Details of MySQL's MEM_ROOT
This article will explain in detail the MEM_ROOT structure that is widely used in MySQL. At the same time, it will omit the debug part of the information and only analyze the normal conditions in mysql. Use MEM_ROOT to do the memory allocation part.Before the specific analysis, let’s first enumerate some macros used in the use of this structure:
<ol style="margin:0 1px 0 0px;padding-left:40px;" start="1" class="dp-css"><li>#define MALLOC_OVERHEAD 8 //分配过程中,需要保留一部分额外的空间<br /> </li><li>#define ALLOC_MAX_BLOCK_TO_DROP 4096 //后续会继续分析该宏的用途<br /></li><li>#define ALLOC_MAX_BLOCK_USAGE_BEFORE_DROP 10 //后续会继续分析该宏的用途<br /></li><li><br /></li><li>#define ALIGN_SIZE(A) MY_ALIGN((A),sizeof(double))<br /></li><li>#define MY_ALIGN(A,L) (((A) + (L) - 1) & ~((L) - 1))<br /></li><li><br /></li><li>#define ALLOC_ROOT_MIN_BLOCK_SIZE (MALLOC_OVERHEAD + sizeof(USED_MEM) + 8)<br /></li><li>/* Define some useful general macros (should be done after all headers). */<br /></li><li>#define MY_MAX(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b)) //求两个数值之间的最大值<br /></li><li>#define MY_MIN(a, b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b)) //求两个数值之间的最小值</li></ol>
Let’s take a look at the information related to the MEM_ROOT structure:
<ol style="margin:0 1px 0 0px;padding-left:40px;" start="1" class="dp-css"><li>typedef struct st_mem_root<br /> </li><li>{<br /></li><li>USED_MEM *free; //free block link list的链表头指针<br /></li><li>USED_MEM *used;//used block link list的链表头指针<br /></li><li>USED_MEM *pre_alloc; //预先分配的block<br /></li><li>size_t min_malloc; //如果block剩下的可用空间小于该值,将会从free list移动到used list<br /></li><li>size_t block_size; //每次初始化的空间大小<br /></li><li>unsigned int block_num; //记录实际的block数量,初始化为4<br /></li><li>unsigned int first_block_usage; //free list中的第一个block 测试不满足分配空间大小的次数<br /></li><li>void (*error_handler)(void);//分配失败的错误处理函数<br /></li><li>} MEM_ROOT; </li></ol>The following is the specific block information allocated.
<ol style="margin:0 1px 0 0px;padding-left:40px;" start="1" class="dp-css"><li>typedef struct st_used_mem<br /> </li><li>{ <br /></li><li>struct st_used_mem *next; //指向下一个分配的block<br /></li><li>unsigned int left; //该block剩余的空间大小<br /></li><li>unsigned int size; //该block的总大小<br /></li><li>} USED_MEM; </li></ol>In fact, during the allocation process, MEM_ROOT manages used and free blocks through a doubly linked list:
The initialization process of MEM_ROOT is as follows:
<ol style="margin:0 1px 0 0px;padding-left:40px;" start="1" class="dp-css"><li>void init_alloc_root(MEM_ROOT *mem_root, size_t block_size,size_t pre_alloc_size __attribute__((unused)))<br /> </li><li>{<br /></li><li>mem_root->free= mem_root->used= mem_root->pre_alloc= 0;<br /></li><li>mem_root->min_malloc= 32;<br /></li><li>mem_root->block_size= block_size - ALLOC_ROOT_MIN_BLOCK_SIZE;<br /></li><li>mem_root->error_handler= 0;<br /></li><li>mem_root->block_num= 4; /* We shift this with >>2 */<br /></li><li>mem_root->first_block_usage= 0;<br /></li><li>} </li></ol>During the initialization process, the block_size space is block_size-ALLOC_ROOT_MIN_BLOCK_SIZE. Because when the memory is not enough and needs to be expanded, the capacity is expanded through mem_root->block_num >>2 *block_size, so mem_root->block_num >>2 is at least 1, so during the initialization process mem_root->block_num=4 (Note :4>>2=1).

Let’s take a look at the specific steps of allocating memory:
<ol style="margin:0 1px 0 0px;padding-left:40px;" start="1" class="dp-css"><li>void *alloc_root(MEM_ROOT *mem_root, size_t length)<br /> </li><li>{<br /></li><li>size_t get_size, block_size;<br /></li><li>uchar* point;<br /></li><li>reg1 USED_MEM *next= 0;<br /></li><li>reg2 USED_MEM **prev;<br /></li><li><br /></li><li>length= ALIGN_SIZE(length);<br /></li><li>if ((*(prev= &mem_root->free)) != NULL)<br /></li><li>{<br /></li><li>if ((*prev)->left < length &&<br /></li><li>mem_root->first_block_usage++ >= ALLOC_MAX_BLOCK_USAGE_BEFORE_DROP &&<br /></li><li>(*prev)->left < ALLOC_MAX_BLOCK_TO_DROP)<br /></li><li>{<br /></li><li>next= *prev;<br /></li><li>*prev= next->next; /* Remove block from list */<br /></li><li>next->next= mem_root->used;<br /></li><li>mem_root->used= next;<br /></li><li>mem_root->first_block_usage= 0;<br /></li><li>}<br /></li><li>for (next= *prev ; next && next->left < length ; next= next->next)<br /></li><li>prev= &next->next;<br /></li><li>}<br /></li><li>if (! next)<br /></li><li>{ /* Time to alloc new block */<br /></li><li>block_size= mem_root->block_size * (mem_root->block_num >> 2);<br /></li><li>get_size= length+ALIGN_SIZE(sizeof(USED_MEM));<br /></li><li>get_size= MY_MAX(get_size, block_size);<br /></li><li><br /></li><li>if (!(next = (USED_MEM*) my_malloc(get_size,MYF(MY_WME | ME_FATALERROR))))<br /></li><li>{<br /></li><li>if (mem_root->error_handler)<br /></li><li>(*mem_root->error_handler)();<br /></li><li>DBUG_RETURN((void*) 0); /* purecov: inspected */<br /></li><li>}<br /></li><li>mem_root->block_num++;<br /></li><li>next->next= *prev;<br /></li><li>next->size= get_size;<br /></li><li>next->left= get_size-ALIGN_SIZE(sizeof(USED_MEM)); //bug:如果该block是通过mem_root->block_size * (mem_root->block_num >> 2)计算出来的,则已经去掉了ALIGN_SIZE(sizeof(USED_MEM),这里重复了。<br /></li><li>*prev=next;<br /></li><li>}<br /></li><li><br /></li><li>point= (uchar*) ((char*) next+ (next->size-next->left));<br /></li><li>/*TODO: next part may be unneded due to mem_root->first_block_usage counter*/<br /></li><li>if ((next->left-= length) < mem_root->min_malloc)<br /></li><li>{ /* Full block */<br /></li><li>*prev= next->next; /* Remove block from list */<br /></li><li>next->next= mem_root->used;<br /></li><li>mem_root->used= next;<br /></li><li>mem_root->first_block_usage= 0;<br /></li><li>}<br /></li><li>} </li></ol>The specific logic of the above code is as follows: 1. Check the free linked list to find a block that meets the space. If a suitable block is found, then: 1.1 Directly return the initial address of the block from size-left. Of course, during the free list traversal process, it will be judged that the left space in the first block in the freelist does not meet the space that needs to be allocated, and the block has been searched 10 times (ALLOC_MAX_BLOCK_USAGE_BEFORE_DROP) and does not meet the allocation length, and If the remaining space of the block is less than 4k (ALLOC_MAX_BLOCK_TO_DROP), the block will be moved to the used linked list. 2. If there is no suitable block in the free linked list, then: 2.1 Allocate the larger of mem_root->block_size * (mem_root->block_num >> 2) and length ALIGN_SIZE(sizeof(USED_MEM)) as the new block memory space. 2.2 Depending on the usage of the block, hang the block on the used or free linked list.
What needs to be noted here is the use of secondary pointers:
<ol style="margin:0 1px 0 0px;padding-left:40px;" start="1" class="dp-css"><li>for (next= *prev ; next && next->left < length ; next= next->next)<br /> </li><li>prev= &next->next;<br /></li><li>} </li></ol>prev points to the address pointed to by next of the last block:

So replace the address of prev is the address of the new block, that is, the new block is added to the end of the free list: *prev=next;

Summary: MEM_ROOT uses a heuristic allocation algorithm for memory allocation. The greater the number of blocks, the larger the memory of a single block will be: block_size= mem_root->block_size * (mem_root->block_num >> 2).
 如何在 iPhone 和 Android 上关闭蓝色警报Feb 29, 2024 pm 10:10 PM
如何在 iPhone 和 Android 上关闭蓝色警报Feb 29, 2024 pm 10:10 PM根据美国司法部的解释,蓝色警报旨在提供关于可能对执法人员构成直接和紧急威胁的个人的重要信息。这种警报的目的是及时通知公众,并让他们了解与这些罪犯相关的潜在危险。通过这种主动的方式,蓝色警报有助于增强社区的安全意识,促使人们采取必要的预防措施以保护自己和周围的人。这种警报系统的建立旨在提高对潜在威胁的警觉性,并加强执法机构与公众之间的沟通,以共尽管这些紧急通知对我们社会至关重要,但有时可能会对日常生活造成干扰,尤其是在午夜或重要活动时收到通知时。为了确保安全,我们建议您保持这些通知功能开启,但如果
 在Android中实现轮询的方法是什么?Sep 21, 2023 pm 08:33 PM
在Android中实现轮询的方法是什么?Sep 21, 2023 pm 08:33 PMAndroid中的轮询是一项关键技术,它允许应用程序定期从服务器或数据源检索和更新信息。通过实施轮询,开发人员可以确保实时数据同步并向用户提供最新的内容。它涉及定期向服务器或数据源发送请求并获取最新信息。Android提供了定时器、线程、后台服务等多种机制来高效地完成轮询。这使开发人员能够设计与远程数据源保持同步的响应式动态应用程序。本文探讨了如何在Android中实现轮询。它涵盖了实现此功能所涉及的关键注意事项和步骤。轮询定期检查更新并从服务器或源检索数据的过程在Android中称为轮询。通过
 如何在Android中实现按下返回键再次退出的功能?Aug 30, 2023 am 08:05 AM
如何在Android中实现按下返回键再次退出的功能?Aug 30, 2023 am 08:05 AM为了提升用户体验并防止数据或进度丢失,Android应用程序开发者必须避免意外退出。他们可以通过加入“再次按返回退出”功能来实现这一点,该功能要求用户在特定时间内连续按两次返回按钮才能退出应用程序。这种实现显著提升了用户参与度和满意度,确保他们不会意外丢失任何重要信息Thisguideexaminesthepracticalstepstoadd"PressBackAgaintoExit"capabilityinAndroid.Itpresentsasystematicguid
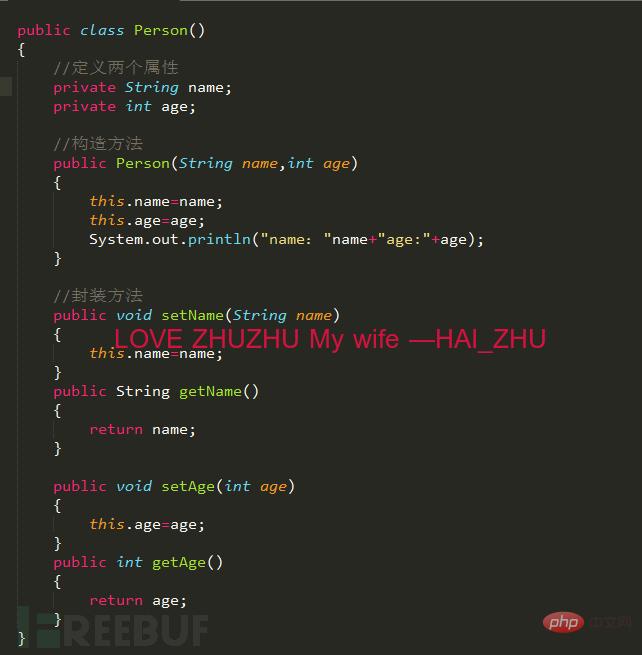 Android逆向中smali复杂类实例分析May 12, 2023 pm 04:22 PM
Android逆向中smali复杂类实例分析May 12, 2023 pm 04:22 PM1.java复杂类如果有什么地方不懂,请看:JAVA总纲或者构造方法这里贴代码,很简单没有难度。2.smali代码我们要把java代码转为smali代码,可以参考java转smali我们还是分模块来看。2.1第一个模块——信息模块这个模块就是基本信息,说明了类名等,知道就好对分析帮助不大。2.2第二个模块——构造方法我们来一句一句解析,如果有之前解析重复的地方就不再重复了。但是会提供链接。.methodpublicconstructor(Ljava/lang/String;I)V这一句话分为.m
 如何在2023年将 WhatsApp 从安卓迁移到 iPhone 15?Sep 22, 2023 pm 02:37 PM
如何在2023年将 WhatsApp 从安卓迁移到 iPhone 15?Sep 22, 2023 pm 02:37 PM如何将WhatsApp聊天从Android转移到iPhone?你已经拿到了新的iPhone15,并且你正在从Android跳跃?如果是这种情况,您可能还对将WhatsApp从Android转移到iPhone感到好奇。但是,老实说,这有点棘手,因为Android和iPhone的操作系统不兼容。但不要失去希望。这不是什么不可能完成的任务。让我们在本文中讨论几种将WhatsApp从Android转移到iPhone15的方法。因此,坚持到最后以彻底学习解决方案。如何在不删除数据的情况下将WhatsApp
 同样基于linux为什么安卓效率低Mar 15, 2023 pm 07:16 PM
同样基于linux为什么安卓效率低Mar 15, 2023 pm 07:16 PM原因:1、安卓系统上设置了一个JAVA虚拟机来支持Java应用程序的运行,而这种虚拟机对硬件的消耗是非常大的;2、手机生产厂商对安卓系统的定制与开发,增加了安卓系统的负担,拖慢其运行速度影响其流畅性;3、应用软件太臃肿,同质化严重,在一定程度上拖慢安卓手机的运行速度。
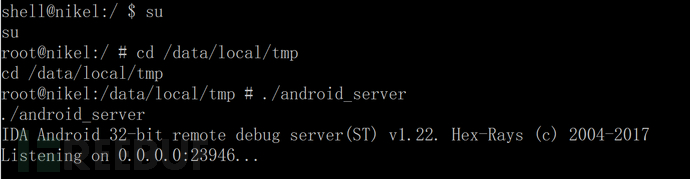 Android中动态导出dex文件的方法是什么May 30, 2023 pm 04:52 PM
Android中动态导出dex文件的方法是什么May 30, 2023 pm 04:52 PM1.启动ida端口监听1.1启动Android_server服务1.2端口转发1.3软件进入调试模式2.ida下断2.1attach附加进程2.2断三项2.3选择进程2.4打开Modules搜索artPS:小知识Android4.4版本之前系统函数在libdvm.soAndroid5.0之后系统函数在libart.so2.5打开Openmemory()函数在libart.so中搜索Openmemory函数并且跟进去。PS:小知识一般来说,系统dex都会在这个函数中进行加载,但是会出现一个问题,后
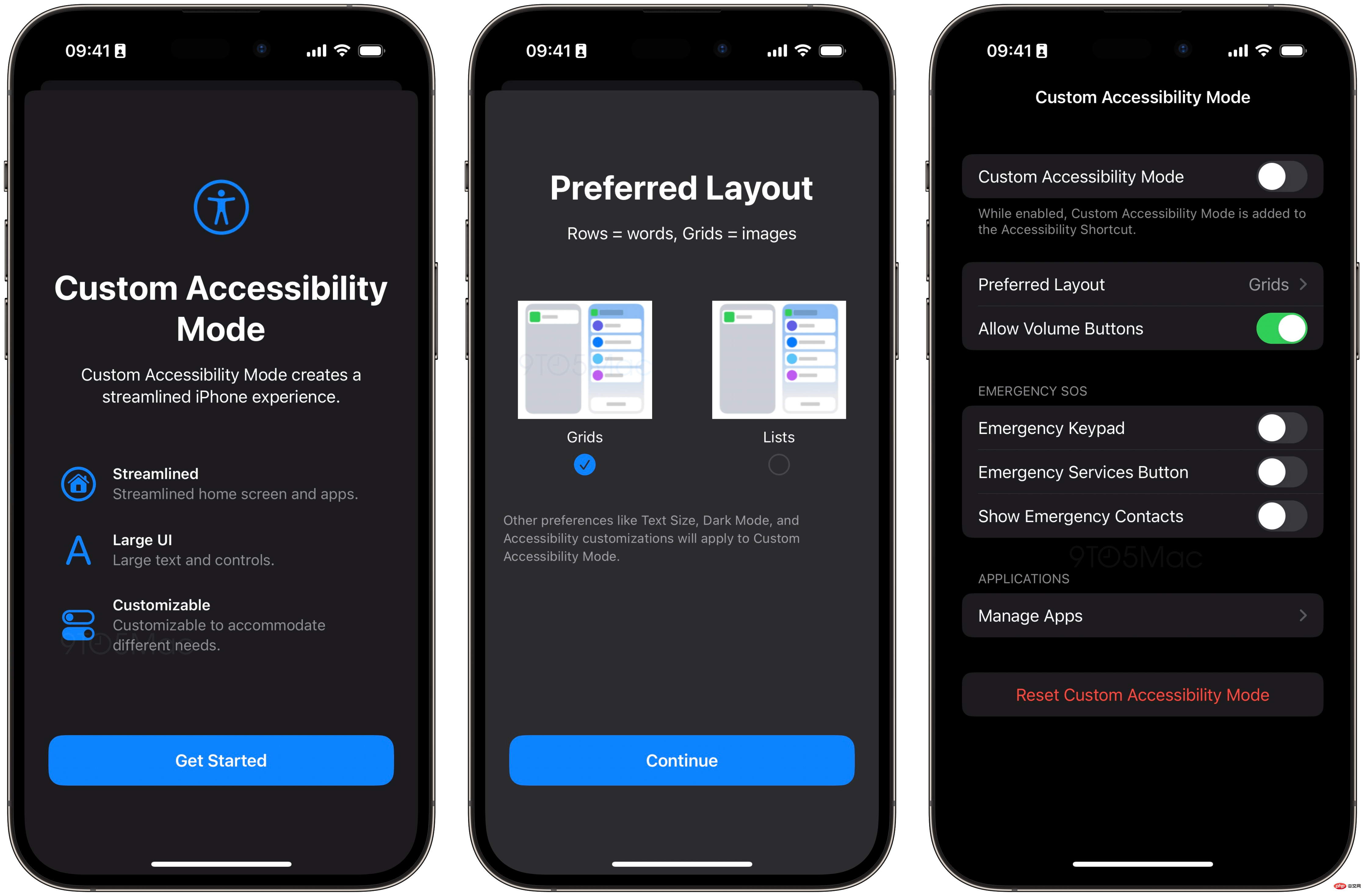 iOS 16.2 引入“自定义辅助功能模式”,为 iPhone 和 iPad 提供简化的体验Apr 13, 2023 am 11:07 AM
iOS 16.2 引入“自定义辅助功能模式”,为 iPhone 和 iPad 提供简化的体验Apr 13, 2023 am 11:07 AM苹果公司周二向开发人员发布了iOS 16.2 beta 2,因为该公司准备在 12 月向公众提供更新。正式地,它添加了新的 Freeform 协作应用程序和对 Home 应用程序的改进。在后台,9to5Mac发现 Apple 一直在开发一种新的“自定义辅助功能模式”,该模式将为 iPhone 和 iPad 提供“流线型”体验。自定义辅助功能模式这种代号为“Clarity”的新模式基本上用更精简的模式取代了 Springboard(这是 iOS 的主要界面)。该功能在当前测试版中仍对用户不可用,将


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools






