For example:
head>
$ creates a wrapping element for the p element. This wrapping element is the same as the element selected using the selector mentioned above. You can also call some methods of jQuery, and finally use appendTo (described later) to move the element into the div. The final result is:
The following introduces the functions that operate on packaging sets.
1. html(),html(text). The first function returns the html inside the first element in the packaging set , and the second function returns all in the packaging set The element's inner html is set to text.
2.size(). Returns the elements contained in the wrapped set.3.get(),get(n). The first function returns the HTML elements in the wrapped collection as a javascript array, and the second element returns the nth HTML element.
4.index(elem). Returns the position of the passed HTML element elem in the packaging set. If not in the packaging set, returns -1.
5.add(s),add(elem),add(array). The add function is used to add elements to the packaging set. If it is a selector, all selected elements are added. If it is an HTML fragment, an HTML element is created based on this fragment and this element is added; if it is an HTML element or an array of HTML elements, it is added directly.
6. not(expression),filter(expression). These two functions are used to filter the elements of the packaging set. expression can be a string (selector), an html element or an array of elements. The not function removes elements that match the selector or are contained in an array. Filter, on the other hand, leaves elements that match the selector or elements contained in the array.
7.slice(begin,end) This function returns a new packaging set, the content of which is the element from begin to end of the original packaging set. If end is omitted, the maximum length is indicated.
Let’s look at a few examples first.
- First Item
- Third Item
- Forth Item
- Fifth Item
< ;li>Second Item
I am a lonely p.
The UL has elements.
Hello jQuery.
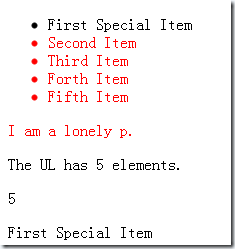
第一行演示了html和size的用法。按上面的介绍,两个span中的内容都应该会变成5. 第二行演示了not和add的一个用法。最终后四个li和第一个p会变成红色。第三行演示了get的用法,一旦调用get之后,返回值就不是包装元素而是HTML元素,因此可以使用HTML DOM提供的方法设置innerHTML。最后一行还是演示html()的用法,要注意html()返回的是第一个元素的内部内容,但是html(text)会把所有元素的内容都设置成text。 最终的结果如下:
9. 这是一大类非常有用的函数,可以根据位置关系筛选元素。
| children() | 返回包装集内元素的子元素(儿子元素,往下多层的不算) |
| contents() | 返回包装集的内容的包装集,可能有文本节点(这个包装集有些特殊,下面介绍) |
| next() | 包装集元素中不重复的下一个元素。 |
| nextAll() | 包装集元素中所有的下一个元素。 |
| parent() | 包装集中元素不重复的父元素的包装集 |
| parents() | 同上,但是一直向上追溯到文档根元素(不包括根元素) |
| prev() | 类似next(),所有不重复的前一个元素 |
| prevAll() | 类型nextAll(),所有前一个元素 |
| siblings() | 包装集中所有不重复的兄弟元素。 |
Let’s first look at the difference between the first two functions. The HTML code still uses the previous example. The js script is as follows:
$(function() {
var ul = $('ul:first');
$('p span').html(ul.children ().size());
var content = ul.contents();
alert(content.size());
});
children() The number of wrapped sets returned is 6, indicating that the last nested
- only counts as one element. But the number of wrapper sets returned by contents() is as high as 13. Use the debugger to view its content:
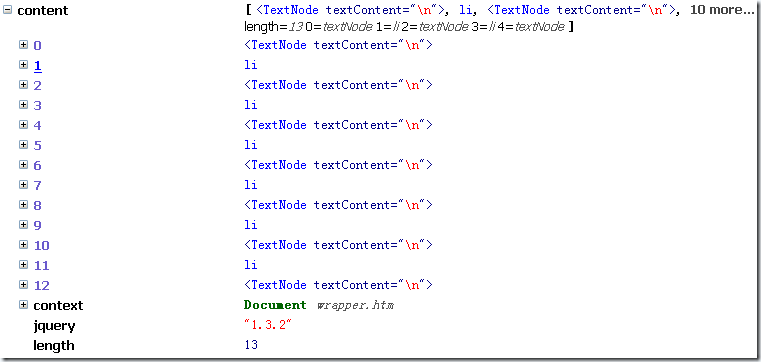
The difference between it and children is that it contains a large number of Text nodes, including text nodes that are just a blank line.
Look at the next and nextAll methods again, still using the above HTML code, the js steps are as follows:
$(function() {
$('span:last').html($('ul').next().html());
$('p:last').html($('ul').nextAll().size());
}); The next element of ul should be I am a lonely p. All the following There are 4 elements in total. Therefore, the result is:

Other functions are used similarly, so no examples will be given.
10.find
The find method and the filter method are easily confused. They also pass in a selector to filter the elements in the package set. However, find filters the child elements of the elements in the packaging set, and filter filters the elements in the packaging set. An example will be given below.
11 clone
The clone method returns a copy of the packaging set.
Example:
I am a lonely p.
Inner P
elements.Hello jQuery.
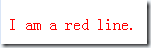
This is an interesting example. The first line filters out the first p and sets it to red, and then moves it to the last div. The second line filters out p included in the packaging set, sets it to green, and moves it to the last div. Note here that there are two ps filtered out by this sentence at this time, one is Inner P, and the other is the first one. Move the sentence to I am a lonely p in the last div. Then add these two elements to the last div. Since InnerP itself is in this div, it is equivalent to no movement. Finally, copy the last p, set it to red, and add it to the end of the body. Therefore, the final pages and colors are as follows:

Finally, the management of the chain is introduced. The so-called chaining is also reflected in the above example, that is, every time a jQuery method is called, it returns a packaging set. This packaging set serves as the caller of the next method, forming a chain. During this process, new packaging sets may be generated (such as calling the clone()) method. In a chain, if the end method is called, the previous packaging set is returned. If the andSelf method is called, the current and previous packaging sets are combined into one packaging set and returned. As you can imagine, jQuery internally stores these concatenated wrapper sets in a stack. The following simple example demonstrates the above principle:
 JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use CasesApr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use CasesApr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AMThe main uses of JavaScript in web development include client interaction, form verification and asynchronous communication. 1) Dynamic content update and user interaction through DOM operations; 2) Client verification is carried out before the user submits data to improve the user experience; 3) Refreshless communication with the server is achieved through AJAX technology.
 Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation DetailsApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation DetailsApr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AMUnderstanding how JavaScript engine works internally is important to developers because it helps write more efficient code and understand performance bottlenecks and optimization strategies. 1) The engine's workflow includes three stages: parsing, compiling and execution; 2) During the execution process, the engine will perform dynamic optimization, such as inline cache and hidden classes; 3) Best practices include avoiding global variables, optimizing loops, using const and lets, and avoiding excessive use of closures.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of UseApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of UseApr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AMPython is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and ResourcesApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AMPython and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All WorksApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AMThe shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing ImplementationsApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AMDifferent JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Beyond the Browser: JavaScript in the Real WorldApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AMJavaScript's applications in the real world include server-side programming, mobile application development and Internet of Things control: 1. Server-side programming is realized through Node.js, suitable for high concurrent request processing. 2. Mobile application development is carried out through ReactNative and supports cross-platform deployment. 3. Used for IoT device control through Johnny-Five library, suitable for hardware interaction.
 Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AMI built a functional multi-tenant SaaS application (an EdTech app) with your everyday tech tool and you can do the same. First, what’s a multi-tenant SaaS application? Multi-tenant SaaS applications let you serve multiple customers from a sing


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)