
 如何在Safari中关闭iPhone的隐私浏览身份验证?Nov 29, 2023 pm 11:21 PM
如何在Safari中关闭iPhone的隐私浏览身份验证?Nov 29, 2023 pm 11:21 PM在iOS17中,Apple为其移动操作系统引入了几项新的隐私和安全功能,其中之一是能够要求对Safari中的隐私浏览选项卡进行二次身份验证。以下是它的工作原理以及如何将其关闭。在运行iOS17或iPadOS17的iPhone或iPad上,如果您在Safari浏览器中打开了任何“无痕浏览”标签页,然后退出会话或App,Apple的浏览器现在需要面容ID/触控ID认证或密码才能再次访问它们。换句话说,如果有人在解锁您的iPhone或iPad时拿到了它,他们仍然无法在不知道您的密码的情况下查看您的隐私


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor






