 Backend Development
Backend Development PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial A complete guide to setting up a complete WordPress site in Docker_php skills
A complete guide to setting up a complete WordPress site in Docker_php skillsA complete guide to setting up a complete WordPress site in Docker_php skills
1. Install Docker
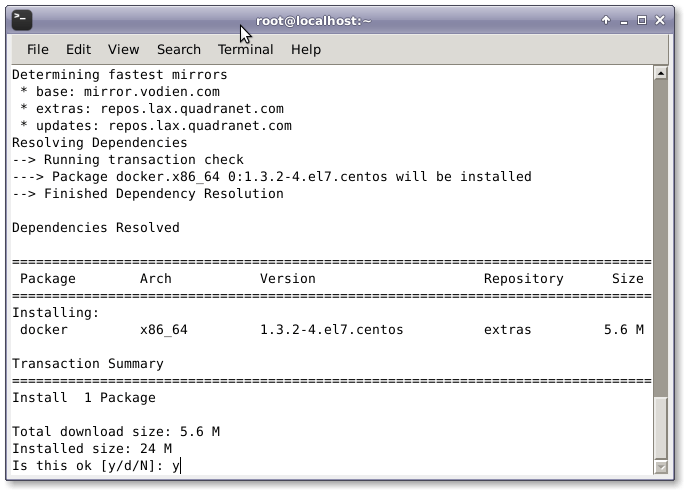
Before we actually get started, we need to make sure Docker is installed on our Linux machine. The host we are using is CentOS 7, so we install docker using the yum manager using the following command.
# yum install docker
# systemctl restart docker.service
2. Create WordPress Dockerfile
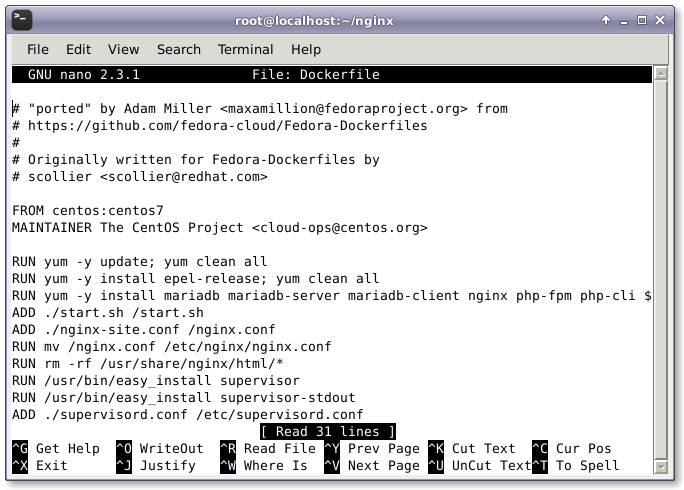
We need to create a Dockerfile for automatically installing wordpress and its prerequisites. This Dockerfile will be used to build the WordPress installation image. This WordPress Dockerfile will fetch the CentOS 7 image from the Docker Registry Hub and upgrade the system with the latest available updates. It then installs the necessary software, such as Nginx web server, PHP, MariaDB, Open SSH server, and other components that are indispensable for the proper functioning of Docker containers. Finally it executes a script that initializes the WordPress installation.
# nano Dockerfile
Then, we need to add the following configuration lines to the Dockerfile.
FROM centos:centos7 MAINTAINER The CentOS Project <cloud-ops@centos.org> RUN yum -y update; yum clean all RUN yum -y install epel-release; yum clean all RUN yum -y install mariadb mariadb-server mariadb-client nginx php-fpm php-cli php-mysql php-gd php-imap php-ldap php-odbc php-pear php-xml php-xmlrpc php-magickwand php-magpierss php-mbstring php-mcrypt php-mssql php-shout php-snmp php-soap php-tidy php-apc pwgen python-setuptools curl git tar; yum clean all ADD ./start.sh /start.sh ADD ./nginx-site.conf /nginx.conf RUN mv /nginx.conf /etc/nginx/nginx.conf RUN rm -rf /usr/share/nginx/html/* RUN /usr/bin/easy_install supervisor RUN /usr/bin/easy_install supervisor-stdout ADD ./supervisord.conf /etc/supervisord.conf RUN echo %sudo ALL=NOPASSWD: ALL >> /etc/sudoers ADD http://wordpress.org/latest.tar.gz /wordpress.tar.gz RUN tar xvzf /wordpress.tar.gz RUN mv /wordpress/* /usr/share/nginx/html/. RUN chown -R apache:apache /usr/share/nginx/ RUN chmod 755 /start.sh RUN mkdir /var/run/sshd EXPOSE 80 EXPOSE 22 CMD ["/bin/bash", "/start.sh"]
3. Create startup script
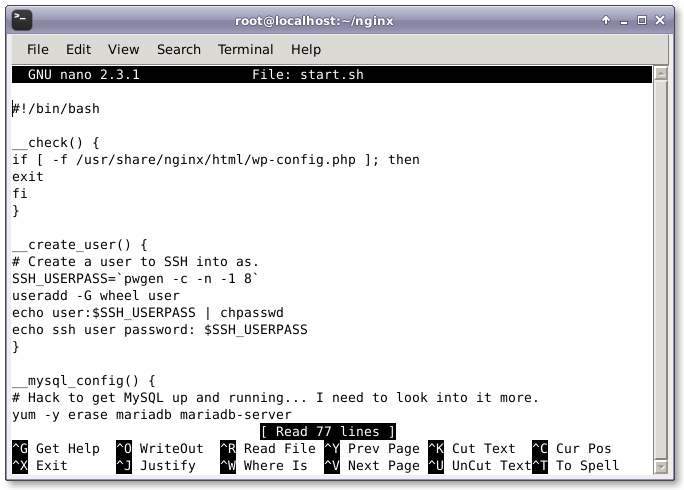
After we create the Dockerfile, we need to create the script that will be used to run and configure the WordPress installation, called start.sh. It creates and configures a database and password for WordPress. Open start.sh with your favorite text editor.
# nano start.sh
After opening start.sh, we need to add the following configuration lines to the file.
#!/bin/bash
__check() {
if [ -f /usr/share/nginx/html/wp-config.php ]; then
exit
fi
}
__create_user() {
# 创建用于 SSH 登录的用户
SSH_USERPASS=`pwgen -c -n -1 8`
useradd -G wheel user
echo user:$SSH_USERPASS | chpasswd
echo ssh user password: $SSH_USERPASS
}
__mysql_config() {
# 启用并运行 MySQL
yum -y erase mariadb mariadb-server
rm -rf /var/lib/mysql/ /etc/my.cnf
yum -y install mariadb mariadb-server
mysql_install_db
chown -R mysql:mysql /var/lib/mysql
/usr/bin/mysqld_safe &
sleep 10
}
__handle_passwords() {
# 在这里我们生成随机密码(多亏了 pwgen)。前面两个用于 mysql 用户,最后一个用于 wp-config.php 的随机密钥。
WORDPRESS_DB="wordpress"
MYSQL_PASSWORD=`pwgen -c -n -1 12`
WORDPRESS_PASSWORD=`pwgen -c -n -1 12`
# 这是在日志中显示的密码。
echo mysql root password: $MYSQL_PASSWORD
echo wordpress password: $WORDPRESS_PASSWORD
echo $MYSQL_PASSWORD > /mysql-root-pw.txt
echo $WORDPRESS_PASSWORD > /wordpress-db-pw.txt
# 这里原来是一个包括 sed、cat、pipe 和 stuff 的很长的行,但多亏了
# @djfiander 的 https://gist.github.com/djfiander/6141138
# 现在没有了
sed -e "s/database_name_here/$WORDPRESS_DB/
s/username_here/$WORDPRESS_DB/
s/password_here/$WORDPRESS_PASSWORD/
/'AUTH_KEY'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'SECURE_AUTH_KEY'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'LOGGED_IN_KEY'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'NONCE_KEY'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'AUTH_SALT'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'SECURE_AUTH_SALT'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'LOGGED_IN_SALT'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'NONCE_SALT'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/" /usr/share/nginx/html/wp-config-sample.php > /usr/share/nginx/html/wp-config.php
}
__httpd_perms() {
chown apache:apache /usr/share/nginx/html/wp-config.php
}
__start_mysql() {
# systemctl 启动 mysqld 服务
mysqladmin -u root password $MYSQL_PASSWORD
mysql -uroot -p$MYSQL_PASSWORD -e "CREATE DATABASE wordpress; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON wordpress.* TO 'wordpress'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '$WORDPRESS_PASSWORD'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;"
killall mysqld
sleep 10
}
__run_supervisor() {
supervisord -n
}
# 调用所有函数
__check
__create_user
__mysql_config
__handle_passwords
__httpd_perms
__start_mysql
__run_supervisor
After adding the above configuration, save and close the file.
4. Create configuration file
Now, we need to create a configuration file for the Nginx web server, named nginx-site.conf.
# nano nginx-site.conf
Then, add the following configuration information to the configuration file.
user nginx;
worker_processes 1;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
#error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log notice;
#error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log info;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
index index.html index.htm index.php;
# Load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory.
# See http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include
# for more information.
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
location ~ \.php$ {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
}

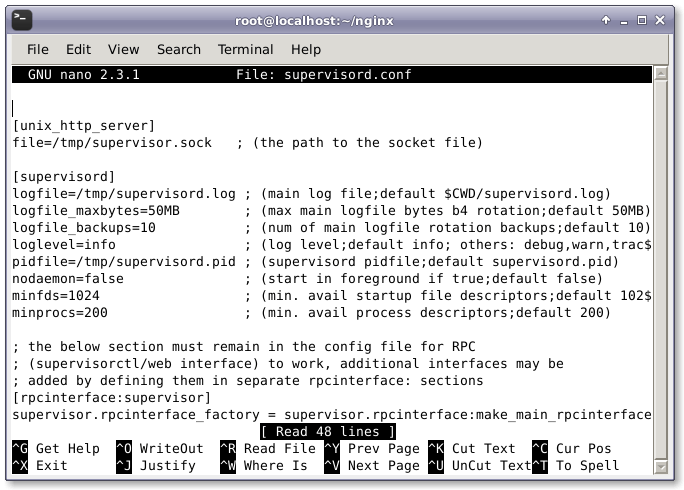
Now, create supervisor.conf file and add the following lines.
# nano supervisord.conf
Then, add the following lines.
[unix_http_server] file=/tmp/supervisor.sock ; (the path to the socket file) [supervisord] logfile=/tmp/supervisord.log ; (main log file;default $CWD/supervisord.log) logfile_maxbytes=50MB ; (max main logfile bytes b4 rotation;default 50MB) logfile_backups=10 ; (num of main logfile rotation backups;default 10) loglevel=info ; (log level;default info; others: debug,warn,trace) pidfile=/tmp/supervisord.pid ; (supervisord pidfile;default supervisord.pid) nodaemon=false ; (start in foreground if true;default false) minfds=1024 ; (min. avail startup file descriptors;default 1024) minprocs=200 ; (min. avail process descriptors;default 200) ; the below section must remain in the config file for RPC ; (supervisorctl/web interface) to work, additional interfaces may be ; added by defining them in separate rpcinterface: sections [rpcinterface:supervisor] supervisor.rpcinterface_factory = supervisor.rpcinterface:make_main_rpcinterface [supervisorctl] serverurl=unix:///tmp/supervisor.sock ; use a unix:// URL for a unix socket [program:php-fpm] command=/usr/sbin/php-fpm -c /etc/php/fpm stdout_events_enabled=true stderr_events_enabled=true [program:php-fpm-log] command=tail -f /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm.log stdout_events_enabled=true stderr_events_enabled=true [program:mysql] command=/usr/bin/mysql --basedir=/usr --datadir=/var/lib/mysql --plugin-dir=/usr/lib/mysql/plugin --user=mysql --log-error=/var/log/mysql/error.log --pid-file=/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid --socket=/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock --port=3306 stdout_events_enabled=true stderr_events_enabled=true [program:nginx] command=/usr/sbin/nginx stdout_events_enabled=true stderr_events_enabled=true [eventlistener:stdout] command = supervisor_stdout buffer_size = 100 events = PROCESS_LOG result_handler = supervisor_stdout:event_handler
After adding, save and close the file.
5. Build WordPress container
Now, after completing the creation of configuration files and scripts, we finally need to use Dockerfile to create the containers needed to install the latest WordPress CMS (Translator’s Note: Content Management System, Content Management System) and configure them according to the configuration file . To do this, we need to run the following command in the corresponding directory.
# docker build --rm -t wordpress:centos7 .
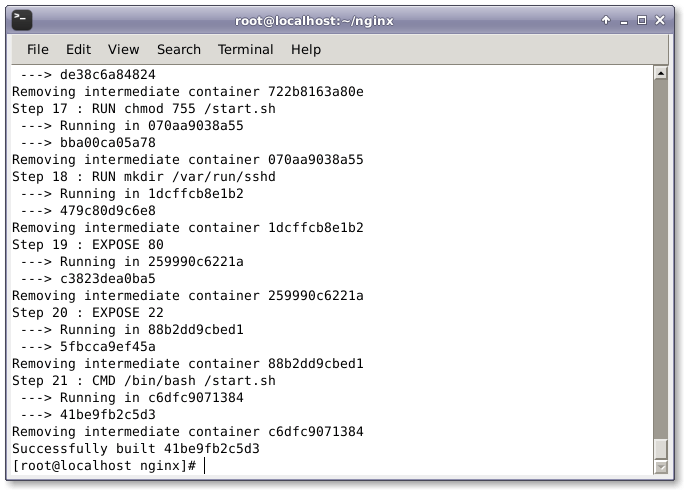
6. Run WordPress container
Now, execute the following command to run the newly built container and open the corresponding ports 88 and 22 for Nginx web server and SSH access.
# CID=$(docker run -d -p 80:80 wordpress:centos7)

Run the following command to check the process and the commands executed inside the container.
# echo "$(docker logs $CID )"
Run the following command to check if the port mapping is correct.
# docker ps
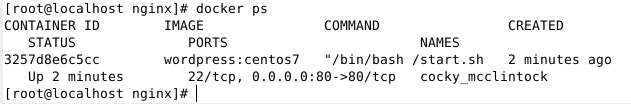
7. Web interface
Finally, if everything goes well, when we open http://ip-address/ or http://mywebsite.com/ with a browser, we will see the WordPress welcome interface.
Now we will set up the WordPress configuration, username and password for the WordPress panel through the web interface.
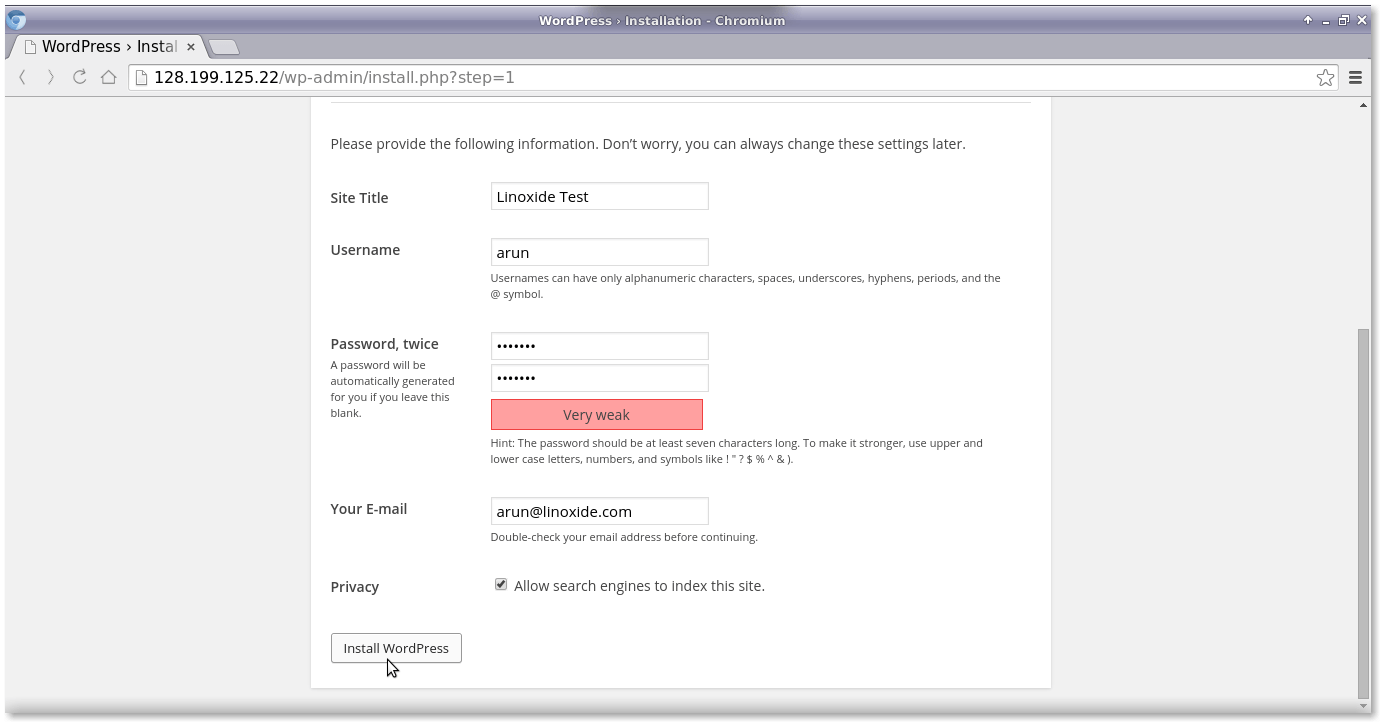
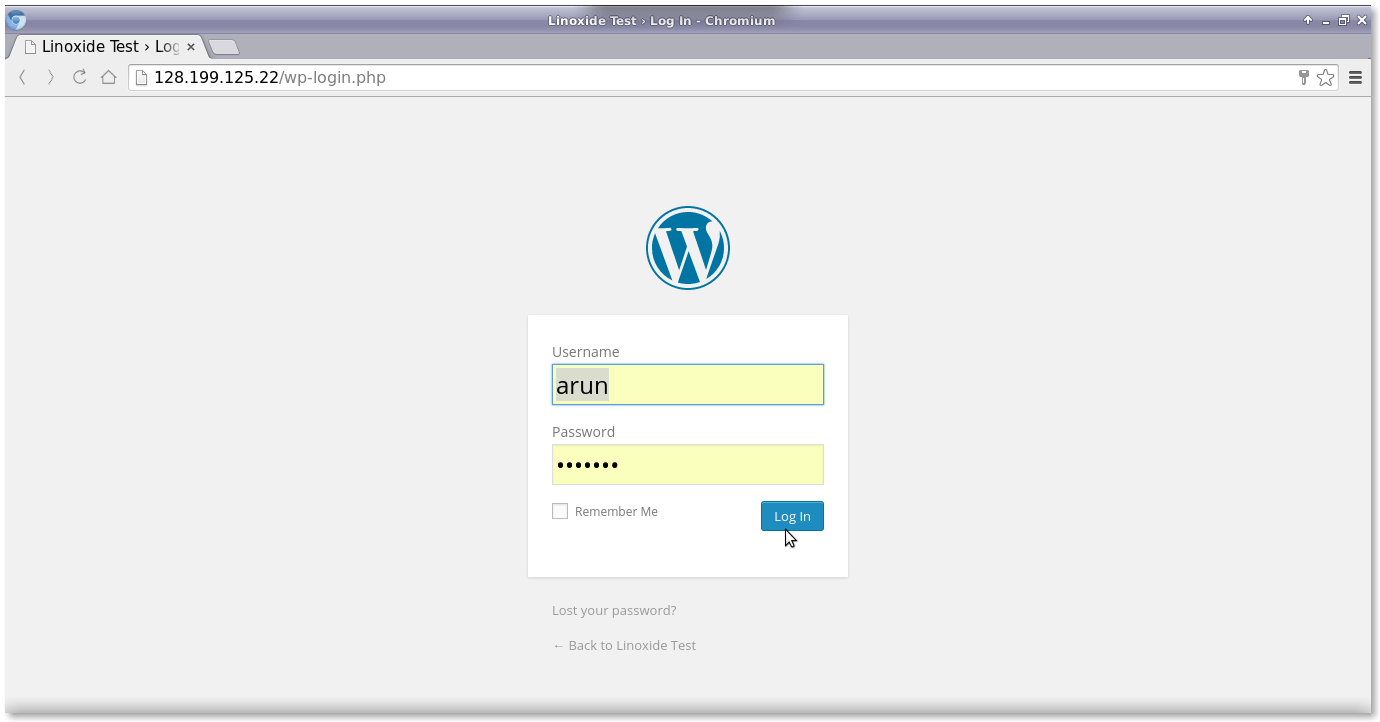
Then, enter the above username and password into the WordPress login interface.
Summary
We have successfully built and run WordPress CMS on LEMP stack with CentOS 7 as docker OS. From a security perspective, running WordPress in a container is more secure and reliable for the host system. This post covers a complete configuration for using WordPress on an Nginx web server running in a Docker container. If you have any questions, suggestions, feedback, please write it down in the comment box below so we can improve and update our content. Thank you so much! Enjoy :-)
 How can you check if a PHP session has already started?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:20 AM
How can you check if a PHP session has already started?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:20 AMIn PHP, you can use session_status() or session_id() to check whether the session has started. 1) Use the session_status() function. If PHP_SESSION_ACTIVE is returned, the session has been started. 2) Use the session_id() function, if a non-empty string is returned, the session has been started. Both methods can effectively check the session state, and choosing which method to use depends on the PHP version and personal preferences.
 Describe a scenario where using sessions is essential in a web application.Apr 30, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Describe a scenario where using sessions is essential in a web application.Apr 30, 2025 am 12:16 AMSessionsarevitalinwebapplications,especiallyfore-commerceplatforms.Theymaintainuserdataacrossrequests,crucialforshoppingcarts,authentication,andpersonalization.InFlask,sessionscanbeimplementedusingsimplecodetomanageuserloginsanddatapersistence.
 How can you manage concurrent session access in PHP?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:11 AM
How can you manage concurrent session access in PHP?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:11 AMManaging concurrent session access in PHP can be done by the following methods: 1. Use the database to store session data, 2. Use Redis or Memcached, 3. Implement a session locking strategy. These methods help ensure data consistency and improve concurrency performance.
 What are the limitations of using PHP sessions?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:04 AM
What are the limitations of using PHP sessions?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:04 AMPHPsessionshaveseverallimitations:1)Storageconstraintscanleadtoperformanceissues;2)Securityvulnerabilitieslikesessionfixationattacksexist;3)Scalabilityischallengingduetoserver-specificstorage;4)Sessionexpirationmanagementcanbeproblematic;5)Datapersis
 Explain how load balancing affects session management and how to address it.Apr 29, 2025 am 12:42 AM
Explain how load balancing affects session management and how to address it.Apr 29, 2025 am 12:42 AMLoad balancing affects session management, but can be resolved with session replication, session stickiness, and centralized session storage. 1. Session Replication Copy session data between servers. 2. Session stickiness directs user requests to the same server. 3. Centralized session storage uses independent servers such as Redis to store session data to ensure data sharing.
 Explain the concept of session locking.Apr 29, 2025 am 12:39 AM
Explain the concept of session locking.Apr 29, 2025 am 12:39 AMSessionlockingisatechniqueusedtoensureauser'ssessionremainsexclusivetooneuseratatime.Itiscrucialforpreventingdatacorruptionandsecuritybreachesinmulti-userapplications.Sessionlockingisimplementedusingserver-sidelockingmechanisms,suchasReentrantLockinJ
 Are there any alternatives to PHP sessions?Apr 29, 2025 am 12:36 AM
Are there any alternatives to PHP sessions?Apr 29, 2025 am 12:36 AMAlternatives to PHP sessions include Cookies, Token-based Authentication, Database-based Sessions, and Redis/Memcached. 1.Cookies manage sessions by storing data on the client, which is simple but low in security. 2.Token-based Authentication uses tokens to verify users, which is highly secure but requires additional logic. 3.Database-basedSessions stores data in the database, which has good scalability but may affect performance. 4. Redis/Memcached uses distributed cache to improve performance and scalability, but requires additional matching
 Define the term 'session hijacking' in the context of PHP.Apr 29, 2025 am 12:33 AM
Define the term 'session hijacking' in the context of PHP.Apr 29, 2025 am 12:33 AMSessionhijacking refers to an attacker impersonating a user by obtaining the user's sessionID. Prevention methods include: 1) encrypting communication using HTTPS; 2) verifying the source of the sessionID; 3) using a secure sessionID generation algorithm; 4) regularly updating the sessionID.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools





