Object-oriented programs are built through a hierarchical structure of classes. In single inheritance languages such as PHP, class inheritance is tree-like. A root class has one or more subclasses, and each class has A subclass inherits one or more lower-level subclasses. Of course, there may be multiple root classes used to implement different functions. In a well-designed system, each root class should have a useful interface. Can be used by application code. If our application code is designed to work with the root class, then it can also work with any subclass that inherits from the root class.
Abstract methods are like subclasses Placeholder (takes up space but does not work) for a general method in a class that is different from a general method? There is no code. If there are one or more abstract methods in a class, then the class becomes an abstract class. You Abstract classes cannot be instantiated. You must inherit from them and then instantiate subclasses. You can also think of abstract classes as a template for subclasses.
If you override all abstract methods, the subclass Become an ordinary class. If all methods are not overridden, the subclass is still abstract. If a class contains an abstract method (even if there is only one), you must declare that the class is abstract, before the class keyword Add abstract.
The syntax of declaring an abstract method is different from declaring a general method. The abstract method does not have the main body contained in curly brackets {} like the general method, and ends with a semicolon;
In the example Figure 1, we defined a class Shape that contains the getArea method. However, since it is impossible to determine the area of the shape without knowing the shape, we declared the getArea method as an abstract method. You cannot instantiate a Shape object, but you can inherit from it or use it in an expression, as in Example 6.13.
If you create a class with only abstract methods, you define an interface. To illustrate this situation, PHP has the interface and implements keywords. You can use interface instead of abstract classes, and implements instead of extends to describe your class definition or use an interface. For example, you can write a myClass implements myIterface. These two methods can be chosen according to personal preference.
/*Note:
The two methods refer to:
1. abstract class aaa {} (Note that there are only abstract methods in aaa, no general methods)
class bbb extends aaa{} (overwrite the abstract methods in aaa in bbb)
2. interface aaa{}
class bbb implements aaa{} (override abstract methods in aaa in bbb)
*/
Abstract classes
<?php //abstract root class 抽象根类 abstract class Shape { abstract function getArea(); //定义一个抽象方法 } //abstract child class 抽象子类 abstract class Polygon extends Shape //多边形 { abstract function getNumberOfSides(); } //concrete class 实体类 三角形类 class Triangle extends Polygon { public $base; public $height; public function getArea() //覆写计算面积方法 { return(($this->base * $this->height)/2); } public function getNumberOfSides() //覆写边数统计方法 { return(3); } } //concrete class 实体类四边形 class Rectangle extends Polygon { public $width; public $height; public function getArea() { return($this->width * $this->height); } public function getNumberOfSides() { return(4); } } //concrete class 实体类 圆形 class Circle extends Shape { public $radius; public function getArea() { return(pi() * $this->radius * $this->radius); } } //concrete root class 定义一个颜色类 class Color { public $name; } $myCollection = array(); //建立形状的集合,放入数组 //make a rectangle $r = new Rectangle; $r->width = 5; $r->height = 7; $myCollection[] = $r; unset($r); //make a triangle $t = new Triangle; $t->base = 4; $t->height = 5; $myCollection[] = $t; unset($t); //make a circle $c = new Circle; $c->radius = 3; $myCollection[] = $c; unset($c); //make a color $c = new Color; $c->name = "blue"; $myCollection[] = $c; unset($c); foreach($myCollection as $s) { if($s instanceof Shape) //如果$s是Shape类的实例 { print("Area: " . $s->getArea() . "<br>n"); } if($s instanceof Polygon) { print("Sides: " . $s->getNumberOfSides() . "<br>n"); } if($s instanceof Color) { print("Color: $s->name<br>n"); } print("<br>n"); } ?> |
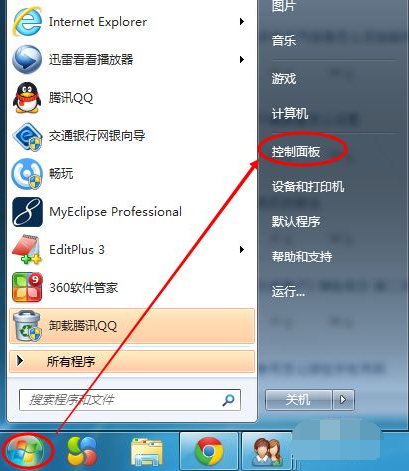 演示win7调整屏幕亮度的方法Jul 08, 2023 pm 07:49 PM
演示win7调整屏幕亮度的方法Jul 08, 2023 pm 07:49 PM不同的电脑系统在调整屏幕亮度的操作方法上会有些不同,最近就有使用win7系统的网友不知道win7怎么调整屏幕亮度,看久了电脑眼睛比较酸痛。下面小编就教下大家win7调整屏幕亮度的方法。具体的操作步骤如下:1、点击win7电脑左下角的“开始”,在弹出的开始菜单中选择“控制面板”打开。2、在打开的控制面板中找到“电源选项”打开。3、也可以用鼠标右键电脑右下角的电源图标,在弹出的菜单中,点击“调整屏幕亮度”,如下图所示。两种方法都可以用。4、在打开的电源选项窗口的最下面可以看到屏幕亮度调整的滚动条,直
 win10监控摄像头打开照片的方法Jul 10, 2023 pm 09:41 PM
win10监控摄像头打开照片的方法Jul 10, 2023 pm 09:41 PM如果我们手头没有手机,只有电脑,但我们必须拍照,我们可以使用电脑内置的监控摄像头拍照,那么如何打开win10监控摄像头,事实上,我们只需要下载一个相机应用程序。打开win10监控摄像头的具体方法。win10监控摄像头打开照片的方法:1.首先,盘快捷键Win+i打开设置。2.打开后,进入个人隐私设置。3.然后在相机手机权限下打开访问限制。4.打开后,您只需打开相机应用软件。(如果没有,可以去微软店下载一个)5.打开后,如果计算机内置监控摄像头或组装了外部监控摄像头,则可以拍照。(因为人们没有安装摄
 基于Java的机器视觉实践和方法介绍Jun 18, 2023 am 11:21 AM
基于Java的机器视觉实践和方法介绍Jun 18, 2023 am 11:21 AM随着科技的不断发展,机器视觉技术在各个领域得到了广泛应用,如工业自动化、医疗诊断、安防监控等。Java作为一种流行的编程语言,其在机器视觉领域也有着重要的应用。本文将介绍基于Java的机器视觉实践和相关方法。一、Java在机器视觉中的应用Java作为一种跨平台的编程语言,具有跨操作系统、易于维护、高度可扩展等优点,对于机器视觉的应用具有一定的优越性。Java
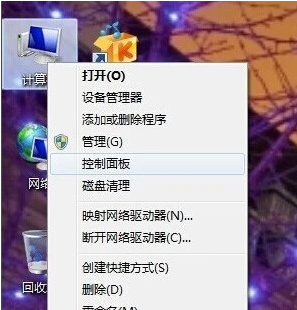 win7怎么调屏幕亮度的两种简单方法Jul 08, 2023 pm 06:33 PM
win7怎么调屏幕亮度的两种简单方法Jul 08, 2023 pm 06:33 PM目前有很多屏幕亮度调整软件,我们可以通过使用软件进行快速调整或者通过显示器上自带的亮度功能进行调整。以下是详细的Win7屏幕亮度调整方式,您可以通过教程中的方法进行快速调整即可。Win7系统电脑怎么调节屏幕亮度教程:1、依次点击“计算机—右键—控制面板”,如果没有也可以在搜索框中进行搜索。2、点击控制面板下的“硬件和声音”,或者点击“外观和个性化”都可以。3、点击“NVIDIA控制面板”,有些显卡可能是AMD或者Intel的,请根据实际情况选择。4、调节图示中亮度滑块即可。5、还有一种方法,就是
 PHP文件下载方法及常见问题解答Jun 09, 2023 pm 12:37 PM
PHP文件下载方法及常见问题解答Jun 09, 2023 pm 12:37 PMPHP是一个广泛使用的服务器端编程语言,它的许多功能和特性可以将其用于各种任务,包括文件下载。在本文中,我们将了解如何使用PHP创建文件下载脚本,并解决文件下载过程中可能出现的常见问题。一、文件下载方法要在PHP中下载文件,我们需要创建一个PHP脚本。让我们看一下如何实现这一点。创建下载文件的链接通过HTML或PHP在页面上创建一个链接,让用户能够下载文件。
 Go 语言中的方法是怎样定义和使用的?Jun 10, 2023 am 08:16 AM
Go 语言中的方法是怎样定义和使用的?Jun 10, 2023 am 08:16 AMGo语言是近年来备受青睐的编程语言,因其简洁、高效、并发等特点而备受开发者喜爱。其中,方法(Method)也是Go语言中非常重要的概念。接下来,本文就将详细介绍Go语言中方法的定义和使用。一、方法的定义Go语言中的方法是带有接收器(Receiver)的函数,它是一个与某个类型绑定的函数。接收器可以是值类型或者指针类型。用于接收者的参数可以在方法名
 Vue 中的 createApp 方法是什么?Jun 11, 2023 am 11:25 AM
Vue 中的 createApp 方法是什么?Jun 11, 2023 am 11:25 AM随着前端开发的快速发展,越来越多的框架被用来构建复杂的Web应用程序。Vue.js是流行的前端框架之一,它提供了许多功能和工具来简化开发人员构建高质量的Web应用程序。createApp()方法是Vue.js中的一个核心方法之一,它提供了一种简单的方式来创建Vue实例和应用程序。本文将深入探讨Vue中createApp方法的作用,其如何使用以及使用时需要了解
 “PHP面向对象编程入门:从概念到实践”Feb 25, 2024 pm 09:04 PM
“PHP面向对象编程入门:从概念到实践”Feb 25, 2024 pm 09:04 PM什么是面向对象编程?面向对象编程(OOP)是一种编程范式,它将现实世界中的实体抽象为类,并使用对象来表示这些实体。类定义了对象的属性和行为,而对象则实例化了类。OOP的主要优点在于它可以使代码更易于理解、维护和重用。OOP的基本概念OOP的主要概念包括类、对象、属性和方法。类是对象的蓝图,它定义了对象的属性和行为。对象是类的实例,它具有类的所有属性和行为。属性是对象的特征,它可以存储数据。方法是对象的函数,它可以对对象的数据进行操作。OOP的优点OOP的主要优点包括:可重用性:OOP可以使代码更


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools





