jQuery is indeed a very good lightweight JS framework that can help us quickly develop JS applications and, to a certain extent, change our habit of writing JavaScript code.
Without further ado, let’s get straight to the point. Let’s first look at some simple methods. These methods are all methods that encapsulate jQuery.ajax() for our convenience. Of course, if you want to handle complex logic, you still need to Using jQuery.ajax() (this will be discussed later).
1. load( url, [data], [callback] ): Load the remote HTML file code and insert it into the DOM.
url (String): URL address of the requested HTML page.
data (Map): (optional parameter) key/value data sent to the server.
callback (Callback): (optional parameter) The callback function when the request is completed (does not need to be successful).
This method uses the GET method by default. If the [data] parameter has data passed in, it will be automatically converted to the POST method. In jQuery 1.2, you can specify a selector to filter the loaded HTML document, and only the filtered HTML code will be inserted into the DOM. The syntax is "url #some > selector".
This method can easily dynamically load some HTML files, such as forms.
Sample code:
$(".ajax. load").load("http://www.cnblogs.com/QLeelulu/archive/2008/03/30/1130270.html .post",
function (responseText, textStatus, XMLHttpRequest){
this ;//Here this points to the current DOM object, that is, $(".ajax.load")[0]
//alert(responseText);//The content returned by the request
//alert( textStatus);//Request status: success, error
//alert(XMLHttpRequest);//XMLHttpRequest object
});
The results will be displayed here.
Note: I don’t know why writing absolute paths in URLs causes errors in FF. If you know, please let me know. The get() and post() examples below use absolute paths, so under FF you will get errors and will not see the results returned. There are also get() and post() examples that are called cross-domain. I found that there was no way to get the results after uploading them, so I removed the run button.
2. jQuery.get( url, [data], [callback] ): Use GET method to make asynchronous requests
Parameters:
url (String): URL address to send the request.
data (Map): (Optional) The data to be sent to the server, expressed in the form of Key/value pairs, will be appended to the request URL as QueryString.
callback (Function): (optional) Callback function when loading is successful (this method is called only when the return status of Response is success).
This is a simple GET request function to replace the complex $.ajax. The callback function can be called when the request is successful. If you need to execute a function on error, use $.ajax. Sample code:
$.get("./Ajax.aspx", {Action:"get",Name:"lulu"}, function (data, textStatus){
, jsonObj, html, text, etc.
this; // Here this points to the option configuration information of the Ajax request, please refer to the picture below
alert(data);
alert(textStatus) ; :
This in the jQuery.get() callback function points to the option configuration information of the Ajax request:
 3. jQuery.post( url, [data ], [callback], [type] ): Use POST method to make asynchronous requests Parameters:
3. jQuery.post( url, [data ], [callback], [type] ): Use POST method to make asynchronous requests Parameters: url (String): URL address to send the request.
data (Map): (Optional) Required The data sent to the server is expressed in the form of Key/value pairs.
callback (Function): (optional) Callback function when loading is successful (this method is called only when the return status of Response is success).
type (String): (optional) The official description is: Type of data to be sent. It should actually be the type of client request (JSON, XML, etc.)
This is a simple POST request function to replace the complex $.ajax. The callback function can be called when the request is successful. If you need to execute a function on error, use $.ajax. Sample code:
Ajax.aspx:
Response.ContentType = "application/json";
Response.Write("{result: '" Request["Name"] ",Hello! (This message From server)'}");jQuery code:
$.post("Ajax.aspx", { Action: "post", Name: "lulu" },
function (data, textStatus){
// data can be xmlDoc, jsonObj, html, text, etc.
// this; // For the option configuration information of this Ajax request, please refer to this mentioned in jQuery.get()
alert( data.result);
}, "json"); Click to submit:
Here the request format is set to "json":
 If you set The format of the request is "json", and you have not set the ContentType returned by the Response to: Response.ContentType = "application/json"; then you will not be able to capture the returned data. Note that alert(data.result); since the Accept header is set to "json", the data returned here is an object, and there is no need to use eval() to convert it into an object.
If you set The format of the request is "json", and you have not set the ContentType returned by the Response to: Response.ContentType = "application/json"; then you will not be able to capture the returned data. Note that alert(data.result); since the Accept header is set to "json", the data returned here is an object, and there is no need to use eval() to convert it into an object. 4. jQuery.getScript( url, [callback] ): Request to load and execute a JavaScript file through GET method.
Parameters
url (String): The address of the JS file to be loaded.
callback (Function): (optional) Callback function after successful loading.
Before jQuery 1.2, getScript could only call JS files in the same domain. In 1.2, you can call JavaScript files across domains. Note: Safari 2 or earlier cannot execute scripts synchronously in the global scope.If you add a script via getScript, please add a delay function.
This method can be used, for example, to load the JS files required by the editor when only the editor is focus(). Here are some sample codes:
Load and execute test.js.
jQuery code:
$.getScript("test.js");
-------------------------- -------------------------------------------------- ---
Load and execute AjaxEvent.js, and display information after success.
jQuery code:
$.getScript("AjaxEvent.js", function(){
alert("AjaxEvent.js is loaded and executed. Click the Get or Post button above to see if What's the difference? ");
});
After loading, please click the Load request above again to see the difference.
jQuery Ajax Events
Ajax requests generate several different events that we can subscribe to and process our logic in them. There are two types of Ajax events in jQuery: local events and global events.
Local events are defined within the method during each Ajax request, for example:
$.ajax({
beforeSend: function(){
// Handle the beforeSend event
},
complete: function(){
// Handle the complete event
}
// ...
}); The global event is triggered by every Ajax request. It broadcasts to all elements in the DOM. The script loaded in the getScript() example above is the global Ajax event. Global events can be defined as follows:
$("#loading").bind("ajaxSend", function(){
$(this).show();
}).bind("ajaxComplete" , function(){
$(this).hide();
}); or:
$("#loading").ajaxStart(function(){
$(this). show();
}); We can disable global events for specific requests by setting the global option:
$.ajax({
url: "test.html",
global: false,// Disable global Ajax events.
// ...
}); The following is the complete list of Ajax events officially given by jQuery:
ajaxStart (Global Event)
This event is broadcast if an Ajax request is started and no other Ajax requests are currently running.
beforeSend (Local Event)
This event, which is triggered before an Ajax request is started, allows you to modify the XMLHttpRequest object (setting additional headers, if need be.)
ajaxSend (Global Event)
This global event is also triggered before the request is run.
success (Local Event)
This event is only called if the request was successful (no errors from the server, no errors with the data).
ajaxSuccess (Global Event)
This event is also only called if the request was successful.
error (Local Event)
This event is only called if an error occurred with the request (you can never have both an error and a success callback with a request).
ajaxError (Global Event)
This global event behaves the same as the local error event.
complete (Local Event)
This event is called regardless of if the request was successful, or not. You will always receive a complete callback, even for synchronous requests.
ajaxComplete (Global Event)
This event behaves the same as the complete event and will be triggered every time an Ajax request finishes.
ajaxStop (Global Event)
This global event is triggered if there are no more Ajax requests being processed .
Please refer to the API documentation for specific global events.
Okay, let’s start with the most powerful Ajax request method in jQuery, $.ajax();
jQuery.ajax( options ): load remote data through HTTP requests
This is the underlying AJAX implementation of jQuery . For simple and easy-to-use high-level implementations, see $.get, $.post, etc.
$.ajax() returns the XMLHttpRequest object it created. In most cases you will not need to manipulate this object directly, but in special cases it can be used to manually terminate the request.
Note: If you specify the dataType option, please ensure that the server returns the correct MIME information (e.g. xml returns "text/xml"). Incorrect MIME types can cause unpredictable errors. See Specifying the Data Type for AJAX Requests.
When setting the datatype to 'script', all remote (not in the same domain) POST requests will be converted to GET.
$.ajax() has only one parameter: parameter key/value object, including each configuration and callback function information. See detailed parameter options below.
In jQuery 1.2, you can load JSON data across domains. When using it, you need to set the data type to JSONP. When calling a function using JSONP format, such as "myurl?callback=?" jQuery will automatically replace ? with the correct function name to execute the callback function. When the data type is set to "jsonp", jQuery will automatically call the callback function. (I don’t understand this very well)
Parameter list:
| Name | Type | Description |
| url | String | (Default: current page address) The address to send the request. |
| type | String | (默认: "GET") 请求方式 ("POST" 或 "GET"), 默认为 "GET"。注意:其它 HTTP 请求方法,如 PUT 和 DELETE 也可以使用,但仅部分浏览器支持。 |
| timeout | Number | 设置请求超时时间(毫秒)。此设置将覆盖全局设置。 |
| async | Boolean | (默认: true) 默认设置下,所有请求均为异步请求。如果需要发送同步请求,请将此选项设置为 false。注意,同步请求将锁住浏览器,用户其它操作必须等待请求完成才可以执行。 |
| beforeSend | Function | 发送请求前可修改 XMLHttpRequest 对象的函数,如添加自定义 HTTP 头。XMLHttpRequest 对象是唯一的参数。<span style="COLOR: #0000ff">function</span> (XMLHttpRequest) {
<span style="COLOR: #0000ff">this</span>; <span style="COLOR: #008000">// the options for this ajax request</span>
}
|
| cache | Boolean | (默认: true) jQuery 1.2 新功能,设置为 false 将不会从浏览器缓存中加载请求信息。 |
| complete | Function | 请求完成后回调函数 (请求成功或失败时均调用)。参数: XMLHttpRequest 对象,成功信息字符串。<span style="COLOR: #0000ff">function</span> (XMLHttpRequest, textStatus) {
<span style="COLOR: #0000ff">this</span>; <span style="COLOR: #008000">// the options for this ajax request</span>
}
|
| contentType | String | (默认: "application/x-www-form-urlencoded") 发送信息至服务器时内容编码类型。默认值适合大多数应用场合。 |
| data | Object, String |
发送到服务器的数据。将自动转换为请求字符串格式。GET 请求中将附加在 URL 后。查看 processData 选项说明以禁止此自动转换。必须为 Key/Value 格式。如果为数组,jQuery 将自动为不同值对应同一个名称。如 {foo:["bar1", "bar2"]} 转换为 '&foo=bar1&foo=bar2'。 |
| dataType | String |
预期服务器返回的数据类型。如果不指定,jQuery 将自动根据 HTTP 包 MIME 信息返回 responseXML 或 responseText,并作为回调函数参数传递,可用值: "xml": 返回 XML 文档,可用 jQuery 处理。 "html": 返回纯文本 HTML 信息;包含 script 元素。 "script": 返回纯文本 JavaScript 代码。不会自动缓存结果。 "json": 返回 JSON 数据 。 "jsonp": JSONP 格式。使用 JSONP 形式调用函数时,如 "myurl?callback=?" jQuery 将自动替换 ? 为正确的函数名,以执行回调函数。 |
| error | Function | (默认: 自动判断 (xml 或 html)) 请求失败时将调用此方法。这个方法有三个参数:XMLHttpRequest 对象,错误信息,(可能)捕获的错误对象。<span style="COLOR: #0000ff">function</span> (XMLHttpRequest, textStatus, errorThrown) {
<span style="COLOR: #008000">// 通常情况下textStatus和errorThown只有其中一个有值 </span>
<span style="COLOR: #0000ff">this</span>; <span style="COLOR: #008000">// the options for this ajax request</span>
}
|
| global | Boolean | (默认: true) 是否触发全局 AJAX 事件。设置为 false 将不会触发全局 AJAX 事件,如 ajaxStart 或 ajaxStop 。可用于控制不同的Ajax事件 |
| ifModified | Boolean | (默认: false) 仅在服务器数据改变时获取新数据。使用 HTTP 包 Last-Modified 头信息判断。 |
| processData | Boolean | (默认: true) 默认情况下,发送的数据将被转换为对象(技术上讲并非字符串) 以配合默认内容类型 "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"。如果要发送 DOM 树信息或其它不希望转换的信息,请设置为 false。 |
| success | Function | 请求成功后回调函数。这个方法有两个参数:服务器返回数据,返回状态<span style="COLOR: #0000ff">function</span> (data, textStatus) {
<span style="COLOR: #008000">// data could be xmlDoc, jsonObj, html, text, etc...</span>
<span style="COLOR: #0000ff">this</span>; <span style="COLOR: #008000">// the options for this ajax request</span>
}
|
Please read the above parameter list carefully. If you want to use jQuery for Ajax development, you must be familiar with these parameters.
Sample code to get the article title on the home page of the blog:
$.ajax({
type: "get",
url: "http://www.cnblogs.com/rss",
beforeSend: function(XMLHttpRequest){
//ShowLoading();
success: function(data, textStatus){
$(" .ajax.ajaxResult").html ("");
$("item",data).each(function(i, domEle){
$(".ajax.ajaxResult").append("
}); ();
},
error: function(){ ;
Others
jQuery.ajaxSetup( options ): Set global AJAX default options.
Set the default address of AJAX requests to "/xmlhttp/", disable triggering of global AJAX events, and use POST instead of the default GET method. Subsequent AJAX requests will not set any option parameters.
jQuery code:
$.ajaxSetup({
url: "/xmlhttp/",
global: false,
type: "POST"
});
$ .ajax({ data: myData });
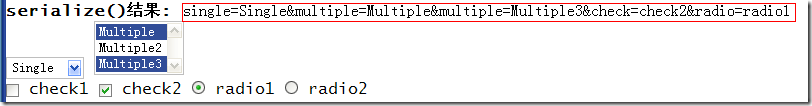
serialize() and serializeArray()
serialize(): The content of the sequence table is a string.
serializeArray(): Serialize table elements (similar to '.serialize()' method) and return JSON data structure data.
Example:
HTML code:
Results:
serializeArray() The result is:
Some resources
A jQuery Ajax Form form plug-in:
http://www.malsup.com/jquery/form/ A site that specializes in generating Loading images:
http://ajaxload.info/ If you think those Loading images are cool, you can post them here for everyone’s convenience. , Gaga
 JavaScript in Action: Real-World Examples and ProjectsApr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AM
JavaScript in Action: Real-World Examples and ProjectsApr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AMJavaScript's application in the real world includes front-end and back-end development. 1) Display front-end applications by building a TODO list application, involving DOM operations and event processing. 2) Build RESTfulAPI through Node.js and Express to demonstrate back-end applications.
 JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use CasesApr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use CasesApr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AMThe main uses of JavaScript in web development include client interaction, form verification and asynchronous communication. 1) Dynamic content update and user interaction through DOM operations; 2) Client verification is carried out before the user submits data to improve the user experience; 3) Refreshless communication with the server is achieved through AJAX technology.
 Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation DetailsApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation DetailsApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AMUnderstanding how JavaScript engine works internally is important to developers because it helps write more efficient code and understand performance bottlenecks and optimization strategies. 1) The engine's workflow includes three stages: parsing, compiling and execution; 2) During the execution process, the engine will perform dynamic optimization, such as inline cache and hidden classes; 3) Best practices include avoiding global variables, optimizing loops, using const and lets, and avoiding excessive use of closures.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of UseApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of UseApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AMPython is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AMPython and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AMThe shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AMDifferent JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AMJavaScript's applications in the real world include server-side programming, mobile application development and Internet of Things control: 1. Server-side programming is realized through Node.js, suitable for high concurrent request processing. 2. Mobile application development is carried out through ReactNative and supports cross-platform deployment. 3. Used for IoT device control through Johnny-Five library, suitable for hardware interaction.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use