1、python多进程编程背景
python中的多进程最大的好处就是充分利用多核cpu的资源,不像python中的多线程,受制于GIL的限制,从而只能进行cpu分配,在python的多进程中,适合于所有的场合,基本上能用多线程的,那么基本上就能用多进程。
在进行多进程编程的时候,其实和多线程差不多,在多线程的包threading中,存在一个线程类Thread,在其中有三种方法来创建一个线程,启动线程,其实在多进程编程中,存在一个进程类Process,也可以使用那集中方法来使用;在多线程中,内存中的数据是可以直接共享的,例如list等,但是在多进程中,内存数据是不能共享的,从而需要用单独的数据结构来处理共享的数据;在多线程中,数据共享,要保证数据的正确性,从而必须要有所,但是在多进程中,锁的考虑应该很少,因为进程是不共享内存信息的,进程之间的交互数据必须要通过特殊的数据结构,在多进程中,主要的内容如下图:
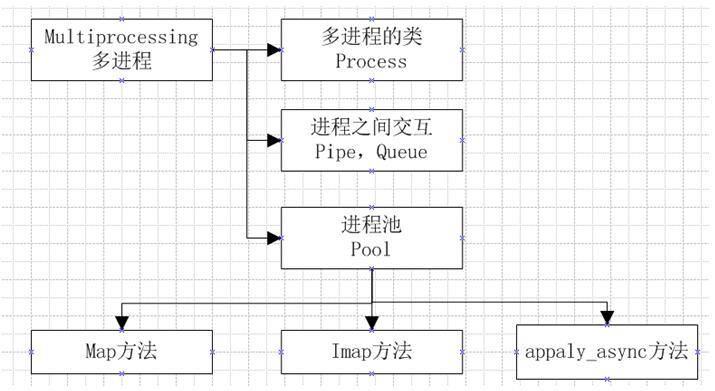
2、多进程的类Process
多进程的类Process和多线程的类Thread差不多的方法,两者的接口基本相同,具体看以下的代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python
from multiprocessing import Process
import os
import time
def func(name):
print 'start a process'
time.sleep(3)
print 'the process parent id :',os.getppid()
print 'the process id is :',os.getpid()
if __name__ =='__main__':
processes = []
for i in range(2):
p = Process(target=func,args=(i,))
processes.append(p)
for i in processes:
i.start()
print 'start all process'
for i in processes:
i.join()
#pass
print 'all sub process is done!'
在上面例子中可以看到,多进程和多线程的API接口是一样一样的,显示创建进程,然后进行start开始运行,然后join等待进程结束。
在需要执行的函数中,打印出了进程的id和pid,从而可以看到父进程和子进程的id号,在linu中,进程主要是使用fork出来的,在创建进程的时候可以查询到父进程和子进程的id号,而在多线程中是无法找到线程的id,执行效果如下:
start all process start a process start a process the process parent id : 8036 the process parent id : 8036 the process id is : 8037 the process id is : 8038 all sub process is done!
在操作系统中查询的id的时候,最好用pstree,清晰:
├─sshd(1508)─┬─sshd(2259)───bash(2261)───python(7520)─┬─python(7521)
│ │ ├─python(7522)
│ │ ├─python(7523)
│ │ ├─python(7524)
│ │ ├─python(7525)
│ │ ├─python(7526)
│ │ ├─python(7527)
│ │ ├─python(7528)
│ │ ├─python(7529)
│ │ ├─python(7530)
│ │ ├─python(7531)
│ │ └─python(7532)
在进行运行的时候,可以看到,如果没有join语句,那么主进程是不会等待子进程结束的,是一直会执行下去,然后再等待子进程的执行。
在多进程的时候,说,我怎么得到多进程的返回值呢?然后写了下面的代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import multiprocessing
class MyProcess(multiprocessing.Process):
def __init__(self,name,func,args):
super(MyProcess,self).__init__()
self.name = name
self.func = func
self.args = args
self.res = ''
def run(self):
self.res = self.func(*self.args)
print self.name
print self.res
return (self.res,'kel')
def func(name):
print 'start process...'
return name.upper()
if __name__ == '__main__':
processes = []
result = []
for i in range(3):
p = MyProcess('process',func,('kel',))
processes.append(p)
for i in processes:
i.start()
for i in processes:
i.join()
for i in processes:
result.append(i.res)
for i in result:
print i
尝试从结果中返回值,从而在主进程中得到子进程的返回值,然而,,,并没有结果,后来一想,在进程中,进程之间是不共享内存的 ,那么使用list来存放数据显然是不可行的,进程之间的交互必须依赖于特殊的数据结构,从而以上的代码仅仅是执行进程,不能得到进程的返回值,但是以上代码修改为线程,那么是可以得到返回值的。
3、进程间的交互Queue
进程间交互的时候,首先就可以使用在多线程里面一样的Queue结构,但是在多进程中,必须使用multiprocessing里的Queue,代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import multiprocessing
class MyProcess(multiprocessing.Process):
def __init__(self,name,func,args):
super(MyProcess,self).__init__()
self.name = name
self.func = func
self.args = args
self.res = ''
def run(self):
self.res = self.func(*self.args)
def func(name,q):
print 'start process...'
q.put(name.upper())
if __name__ == '__main__':
processes = []
q = multiprocessing.Queue()
for i in range(3):
p = MyProcess('process',func,('kel',q))
processes.append(p)
for i in processes:
i.start()
for i in processes:
i.join()
while q.qsize() > 0:
print q.get()
其实这个是上面例子的改进,在其中,并没有使用什么其他的代码,主要就是使用Queue来保存数据,从而可以达到进程间交换数据的目的。
在进行使用Queue的时候,其实用的是socket,感觉,因为在其中使用的还是发送send,然后是接收recv。
在进行数据交互的时候,其实是父进程和所有的子进程进行数据交互,所有的子进程之间基本是没有交互的,除非,但是,也是可以的,例如,每个进程去Queue中取数据,但是这个时候应该是要考虑锁,不然可能会造成数据混乱。
4、 进程之间交互Pipe
在进程之间交互数据的时候还可以使用Pipe,代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import multiprocessing
class MyProcess(multiprocessing.Process):
def __init__(self,name,func,args):
super(MyProcess,self).__init__()
self.name = name
self.func = func
self.args = args
self.res = ''
def run(self):
self.res = self.func(*self.args)
def func(name,q):
print 'start process...'
child_conn.send(name.upper())
if __name__ == '__main__':
processes = []
parent_conn,child_conn = multiprocessing.Pipe()
for i in range(3):
p = MyProcess('process',func,('kel',child_conn))
processes.append(p)
for i in processes:
i.start()
for i in processes:
i.join()
for i in processes:
print parent_conn.recv()
在以上代码中,主要是使用Pipe中返回的两个socket来进行传输和接收数据,在父进程中,使用的是parent_conn,在子进程中使用的是child_conn,从而子进程发送数据的方法send,而在父进程中进行接收方法recv
最好的地方在于,明确的知道收发的次数,但是如果某个出现异常,那么估计pipe不能使用了。
5、进程池pool
其实在使用多进程的时候,感觉使用pool是最方便的,在多线程中是不存在pool的。
在使用pool的时候,可以限制每次的进程数,也就是剩余的进程是在排队,而只有在设定的数量的进程在运行,在默认的情况下,进程是cpu的个数,也就是根据multiprocessing.cpu_count()得出的结果。
在poo中,有两个方法,一个是map一个是imap,其实这两方法超级方便,在执行结束之后,可以得到每个进程的返回结果,但是缺点就是每次的时候,只能有一个参数,也就是在执行的函数中,最多是只有一个参数的,否则,需要使用组合参数的方法,代码如下所示:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import multiprocessing
def func(name):
print 'start process'
return name.upper()
if __name__ == '__main__':
p = multiprocessing.Pool(5)
print p.map(func,['kel','smile'])
for i in p.imap(func,['kel','smile']):
print i
在使用map的时候,直接返回的一个是一个list,从而这个list也就是函数执行的结果,而在imap中,返回的是一个由结果组成的迭代器,如果需要使用多个参数的话,那么估计需要*args,从而使用参数args。
在使用apply.async的时候,可以直接使用多个参数,如下所示:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import multiprocessing
import time
def func(name):
print 'start process'
time.sleep(2)
return name.upper()
if __name__ == '__main__':
results = []
p = multiprocessing.Pool(5)
for i in range(7):
res = p.apply_async(func,args=('kel',))
results.append(res)
for i in results:
print i.get(2.1)
在进行得到各个结果的时候,注意使用了一个list来进行append,要不然在得到结果get的时候会阻塞进程,从而将多进程编程了单进程,从而使用了一个list来存放相关的结果,在进行得到get数据的时候,可以设置超时时间,也就是get(timeout=5),这种设置。
总结:
在进行多进程编程的时候,注意进程之间的交互,在执行函数之后,如何得到执行函数的结果,可以使用特殊的数据结构,例如Queue或者Pipe或者其他,在使用pool的时候,可以直接得到结果,map和imap都是直接得到一个list和可迭代对象,而apply_async得到的结果需要用一个list装起来,然后得到每个结果。
以上这篇深入理解python多进程编程就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
 Learning Python: Is 2 Hours of Daily Study Sufficient?Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Learning Python: Is 2 Hours of Daily Study Sufficient?Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AMIs it enough to learn Python for two hours a day? It depends on your goals and learning methods. 1) Develop a clear learning plan, 2) Select appropriate learning resources and methods, 3) Practice and review and consolidate hands-on practice and review and consolidate, and you can gradually master the basic knowledge and advanced functions of Python during this period.
 Python for Web Development: Key ApplicationsApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python for Web Development: Key ApplicationsApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AMKey applications of Python in web development include the use of Django and Flask frameworks, API development, data analysis and visualization, machine learning and AI, and performance optimization. 1. Django and Flask framework: Django is suitable for rapid development of complex applications, and Flask is suitable for small or highly customized projects. 2. API development: Use Flask or DjangoRESTFramework to build RESTfulAPI. 3. Data analysis and visualization: Use Python to process data and display it through the web interface. 4. Machine Learning and AI: Python is used to build intelligent web applications. 5. Performance optimization: optimized through asynchronous programming, caching and code
 Python vs. C : Exploring Performance and EfficiencyApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Exploring Performance and EfficiencyApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AMPython is better than C in development efficiency, but C is higher in execution performance. 1. Python's concise syntax and rich libraries improve development efficiency. 2.C's compilation-type characteristics and hardware control improve execution performance. When making a choice, you need to weigh the development speed and execution efficiency based on project needs.
 Python in Action: Real-World ExamplesApr 18, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Python in Action: Real-World ExamplesApr 18, 2025 am 12:18 AMPython's real-world applications include data analytics, web development, artificial intelligence and automation. 1) In data analysis, Python uses Pandas and Matplotlib to process and visualize data. 2) In web development, Django and Flask frameworks simplify the creation of web applications. 3) In the field of artificial intelligence, TensorFlow and PyTorch are used to build and train models. 4) In terms of automation, Python scripts can be used for tasks such as copying files.
 Python's Main Uses: A Comprehensive OverviewApr 18, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Python's Main Uses: A Comprehensive OverviewApr 18, 2025 am 12:18 AMPython is widely used in data science, web development and automation scripting fields. 1) In data science, Python simplifies data processing and analysis through libraries such as NumPy and Pandas. 2) In web development, the Django and Flask frameworks enable developers to quickly build applications. 3) In automated scripts, Python's simplicity and standard library make it ideal.
 The Main Purpose of Python: Flexibility and Ease of UseApr 17, 2025 am 12:14 AM
The Main Purpose of Python: Flexibility and Ease of UseApr 17, 2025 am 12:14 AMPython's flexibility is reflected in multi-paradigm support and dynamic type systems, while ease of use comes from a simple syntax and rich standard library. 1. Flexibility: Supports object-oriented, functional and procedural programming, and dynamic type systems improve development efficiency. 2. Ease of use: The grammar is close to natural language, the standard library covers a wide range of functions, and simplifies the development process.
 Python: The Power of Versatile ProgrammingApr 17, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python: The Power of Versatile ProgrammingApr 17, 2025 am 12:09 AMPython is highly favored for its simplicity and power, suitable for all needs from beginners to advanced developers. Its versatility is reflected in: 1) Easy to learn and use, simple syntax; 2) Rich libraries and frameworks, such as NumPy, Pandas, etc.; 3) Cross-platform support, which can be run on a variety of operating systems; 4) Suitable for scripting and automation tasks to improve work efficiency.
 Learning Python in 2 Hours a Day: A Practical GuideApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Learning Python in 2 Hours a Day: A Practical GuideApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AMYes, learn Python in two hours a day. 1. Develop a reasonable study plan, 2. Select the right learning resources, 3. Consolidate the knowledge learned through practice. These steps can help you master Python in a short time.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)





