 Backend Development
Backend Development PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial PHP development experience summary, PHP experience summary_PHP tutorial
PHP development experience summary, PHP experience summary_PHP tutorialPHP development experience summary, PHP experience summary
1. Use embedded HTML code instead of PHP's echo statement.
Because PHP is an embedded Web programming language, HTML code and PHP code can be embedded in each other. However, many programmers are worried that excessive use of "" to embed PHP code in HTML code will call the PHP interpreter multiple times, thereby reducing the running speed of PHP code, so they would rather use PHP's echo statement to output HTML code instead of directly Use HTML code. But the truth is exactly the opposite. Each PHP page only calls the PHP interpreter once to interpret all PHP codes. Therefore, the PHP code is only embedded when needed, and most of the time, the HTML code is used directly to input the results. Not only will it not reduce the running speed of the program, but it will also Because the parsing of echo statements is reduced, the running speed of the code can often be improved.
2. Try to use str-replace instead of ereg-replace
Programmers who are used to programming in Perl are more willing to use ereg_replace to complete string replacement work, because in PHP ereg_replace The usage is similar to the usage of pattern matching in Perl. However, the code below proves that using str_replace instead of ereg_replace will greatly improve the speed of the code.
3. Pay attention to string references
Like many other programming languages, PHP can use double quotes ("") to quote strings, or you can use single quotes. quotation marks(). But in PHP, if you use double quotes to quote a string, the PHP parser will first analyze whether there is a reference to a variable in the string. If there is a variable, it will replace the variable. If it is single quotes, it is not so complicated - all strings enclosed in single quotes are directly displayed. Obviously, in PHP programming, it is faster to use single quotes to quote string variables than double quotes.
4. Determine the maximum number of loops before executing the for loop, do not calculate the maximum value every loop
5. Pay attention to include and require The difference
In PHP programming, include() and require() have the same function, but there are some differences in usage. include() is a conditional inclusion function, while require() is an unconditional one. Contains functions. For example, in the following example, if the variable $somgthing is true, the file somefile will be included
if($something){
include("somefile.txt");
}
but no matter Whatever the value of $something is, the following code will include the file somefile into the file:
if($something){
require(“somefile.txt”);
}
6. When doing database query operations, you should try to avoid joint operations
Compared with other Web programming languages, PHP’s database function is very powerful.
However, running the database in PHP is still a very time-consuming and labor-intensive matter. Therefore, as a Web programmer, you must minimize database query operations and establish appropriate indexes for the database.
Another thing worth noting is that when using PHP to operate a database, try not to use joint operations of multiple data tables. Although joint operations can enhance the query function of the database, it greatly increases the burden on the server.
7. If you want to know the time when the script starts executing (annotation: the server receives the client request), it is better to use $_SERVER[‘REQUEST_TIME’] than the time() function.
8. It does not have to be object-oriented, object-oriented is more time-consuming. Some simple operations are still a quick process.
9.$row['id'] is 7 times faster than $row[id]
10.echo is faster than print, and uses echo's multiplexing Parameters (Translation: refers to using commas instead of periods) instead of string concatenation
such as echo $str1, $str2.
11. When there are many if...else... nestings, you should choose switch...case
12. Release the unused mysql query results in a timely manner ( mysql_free_result())
13. The difference between isset() and empty()
Both are used to test variables
But isset() tests whether the variable is Assignment, and empty() tests whether an assigned variable is empty
If a variable is not assigned a value, it is allowed to be referenced in PHP, but there will be a notice
If a variable is assigned an empty value Value, $foo="" or $foo=0 or $foo=false, then empty($foo) returns true, isset($foo) also returns true, which means assigning an empty value will not cancel a variable.
To unregister a variable, you can use unset($foo) or $foo=NULL
 Working with Flash Session Data in LaravelMar 12, 2025 pm 05:08 PM
Working with Flash Session Data in LaravelMar 12, 2025 pm 05:08 PMLaravel simplifies handling temporary session data using its intuitive flash methods. This is perfect for displaying brief messages, alerts, or notifications within your application. Data persists only for the subsequent request by default: $request-
 cURL in PHP: How to Use the PHP cURL Extension in REST APIsMar 14, 2025 am 11:42 AM
cURL in PHP: How to Use the PHP cURL Extension in REST APIsMar 14, 2025 am 11:42 AMThe PHP Client URL (cURL) extension is a powerful tool for developers, enabling seamless interaction with remote servers and REST APIs. By leveraging libcurl, a well-respected multi-protocol file transfer library, PHP cURL facilitates efficient execution of various network protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP. This extension offers granular control over HTTP requests, supports multiple concurrent operations, and provides built-in security features.
 Simplified HTTP Response Mocking in Laravel TestsMar 12, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
Simplified HTTP Response Mocking in Laravel TestsMar 12, 2025 pm 05:09 PMLaravel provides concise HTTP response simulation syntax, simplifying HTTP interaction testing. This approach significantly reduces code redundancy while making your test simulation more intuitive. The basic implementation provides a variety of response type shortcuts: use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Http; Http::fake([ 'google.com' => 'Hello World', 'github.com' => ['foo' => 'bar'], 'forge.laravel.com' =>
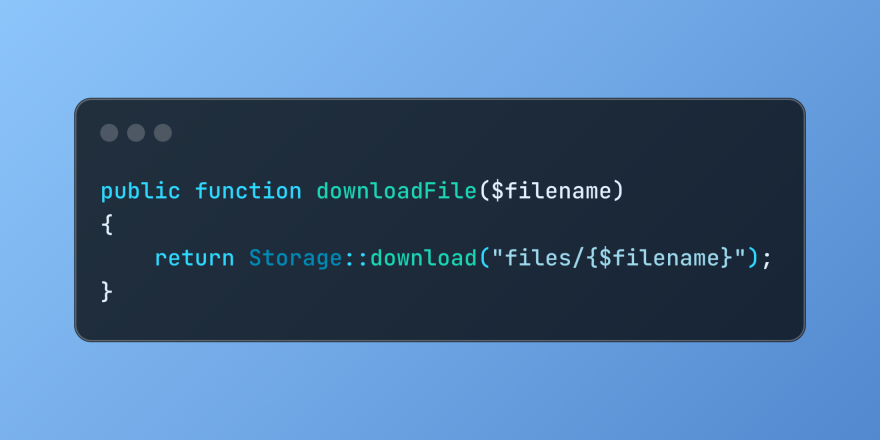 Discover File Downloads in Laravel with Storage::downloadMar 06, 2025 am 02:22 AM
Discover File Downloads in Laravel with Storage::downloadMar 06, 2025 am 02:22 AMThe Storage::download method of the Laravel framework provides a concise API for safely handling file downloads while managing abstractions of file storage. Here is an example of using Storage::download() in the example controller:
 12 Best PHP Chat Scripts on CodeCanyonMar 13, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
12 Best PHP Chat Scripts on CodeCanyonMar 13, 2025 pm 12:08 PMDo you want to provide real-time, instant solutions to your customers' most pressing problems? Live chat lets you have real-time conversations with customers and resolve their problems instantly. It allows you to provide faster service to your custom
 Explain the concept of late static binding in PHP.Mar 21, 2025 pm 01:33 PM
Explain the concept of late static binding in PHP.Mar 21, 2025 pm 01:33 PMArticle discusses late static binding (LSB) in PHP, introduced in PHP 5.3, allowing runtime resolution of static method calls for more flexible inheritance.Main issue: LSB vs. traditional polymorphism; LSB's practical applications and potential perfo
 PHP Logging: Best Practices for PHP Log AnalysisMar 10, 2025 pm 02:32 PM
PHP Logging: Best Practices for PHP Log AnalysisMar 10, 2025 pm 02:32 PMPHP logging is essential for monitoring and debugging web applications, as well as capturing critical events, errors, and runtime behavior. It provides valuable insights into system performance, helps identify issues, and supports faster troubleshoot
 How to Register and Use Laravel Service ProvidersMar 07, 2025 am 01:18 AM
How to Register and Use Laravel Service ProvidersMar 07, 2025 am 01:18 AMLaravel's service container and service providers are fundamental to its architecture. This article explores service containers, details service provider creation, registration, and demonstrates practical usage with examples. We'll begin with an ove


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use






