简介 2.echo 比 print 快。 3.使用echo的多重参数(译注:指用逗号而不是句点)代替字符串连接。 4.在执行for循环之前确定最大循环数,不要每循环一次都计算最大值。 5.注销那些不用的变量尤其是大数组,以便释放内存。 6.尽量避免使用__get,__set,__autoload。 7.require_once()代价昂贵。 8.在包含文件时使用完整路径,解析操作系统路径所需的时间会更少。 9.如果你想知道脚本开始执行(译注:即服务器端收到客户端请求)的时刻,使用$_SERVER[‘REQUEST_TIME’]要好于time()。 10.函数代替正则表达式完成相同功能。 11.str_replace函数比preg_replace函数快,但strtr函数的效率是str_replace函数的四倍。 12.如果一个字符串替换函数,可接受数组或字符作为参数,并且参数长度不太长,那么可以考虑额外写一段替换代码,使得每次传递参数是一个字符,而不是只写一行代码接受数组作为查询和替换的参数。 13.使用选择分支语句(译注:即switch case)好于使用多个if,else if语句。 14.用@屏蔽错误消息的做法非常低效。 15.打开apache的mod_deflate模块。 16.数据库连接当使用完毕时应关掉。 17.$row[‘id’]的效率是$row[id]的7倍。 18.错误消息代价昂贵。 19.尽量不要在for循环中使用函数,比如for ($x=0; $x
20.在方法中递增局部变量,速度是最快的。几乎与在函数中调用局部变量的速度相当。 21.递增一个全局变量要比递增一个局部变量慢2倍。 22.递增一个对象属性(如:$this->prop++)要比递增一个局部变量慢3倍。 23.递增一个未预定义的局部变量要比递增一个预定义的局部变量慢9至10倍。 24.仅定义一个局部变量而没在函数中调用它,同样会减慢速度(其程度相当于递增一个局部变量)。PHP大概会检查看是否存在全局变量。 25.方法调用看来与类中定义的方法的数量无关,因为我(在测试方法之前和之后都)添加了10个方法,但性能上没有变化。 26.派生类中的方法运行起来要快于在基类中定义的同样的方法。 27.调用带有一个参数的空函数,其花费的时间相当于执行7至8次的局部变量递增操作。类似的方法调用所花费的时间接近于15次的局部变量递增操作。 28.用单引号代替双引号来包含字符串,这样做会更快一些。因为PHP会在双引号包围的字符串中搜寻变量,单引号则不会。当然,只有当你不需要在字符串中包含变量时才可以这么做。 29.输出多个字符串时,用逗号代替句点来分隔字符串,速度更快。注意:只有echo能这么做,它是一种可以把多个字符串当作参数的“函数”(译注:PHP手册中说echo是语言结构,不是真正的函数,故把函数加上了双引号)。 30.Apache解析一个PHP脚本的时间要比解析一个静态HTML页面慢2至10倍。尽量多用静态HTML页面,少用脚本。 31.除非脚本可以缓存,否则每次调用时都会重新编译一次。引入一套PHP缓存机制通常可以提升25%至100%的性能,以免除编译开销。 32.尽量做缓存,可使用memcached。memcached是一款高性能的内存对象缓存系统,可用来加速动态Web应用程序,减轻数据库负载。对运算码 (OP code)的缓存很有用,使得脚本不必为每个请求做重新编译。 33.当操作字符串并需要检验其长度是否满足某种要求时,你想当然地会使用strlen()函数。此函数执行起来相当快,因为它不做任何计算,只返回在zval 结构(C的内置数据结构,用于存储PHP变量)中存储的已知字符串长度。但是,由于strlen()是函数,多多少少会有些慢,因为函数调用会经过诸多步骤,如字母小写化(译注:指函数名小写化,PHP不区分函数名大小写)、哈希查找,会跟随被调用的函数一起执行。在某些情况下,你可以使用isset() 技巧加速执行你的代码。 (举例如下) Calling isset() happens to be faster than strlen(), because unlike the latter, isset(), as a language construct, means that its execution does not require function lookup and letter lowercase. That is, you actually don't spend much overhead in the top-level code checking the string length. 34. When executing the increment or decrement of variable $i, $i++ will be slower than ++$i. This difference is specific to PHP and does not apply to other languages, so please don't modify your C or Java code and expect it to be instantly faster, it won't work. ++$i is faster because it only requires 3 instructions (opcodes), while $i++ requires 4 instructions. Post-increment actually creates a temporary variable that is subsequently incremented. Prefix increment increases directly on the original value. This is the most 35. Not everything must be object-oriented (OOP), object-oriented is often very expensive, and each method and object call consumes a lot of memory. 36. It is not necessary to use classes to implement all data structures, arrays are also useful. 37. Don’t subdivide the methods too much. Think carefully about which code you really intend to reuse? 38. You can always break code into methods when you need to. 39. Try to use a large number of PHP built-in functions. 40. If there are a large number of time-consuming functions in the code, you can consider implementing them using C extensions. 41. Profile your code. The checker will tell you which parts of the code take how much time. The Xdebug debugger includes inspection programs that evaluate the overall integrity of your code and reveal bottlenecks in your code. 42.mod_zip can be used as an Apache module to instantly compress your data and reduce data transmission volume by 80%. 43. A type of optimization processing, just like Zend’s PHP optimizer does. It's a good idea to keep this optimization in mind because not all command optimizers do the same optimizations, and there are a large number of Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and servers that don't have command optimizers equipped. Another great article on optimizing PHP, written by John Lim.
英文版权归Reinhold Weber所有,中译文作者yangyang(aka davidkoree)。双语版可用于非商业传播,但须注明英文版作者、版权信息,以及中译文作者。翻译水平有限,请广大PHPer指正。
1.如果一个方法可静态化,就对它做静态声明。速率可提升至4倍。
if (strlen($foo) (与下面的技巧做比较)
if (!isset($foo{5})) { echo “Foo is too short”$$ }
 修复:Windows 11 无法优化游戏的问题Apr 30, 2023 pm 01:28 PM
修复:Windows 11 无法优化游戏的问题Apr 30, 2023 pm 01:28 PMGeforceExperience不仅为您下载最新版本的游戏驱动程序,它还提供更多!最酷的事情之一是它可以根据您的系统规格优化您安装的所有游戏,为您提供最佳的游戏体验。但是一些游戏玩家报告了一个问题,即GeForceExperience没有优化他们系统上的游戏。只需执行这些简单的步骤即可在您的系统上解决此问题。修复1–为所有游戏使用最佳设置您可以设置为所有游戏使用最佳设置。1.在您的系统上打开GeForceExperience应用程序。2.GeForceExperience面
 Nginx性能优化与安全设置Jun 10, 2023 am 09:18 AM
Nginx性能优化与安全设置Jun 10, 2023 am 09:18 AMNginx是一种常用的Web服务器,代理服务器和负载均衡器,性能优越,安全可靠,可以用于高负载的Web应用程序。在本文中,我们将探讨Nginx的性能优化和安全设置。一、性能优化调整worker_processes参数worker_processes是Nginx的一个重要参数。它指定了可以使用的worker进程数。这个值需要根据服务器硬件、网络带宽、负载类型等
 Windows 11 Insiders 现在对在窗口模式下运行的传统游戏进行了优化Apr 25, 2023 pm 04:28 PM
Windows 11 Insiders 现在对在窗口模式下运行的传统游戏进行了优化Apr 25, 2023 pm 04:28 PM如果您在Windows机器上玩旧版游戏,您会很高兴知道Microsoft为它们计划了某些优化,特别是如果您在窗口模式下运行它们。该公司宣布,最近开发频道版本的内部人员现在可以利用这些功能。本质上,许多旧游戏使用“legacy-blt”演示模型在您的显示器上渲染帧。尽管DirectX12(DX12)已经利用了一种称为“翻转模型”的新演示模式,但Microsoft现在也正在向DX10和DX11游戏推出这一增强功能。迁移将改善延迟,还将为自动HDR和可变刷新率(VRR)等进一步增强打
 如何使用缓存优化PHP和MySQLMay 11, 2023 am 08:52 AM
如何使用缓存优化PHP和MySQLMay 11, 2023 am 08:52 AM随着互联网的不断发展和应用的扩展,越来越多的网站和应用需要处理海量的数据和实现高流量的访问。在这种背景下,对于PHP和MySQL这样的常用技术,缓存优化成为了非常必要的优化手段。本文将在介绍缓存的概念及作用的基础上,从两个方面的PHP和MySQL进行缓存优化的实现,希望能够为广大开发者提供一些帮助。一、缓存的概念及作用缓存是指将计算结果或读取数据的结果缓存到
 如何通过优化查询中的LIKE操作来提高MySQL性能May 11, 2023 am 08:11 AM
如何通过优化查询中的LIKE操作来提高MySQL性能May 11, 2023 am 08:11 AMMySQL是目前最流行的关系型数据库之一,但是在处理大量数据时,MySQL的性能可能会受到影响。其中,一种常见的性能瓶颈是查询中的LIKE操作。在MySQL中,LIKE操作是用来模糊匹配字符串的,它可以在查询数据表时用来查找包含指定字符或者模式的数据记录。但是,在大型数据表中,如果使用LIKE操作,它会对数据库的性能造成影响。为了解决这个问题,我们可
 Go语言中的优化和重构的方法Jun 02, 2023 am 10:40 AM
Go语言中的优化和重构的方法Jun 02, 2023 am 10:40 AMGo语言是一门相对年轻的编程语言,虽然从语言本身的设计来看,其已经考虑到了很多优化点,使得其具备高效的性能和良好的可维护性,但是这并不代表着我们在开发Go应用时不需要优化和重构,特别是在长期的代码积累过程中,原来的代码架构可能已经开始失去优势,需要通过优化和重构来提高系统的性能和可维护性。本文将分享一些在Go语言中优化和重构的方法,希望能够对Go开发者有所帮
 Snapchat优化指甲追踪效果,与OPI合推AR指甲油滤镜May 30, 2023 am 09:19 AM
Snapchat优化指甲追踪效果,与OPI合推AR指甲油滤镜May 30, 2023 am 09:19 AM5月26日消息,SnapchatAR试穿滤镜技术升级,并与OPI品牌合作,推出指甲油AR试用滤镜。据悉,为了优化AR滤镜对手指甲的追踪定位,Snap在LensStudio中推出手部和指甲分割功能,允许开发者将AR图像叠加在指甲这种细节部分。据青亭网了解,指甲分割功能在识别到人手后,会给手部和指甲分别设置掩膜,用于渲染2D纹理。此外,还会识别用户个人指甲的底色,来模拟指甲油真实上手的效果。从演示效果来看,新的AR指甲油滤镜可以很好的模拟浅蓝磨砂质地。实际上,此前Snapchat曾推出AR指甲油试用
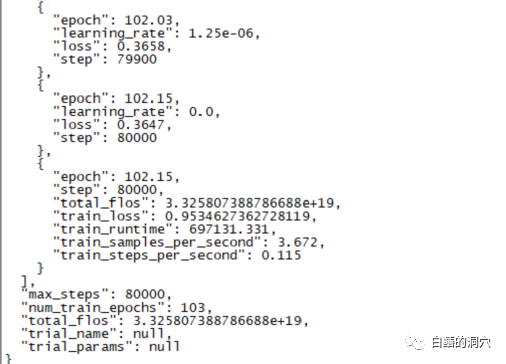 一篇学会本地知识库对LLM的性能优化Jun 12, 2023 am 09:23 AM
一篇学会本地知识库对LLM的性能优化Jun 12, 2023 am 09:23 AM昨天一个跑了220个小时的微调训练完成了,主要任务是想在CHATGLM-6B上微调出一个能够较为精确的诊断数据库错误信息的对话模型来。不过这个等了将近十天的训练最后的结果令人失望,比起我之前做的一个样本覆盖更小的训练来,差的还是挺大的。这样的结果还是有点令人失望的,这个模型基本上是没有实用价值的。看样子需要重新调整参数与训练集,再做一次训练。大语言模型的训练是一场军备竞赛,没有好的装备是玩不起来的。看样子我们也必须要升级一下实验室的装备了,否则没有几个十天可以浪费。从最近的几次失败的微调训练来看


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment






