 Web Front-end
Web Front-end JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial Understand the setTimeout and setInterval_javascript techniques in javascript timers
Understand the setTimeout and setInterval_javascript techniques in javascript timersUnderstand the setTimeout and setInterval_javascript techniques in javascript timers
1. Explanation
1. Overview
setTimeout: Call a function or execute a code fragment after the specified delay time
setInterval: Periodically call a function or execute a piece of code.
2. Grammar
setTimeout:
var timeoutID = window.setTimeout(func, delay, [param1, param2, ...]); var timeoutID = window.setTimeout(code, delay);
- timeoutID is the numeric ID of the delay operation. This ID can then be used as a parameter of the window.clearTimeout method
- func is the function you want to execute after delay milliseconds
- code In the second syntax, it refers to the code you want to execute after delay milliseconds
- delay is the number of milliseconds of delay (one second is equal to 1000 milliseconds). The function call will occur after this delay. But the actual delay time may be slightly longer
- Standard browsers and IE10 support the function of passing extra parameters to the delayed function in the first syntax
setInterval
var intervalID = window.setInterval(func, delay[, param1, param2, ...]); var intervalID = window.setInterval(code, delay);
- intervalID is the unique identifier of this repeated operation and can be passed as a parameter to clearInterval().
- func is the function you want to call repeatedly.
- code is another syntax application, which refers to a code consisting of a string that you want to execute repeatedly
- delay is the number of milliseconds of each delay (one second equals 1000 milliseconds), after which each call to the function will occur. Like setTimeout, the actual delay may be slightly longer.
- Standard browsers and IE10 support the function of passing extra parameters to the delayed function in the first syntax
<script type="text/javascript">
setTimeout( function(param){ alert(param)} , 100, 'ok');
</script>
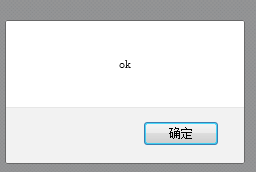
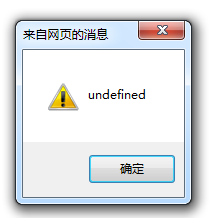
I briefly tested the fifth item, using firefox and IE9 on my computer. The former can pop up ok smoothly, while the latter pops up undefined.
2. “this” question
The code called by setTimeout() runs in an execution environment completely separate from the function in which it is located. This will cause the this keyword contained in these codes to point to the window (global object) object, which is different from the expected this The values are not the same. The situation with setInterval is similar.
<script type="text/javascript">
//this指向window
function shape(name) {
this.name = name;
this.timer = function(){alert('my shape is '+this.name)};
setTimeout(this.timer, 50);
}
new shape('rectangle');
</script>
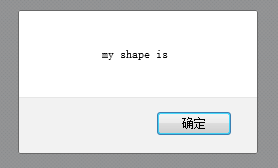
It was not passed in. I tried it with chrome, firefox and IE9, and the result was the same.
Solution 1:
<script type="text/javascript">
function shape(name) {
this.name = name;
this.timer = function(){alert('my shape is '+this.name)};
var _this = this;
setTimeout(function() {_this.timer.call(_this)}, 50);
}
new shape('rectangle');
</script>
Set a local variable _this, and then put it in the function variable of setTimeout. The timer executes call or apply to set the this value.
function can call the local variable _this, thanks to Javascript closures. It involves scope chain and other knowledge. If you are interested, you can learn about it yourself. I will not go into it here.
Solution 2:
This method is a bit fancy. Customized setTimeout and setInterval. It also extends the problem that lower versions of IE browsers do not support passing additional parameters to the delay function.
<script type="text/javascript">
//自定义setTimeout与setInterval
var __nativeST__ = window.setTimeout, __nativeSI__ = window.setInterval;
window.setTimeout = function (vCallback, nDelay /*, argumentToPass1, argumentToPass2, etc. */) {
var oThis = this, aArgs = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 2);
return __nativeST__(vCallback instanceof Function ? function () {
vCallback.apply(oThis, aArgs);
} : vCallback, nDelay);
};
window.setInterval = function (vCallback, nDelay /*, argumentToPass1, argumentToPass2, etc. */) {
var oThis = this, aArgs = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 2);
return __nativeSI__(vCallback instanceof Function ? function () {
vCallback.apply(oThis, aArgs);
} : vCallback, nDelay);
};
function shape(name) {
this.name = name;
this.timer = function(other){
alert('my shape is '+this.name);
alert('extra param is '+ other);
};
}
var rectangle = new shape('rectangle');
setTimeout.call(rectangle, rectangle.timer, 50, 'other');
</script>
1. Set local variables and assign values to native setTimeout and setInterval
2. Extend setTimeout and setInterval, aArgs obtains additional parameter arrays by splitting the arguments variable
3. Use vCallback instanceof Function to determine whether this is a function or code. If it is a function, use apply to execute it
4. SetTimeout is executed with call, and sets this object, as well as other func, delay and other parameters
5. By extending setTimeout, browsers with lower versions of IE can also execute additional parameters
3. The difference between setTimeout and setInterval
<script type="text/javascript">
setTimeout(function(){
/* Some long block of code... */
setTimeout(arguments.callee, 100);
}, 10);
setInterval(function(){
/* Some long block of code... */
}, 100);
</script>
看上去,两个功能是差不多的,但是里面其实是不一样的。
setTimeout回调函数的执行和上一次执行之间的间隔至少有100ms(可能会更多,但不会少于100ms)
setInterval的回调函数将尝试每隔100ms执行一次,不论上次是否执行完毕,时间间隔理论上是会
setInterval:
<script type="text/javascript">
function sleep(ms) {
var start = new Date();
while (new Date() - start <= ms) {}
}
var endTime = null;
var i = 0;
setInterval(count, 100);
function count() {
var elapsedTime = endTime ? (new Date() - endTime) : 100;
i++;
console.log('current count: ' + i + '.' + 'elapsed time: ' + elapsedTime + 'ms');
sleep(200);
endTime = new Date();
}
</script>
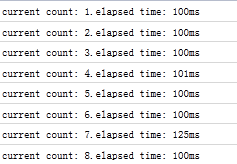
从firefox的firebug可以查看到,时间间隔很不规则。
情况大致是这样的:由于count函数的执行时间远大于setInterval的定时间隔,那么定时触发线程就会源源不断的产生异步定时事件,并放到任务队列尾而不管它们是否已被处理,但一旦一个定时事件任务处理完,这些排列中的剩余定时事件就依次不间断的被执行。
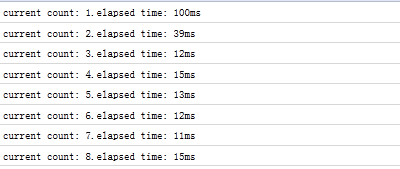
setTimeout:
<script type="text/javascript">
function sleep(ms) {
var start = new Date();
while (new Date() - start <= ms) {}
}
var endTime = null;
var i = 0;
setTimeout(count, 100);
function count() {
var elapsedTime = endTime ? (new Date() - endTime) : 100;
i++;
console.log('current count: ' + i + '.' + 'elapsed time: ' + elapsedTime + 'ms');
sleep(200);
endTime = new Date();
setTimeout(count, 100);
}
</script>
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家学习javascript定时器有所帮助。
 JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use CasesApr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use CasesApr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AMThe main uses of JavaScript in web development include client interaction, form verification and asynchronous communication. 1) Dynamic content update and user interaction through DOM operations; 2) Client verification is carried out before the user submits data to improve the user experience; 3) Refreshless communication with the server is achieved through AJAX technology.
 Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation DetailsApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation DetailsApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AMUnderstanding how JavaScript engine works internally is important to developers because it helps write more efficient code and understand performance bottlenecks and optimization strategies. 1) The engine's workflow includes three stages: parsing, compiling and execution; 2) During the execution process, the engine will perform dynamic optimization, such as inline cache and hidden classes; 3) Best practices include avoiding global variables, optimizing loops, using const and lets, and avoiding excessive use of closures.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of UseApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of UseApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AMPython is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AMPython and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AMThe shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AMDifferent JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AMJavaScript's applications in the real world include server-side programming, mobile application development and Internet of Things control: 1. Server-side programming is realized through Node.js, suitable for high concurrent request processing. 2. Mobile application development is carried out through ReactNative and supports cross-platform deployment. 3. Used for IoT device control through Johnny-Five library, suitable for hardware interaction.
 Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AMI built a functional multi-tenant SaaS application (an EdTech app) with your everyday tech tool and you can do the same. First, what’s a multi-tenant SaaS application? Multi-tenant SaaS applications let you serve multiple customers from a sing


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools




