 Web Front-end
Web Front-end JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial JavaScript component journey (4): Testing JavaScript components_javascript skills
JavaScript component journey (4): Testing JavaScript components_javascript skillsJavaScript component journey (4): Testing JavaScript components_javascript skills
本期,我们要讨论的话题是 JavaScript 的测试,以检查组件的状态和工作方式是否符合预期,还会介绍一个可以方便编写测试用例的测试方法。这里说的测试当然是使用自动化的测试手段,这是软件质量保证(QA)的重要环节。就本系列文章介绍的 Smart Queue 来说,我们的测试目标包括:
- Task 对象的创建:第二期的代码提供了多种创建方式,需要测试对象创建后的状态。
- Queue 内的任务运行次序:我们提供了两种改变运行次序的方式:优先级和依赖配置,同样也要测试各种配置对次序的影响。
对于第一个目标,只需检查对象创建后的属性是否符合预期即可。我们已经多次提到“符合预期”,断言(Assert)正是为此而设计的。简单的说,断言就是确保所测试的表达式结果为“真”,否则,以某种方式通知测试人员,并帮助其定位断言失败的测试用例。
第二个目标稍稍有点复杂。由于我们在组件编码实现的时候,将排序后的队列(<font face="新宋体">_sorted</font>)隐藏在了闭包中,所以外部是无法访问的。有两种方法可以考虑:(1)重构代码,增加代码的可测试性,又有两种重构方法:(a)设置 debug 开关,打开时将 <font face="新宋体">_sorted</font> 暴露给外部;(b)增加独立文件,以构建的方式拼接代码最终生成一个测试版本。(2)测试行为的结果而不是过程,前一种方法实质上是深入到组件的运行时状态,而这个方法只是检查组件的运行结果。本期选用后一种种测试方式,第一种测试方式留给有兴趣的读者练习:)
需要说明的是,我个人不赞成第一种的方法a. 为什么呢?我先说一下这个任务队列的设计理念:
- 它只是一个队列,只负责“按需”调整任务的运行次序,不关注任务的个体细节。换句话说,它操作整体的任务,而不关心任务具体的行为和表现。
- 它是个安全的队列,使用者(第一期提到的“客户”)可以放心把任务添加进去,不用担心这个任务信息会被其他客户看到。需要说明的是,第二期实现代码中有
<font face="新宋体">SmartQueue.Queue = [[], [], []]</font>, 结果是外部可以访问到队列项。代码仅供介绍之用,你可以安全地删除<font face="新宋体">SmartQueue.Queue = </font>来达成安全控制。
回到刚才讨论的话题,设置 debug 开关后,任务信息就潜在的泄漏可能性。进一步地,继续改造代码也可以达成在使用 debug 开关时的安全性,做法是将开关的控制放在 SmartQueue 的构造函数中,这样要求 SmartQueue 实现 Singleton 模式(见上一篇文章);一旦创建对象后,不允许修改闭包内的 debug 标记。
在编写具体测试代码前,我们设计了一个测试方法,以简化测试代码(主要是用例)的编写。简单地说,就是将测试用例与测试本身的代码分离——前者以语义良好的方式编写,后者是一次性编写,用于处理前者设定的测试用例。用例编写者需要写格式形如这样的代码:
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"><span style="COLOR: #c00000">ul</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0"> </span><span style="COLOR: #0000c0">id</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">=</span><span style="COLOR: #008000">"J_test_cases"</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"><span style="COLOR: #c00000">li</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>
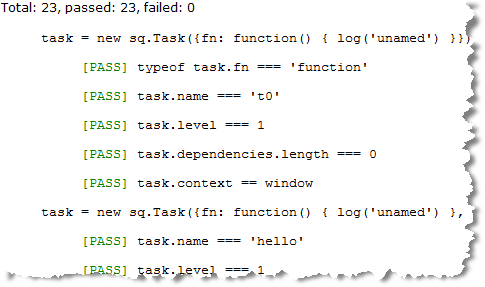
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"><span style="COLOR: #c00000">pre</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>task = new sq.Task({fn: function() { log('unamed') }})<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"></span><span style="COLOR: #c00000">pre</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"><span style="COLOR: #c00000">ul</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"><span style="COLOR: #c00000">li</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>typeof task.fn === 'function'<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"></span><span style="COLOR: #c00000">li</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"><span style="COLOR: #c00000">li</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>task.name === 't0'<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"></span><span style="COLOR: #c00000">li</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"><span style="COLOR: #c00000">li</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>task.level === 1<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"></span><span style="COLOR: #c00000">li</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"><span style="COLOR: #c00000">li</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>task.dependencies.length === 0<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"></span><span style="COLOR: #c00000">li</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"><span style="COLOR: #c00000">li</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>task.context == window<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"></span><span style="COLOR: #c00000">li</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"></span><span style="COLOR: #c00000">ul</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"></span><span style="COLOR: #c00000">li</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"><span style="COLOR: #c00000">li</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"><span style="COLOR: #c00000">pre</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>task = new sq.Task({fn: function() { log('unamed') }, name: 'hello'})<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"></span><span style="COLOR: #c00000">pre</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"><span style="COLOR: #c00000">ul</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"><span style="COLOR: #c00000">li</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>task.name === 'hello'<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"></span><span style="COLOR: #c00000">li</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"><span style="COLOR: #c00000">li</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>task.level === 1<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"></span><span style="COLOR: #c00000">li</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"></span><span style="COLOR: #c00000">ul</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"></span><span style="COLOR: #c00000">li</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span>
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0"></span><span style="COLOR: #c00000">ul</span><span style="COLOR: #b000b0">></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span></span>
ul li pre (CSS 选择器路径,下同)中写要测试的代码,相当于前置操作;ul ul li 中对这个代码进行断言测试,可以编写多条断言。这里建议对基本数据类型使用 <font face="新宋体">===</font> 和 <font face="新宋体">!===</font> 运算符以加强对数据类型的预期判断。
接下来,我们编写两个 helper 方法用来输出和测试:
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0">function</span> log(str) {
node.value += str + <span style="COLOR: #008000">'</span><span style="COLOR: #606060">\n</span><span style="COLOR: #008000">'</span>;
}
<span style="COLOR: #b000b0">function</span> assert(expression) {
<span style="COLOR: #0000c0">var</span> flag;
eval(<span style="COLOR: #008000">'flag = '</span> + expression);
<span style="COLOR: #c00000">return</span> <span style="COLOR: #c00000">typeof</span>(flag) === <span style="COLOR: #008000">'boolean'</span> && flag;
}
<font face="新宋体">log</font> 用来向文本框追加信息,<font face="新宋体">assert</font> 用来测试传入表达式的值。测试方法如下(这里使用了 jQuery):
<span style="COLOR: #0000c0">var</span><span style="COLOR: #606060"> sq = SmartQueue, task, total = </span><span style="COLOR: #008000">0</span><span style="COLOR: #606060">, passed = </span><span style="COLOR: #008000">0</span><span style="COLOR: #606060">, failed = </span><span style="COLOR: #008000">0</span><span style="COLOR: #606060">;</span>
<span style="COLOR: #606060">$</span>(<span style="COLOR: #008000">'#J_test_cases'</span><span style="COLOR: #606060">).children</span>(<span style="COLOR: #606060">).each</span>(<span style="COLOR: #b000b0">function</span>(index)<span style="COLOR: #606060"> </span>{
eval($(<span style="COLOR: #008000">'pre'</span>, <span style="COLOR: #0000c0">this</span>).text());
task.register();
$(<span style="COLOR: #008000">'li'</span>, <span style="COLOR: #0000c0">this</span>).each(<span style="COLOR: #b000b0">function</span>() {
<span style="COLOR: #0000c0">var</span> item = $(<span style="COLOR: #0000c0">this</span>);
<span style="COLOR: #0000c0">var</span> flag = assert(item.text());
<span style="COLOR: #c00000">if</span>(flag) passed ++; <span style="COLOR: #c00000">else</span> failed ++;
item.prepend((flag ? <span style="COLOR: #008000">'<font color="green">[PASS]</font>'</span> : <span style="COLOR: #008000">'<font color="red">[FAIL]</font>'</span>) + <span style="COLOR: #008000">' '</span>);
total++;
}).wrap(<span style="COLOR: #008000">'<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">');
}).end().before('Total: '
+ total + ', passed: '+ passed +', failed: ' + failed + ''); sq.fire();这个结构还可改进一下,比如输出测试说明而不是具体的代码,也可以增加后置操作,这里就不再演示了。你还可以查看完整的测试页面,含有 23 个测试用例和完整的测试实现。
~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Bagua Dividing Line ~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Okay, we’ve come to the end of this series of articles experiencing the joy of thinking and doing, but this is just the beginning. We have gone through the entire process of implementing a small practical component and experienced the excitement of the JavaScript world. Let us move on~
 Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation DetailsApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation DetailsApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AMUnderstanding how JavaScript engine works internally is important to developers because it helps write more efficient code and understand performance bottlenecks and optimization strategies. 1) The engine's workflow includes three stages: parsing, compiling and execution; 2) During the execution process, the engine will perform dynamic optimization, such as inline cache and hidden classes; 3) Best practices include avoiding global variables, optimizing loops, using const and lets, and avoiding excessive use of closures.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of UseApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of UseApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AMPython is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AMPython and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AMThe shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AMDifferent JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AMJavaScript's applications in the real world include server-side programming, mobile application development and Internet of Things control: 1. Server-side programming is realized through Node.js, suitable for high concurrent request processing. 2. Mobile application development is carried out through ReactNative and supports cross-platform deployment. 3. Used for IoT device control through Johnny-Five library, suitable for hardware interaction.
 Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AMI built a functional multi-tenant SaaS application (an EdTech app) with your everyday tech tool and you can do the same. First, what’s a multi-tenant SaaS application? Multi-tenant SaaS applications let you serve multiple customers from a sing
 How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AMThis article demonstrates frontend integration with a backend secured by Permit, building a functional EdTech SaaS application using Next.js. The frontend fetches user permissions to control UI visibility and ensures API requests adhere to role-base


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function




